-
The
@cloudflare/codemode↗ package has been rewritten into a modular, runtime-agnostic SDK.Code Mode ↗ enables LLMs to write and execute TypeScript that orchestrates your tools, instead of calling them one at a time. This can (and does) yield significant token savings, reduces context window pressure and improves overall model performance on a task.
The new
Executorinterface is runtime agnostic and comes with a prebuiltDynamicWorkerExecutorto run generated code in a Dynamic Worker Loader.- Removed
experimental_codemode()andCodeModeProxy— the package no longer owns an LLM call or model choice - New import path:
createCodeTool()is now exported from@cloudflare/codemode/ai
createCodeTool()— Returns a standard AI SDKToolto use in your AI agents.Executorinterface — Minimalexecute(code, fns)contract. Implement for any code sandboxing primitive or runtime.
Runs code in a Dynamic Worker. It comes with the following features:
- Network isolation —
fetch()andconnect()blocked by default (globalOutbound: null) when usingDynamicWorkerExecutor - Console capture —
console.log/warn/errorcaptured and returned inExecuteResult.logs - Execution timeout — Configurable via
timeoutoption (default 30s)
JavaScript import { createCodeTool } from "@cloudflare/codemode/ai";import { DynamicWorkerExecutor } from "@cloudflare/codemode";import { streamText } from "ai";const executor = new DynamicWorkerExecutor({ loader: env.LOADER });const codemode = createCodeTool({ tools: myTools, executor });const result = streamText({model,tools: { codemode },messages,});TypeScript import { createCodeTool } from "@cloudflare/codemode/ai";import { DynamicWorkerExecutor } from "@cloudflare/codemode";import { streamText } from "ai";const executor = new DynamicWorkerExecutor({ loader: env.LOADER });const codemode = createCodeTool({ tools: myTools, executor });const result = streamText({model,tools: { codemode },messages,});{"worker_loaders": [{ "binding": "LOADER" }],}[[worker_loaders]]binding = "LOADER"See the Code Mode documentation for full API reference and examples.
Terminal window npm i @cloudflare/codemode@latest - Removed
-
Cloudflare Tunnel is now available in the main Cloudflare Dashboard at Networking > Tunnels ↗, bringing first-class Tunnel management to developers using Tunnel for securing origin servers.
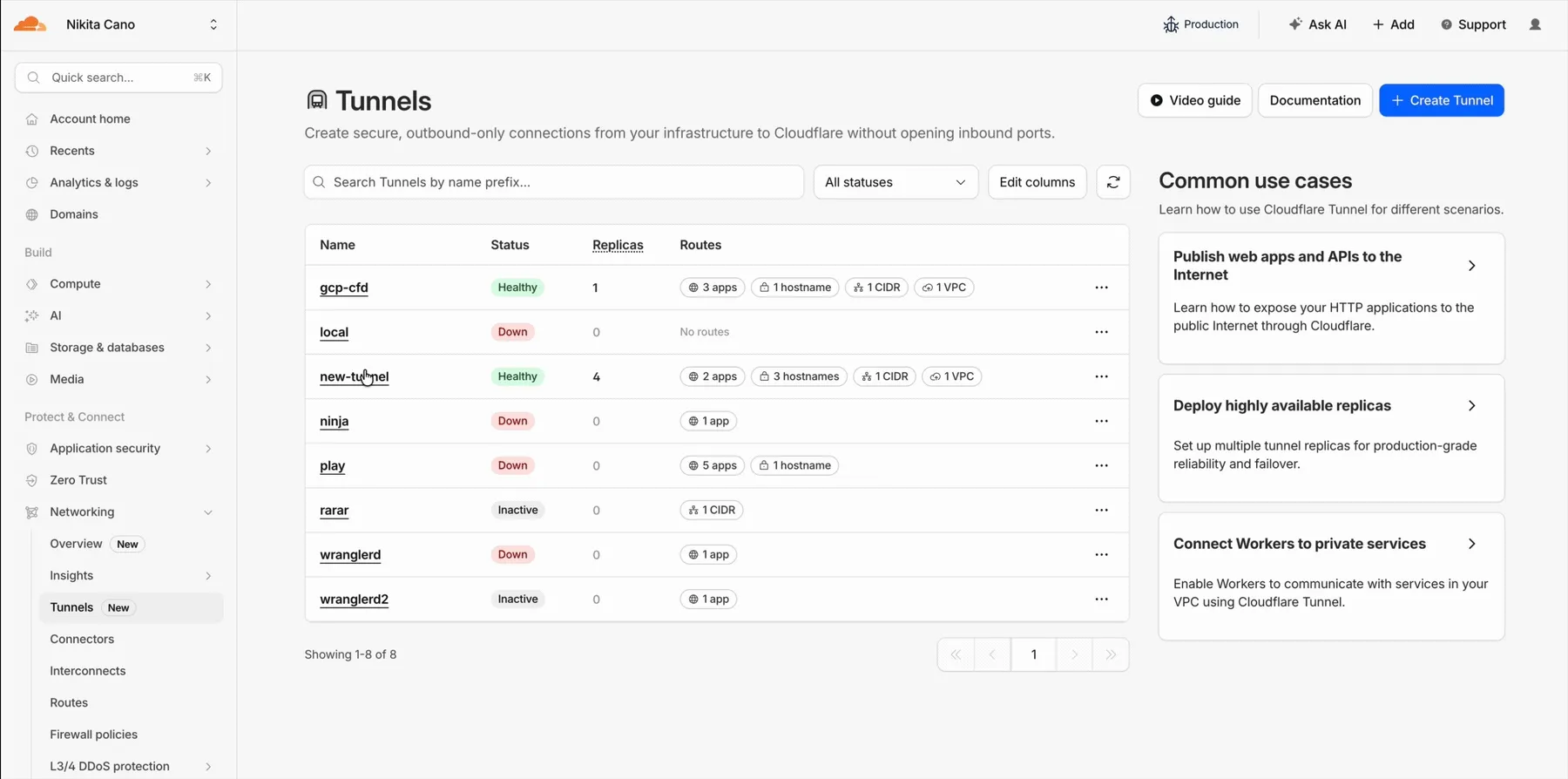
This new experience provides everything you need to manage Tunnels for public applications, including:
- Full Tunnel lifecycle management: Create, configure, delete, and monitor all your Tunnels in one place.
- Native integrations: View Tunnels by name when configuring DNS records and Workers VPC — no more copy-pasting UUIDs.
- Real-time visibility: Monitor replicas and Tunnel health status directly in the dashboard.
- Routing map: Manage all ingress routes for your Tunnel, including public applications, private hostnames, private CIDRs, and Workers VPC services, from a single interactive interface.
Core Dashboard: Navigate to Networking > Tunnels ↗ to manage Tunnels for:
- Securing origin servers and public applications with CDN, WAF, Load Balancing, and DDoS protection
- Connecting Workers to private services via Workers VPC
Cloudflare One Dashboard: Navigate to Zero Trust > Networks > Connectors ↗ to manage Tunnels for:
- Securing your public applications with Zero Trust access policies
- Connecting users to private applications
- Building a private mesh network
Both dashboards provide complete Tunnel management capabilities — choose based on your primary workflow.
New to Tunnel? Learn how to get started with Cloudflare Tunnel or explore advanced use cases like securing SSH servers or running Tunnels in Kubernetes.
-
We have introduced dynamic visualizations to the Threat Events dashboard to help you better understand the threat landscape and identify emerging patterns at a glance.
What's new:
- Sankey Diagrams: Trace the flow of attacks from country of origin to target country to identify which regions are being hit hardest and where the threat infrastructure resides.

- Dataset Distribution over time: Instantly pivot your view to understand if a specific campaign is targeting your sector or if it is a broad-spectrum commodity attack.

- Enhanced Filtering: Use these visual tools to filter and drill down into specific attack vectors directly from the charts.
Cloudforce One subscribers can explore these new views now in Application Security > Threat Intelligence > Threat Events ↗.
-
A new Allow clientless access setting makes it easier to enable access to private self-hosted applications without a device client.
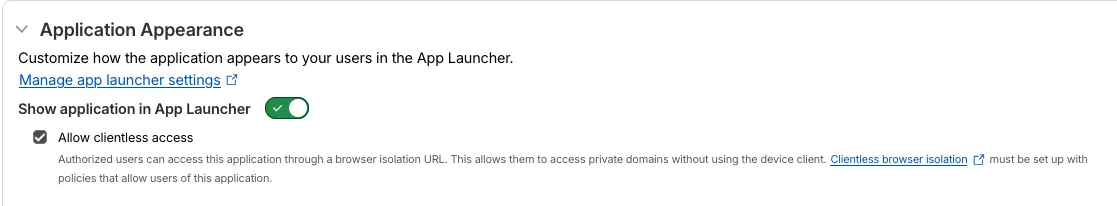
Previously, to provide clientless access to a private hostname or IP, you had to create a separate bookmark application pointing to a prefixed Clientless Web Isolation URL (for example,
https://<your-teamname>.cloudflareaccess.com/browser/https://10.0.0.1/). This bookmark was visible to all users in the App Launcher, regardless of whether they had access to the underlying application.Now, you can manage clientless access directly within your private self-hosted application. When Allow clientless access is turned on, users who pass your Access application policies will see a tile in their App Launcher pointing to the prefixed URL. Users must have remote browser permissions to open the link.
-
You can now assign Access policies to bookmark applications. This lets you control which users see a bookmark in the App Launcher based on identity, device posture, and other policy rules.
Previously, bookmark applications were visible to all users in your organization. With policy support, you can now:
- Tailor the App Launcher to each user — Users only see the applications they have access to, reducing clutter and preventing accidental clicks on irrelevant resources.
- Restrict visibility of sensitive bookmarks — Limit who can view bookmarks to internal tools or partner resources based on group membership, identity provider, or device posture.
Bookmarks support all Access policy configurations except purpose justification, temporary authentication, and application isolation. If no policy is assigned, the bookmark remains visible to all users (maintaining backwards compatibility).
For more information, refer to Add bookmarks.
-
The latest release of the Agents SDK ↗ adds built-in retry utilities, per-connection protocol message control, and a fully rewritten
@cloudflare/ai-chatwith data parts, tool approval persistence, and zero breaking changes.A new
this.retry()method lets you retry any async operation with exponential backoff and jitter. You can pass an optionalshouldRetrypredicate to bail early on non-retryable errors.JavaScript class MyAgent extends Agent {async onRequest(request) {const data = await this.retry(() => callUnreliableService(), {maxAttempts: 4,shouldRetry: (err) => !(err instanceof PermanentError),});return Response.json(data);}}TypeScript class MyAgent extends Agent {async onRequest(request: Request) {const data = await this.retry(() => callUnreliableService(), {maxAttempts: 4,shouldRetry: (err) => !(err instanceof PermanentError),});return Response.json(data);}}Retry options are also available per-task on
queue(),schedule(),scheduleEvery(), andaddMcpServer():JavaScript // Per-task retry configuration, persisted in SQLite alongside the taskawait this.schedule(Date.now() + 60_000,"sendReport",{ userId: "abc" },{retry: { maxAttempts: 5 },},);// Class-level retry defaultsclass MyAgent extends Agent {static options = {retry: { maxAttempts: 3 },};}TypeScript // Per-task retry configuration, persisted in SQLite alongside the taskawait this.schedule(Date.now() + 60_000, "sendReport", { userId: "abc" }, {retry: { maxAttempts: 5 },});// Class-level retry defaultsclass MyAgent extends Agent {static options = {retry: { maxAttempts: 3 },};}Retry options are validated eagerly at enqueue/schedule time, and invalid values throw immediately. Internal retries have also been added for workflow operations (
terminateWorkflow,pauseWorkflow, and others) with Durable Object-aware error detection.Agents automatically send JSON text frames (identity, state, MCP server lists) to every WebSocket connection. You can now suppress these per-connection for clients that cannot handle them — binary-only devices, MQTT clients, or lightweight embedded systems.
JavaScript class MyAgent extends Agent {shouldSendProtocolMessages(connection, ctx) {// Suppress protocol messages for MQTT clientsconst subprotocol = ctx.request.headers.get("Sec-WebSocket-Protocol");return subprotocol !== "mqtt";}}TypeScript class MyAgent extends Agent {shouldSendProtocolMessages(connection: Connection, ctx: ConnectionContext) {// Suppress protocol messages for MQTT clientsconst subprotocol = ctx.request.headers.get("Sec-WebSocket-Protocol");return subprotocol !== "mqtt";}}Connections with protocol messages disabled still fully participate in RPC and regular messaging. Use
isConnectionProtocolEnabled(connection)to check a connection's status at any time. The flag persists across Durable Object hibernation.See Protocol messages for full documentation.
The first stable release of
@cloudflare/ai-chatships alongside this release with a major refactor ofAIChatAgentinternals — newResumableStreamclass, WebSocketChatTransport, and simplified SSE parsing — with zero breaking changes. Existing code usingAIChatAgentanduseAgentChatworks as-is.Key new features:
- Data parts — Attach typed JSON blobs (
data-*) to messages alongside text. Supports reconciliation (type+id updates in-place), append, and transient parts (ephemeral viaonDatacallback). See Data parts. - Tool approval persistence — The
needsApprovalapproval UI now survives page refresh and DO hibernation. The streaming message is persisted to SQLite when a tool entersapproval-requestedstate. maxPersistedMessages— Cap SQLite message storage with automatic oldest-message deletion.bodyoption onuseAgentChat— Send custom data with every request (static or dynamic).- Incremental persistence — Hash-based cache to skip redundant SQL writes.
- Row size guard — Automatic two-pass compaction when messages approach the SQLite 2 MB limit.
autoContinueAfterToolResultdefaults totrue— Client-side tool results and tool approvals now automatically trigger a server continuation, matching server-executed tool behavior. SetautoContinueAfterToolResult: falseinuseAgentChatto restore the previous behavior.
Notable bug fixes:
- Resolved stream resumption race conditions
- Resolved an issue where
setMessagesfunctional updater sent empty arrays - Resolved an issue where client tool schemas were lost after DO hibernation
- Resolved
InvalidPromptErrorafter tool approval (approval.idwas dropped) - Resolved an issue where message metadata was not propagated on broadcast/resume paths
- Resolved an issue where
clearAll()did not clear in-memory chunk buffers - Resolved an issue where
reasoning-deltasilently dropped data whenreasoning-startwas missed during stream resumption
getQueue(),getQueues(),getSchedule(),dequeue(),dequeueAll(), anddequeueAllByCallback()were unnecessarilyasyncdespite only performing synchronous SQL operations. They now return values directly instead of wrapping them in Promises. This is backward compatible — existing code usingawaiton these methods will continue to work.- Fix TypeScript "excessively deep" error — A depth counter on
CanSerializeandIsSerializableParamtypes bails out totrueafter 10 levels of recursion, preventing the "Type instantiation is excessively deep" error with deeply nested types like AI SDKCoreMessage[]. - POST SSE keepalive — The POST SSE handler now sends
event: pingevery 30 seconds to keep the connection alive, matching the existing GET SSE handler behavior. This prevents POST response streams from being silently dropped by proxies during long-running tool calls. - Widened peer dependency ranges — Peer dependency ranges across packages have been widened to prevent cascading major bumps during 0.x minor releases.
@cloudflare/ai-chatand@cloudflare/codemodeare now marked as optional peer dependencies.
To update to the latest version:
Terminal window npm i agents@latest @cloudflare/ai-chat@latest - Data parts — Attach typed JSON blobs (
-
We are updating naming related to some of our Networking products to better clarify their place in the Zero Trust and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) journey.
We are retiring some older brand names in favor of names that describe exactly what the products do within your network. We are doing this to help customers build better, clearer mental models for comprehensive SASE architecture delivered on Cloudflare.
- Magic WAN → Cloudflare WAN
- Magic WAN IPsec → Cloudflare IPsec
- Magic WAN GRE → Cloudflare GRE
- Magic WAN Connector → Cloudflare One Appliance
- Magic Firewall → Cloudflare Network Firewall
- Magic Network Monitoring → Network Flow
- Magic Cloud Networking → Cloudflare One Multi-cloud Networking
No action is required by you — all functionality, existing configurations, and billing will remain exactly the same.
For more information, visit the Cloudflare One documentation.
-
Sandboxes and Containers now support running Docker for "Docker-in-Docker" setups. This is particularly useful when your end users or agents want to run a full sandboxed development environment.
This allows you to:
- Develop containerized applications with your Sandbox
- Run isolated test environments for images
- Build container images as part of CI/CD workflows
- Deploy arbitrary images supplied at runtime within a container
For Sandbox SDK users, see the Docker-in-Docker guide for instructions on combining Docker with the SandboxSDK. For general Containers usage, see the Containers FAQ.
-
When AI systems request pages from any website that uses Cloudflare and has Markdown for Agents enabled, they can express the preference for
text/markdownin the request: our network will automatically and efficiently convert the HTML to markdown, when possible, on the fly.This release adds the following improvements:
- The origin response limit was raised from 1 MB to 2 MB (2,097,152 bytes).
- We no longer require the origin to send the
content-lengthheader. - We now support content encoded responses from the origin.
If you haven’t enabled automatic Markdown conversion yet, visit the AI Crawl Control ↗ section of the Cloudflare dashboard and enable Markdown for Agents.
Refer to our developer documentation for more details.
-
This week’s release introduces new detections for CVE-2025-68645 and CVE-2025-31125.
Key Findings
- CVE-2025-68645: A Local File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability in the Webmail Classic UI of Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) 10.0 and 10.1 allows unauthenticated remote attackers to craft requests to the
/h/restendpoint, improperly influence internal dispatching, and include arbitrary files from the WebRoot directory. - CVE-2025-31125: Vite, the JavaScript frontend tooling framework, exposes content of non-allowed files via
?inline&importwhen its development server is network-exposed, enabling unauthorized attackers to read arbitrary files and potentially leak sensitive information.
Ruleset Rule ID Legacy Rule ID Description Previous Action New Action Comments Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A Zimbra - Local File Inclusion - CVE:CVE-2025-68645 Log Block This is a new detection. Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A Vite - WASM Import Path Traversal - CVE:CVE-2025-31125 Log Block This is a new detection. - CVE-2025-68645: A Local File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability in the Webmail Classic UI of Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) 10.0 and 10.1 allows unauthenticated remote attackers to craft requests to the
-
A new Workers Best Practices guide provides opinionated recommendations for building fast, reliable, observable, and secure Workers. The guide draws on production patterns, Cloudflare internal usage, and best practices observed from developers building on Workers.
Key guidance includes:
- Keep your compatibility date current and enable
nodejs_compat— Ensure you have access to the latest runtime features and Node.js built-in modules.
{"name": "my-worker","main": "src/index.ts",// Set this to today's date"compatibility_date": "2026-02-20","compatibility_flags": ["nodejs_compat"],}name = "my-worker"main = "src/index.ts"# Set this to today's datecompatibility_date = "2026-02-20"compatibility_flags = [ "nodejs_compat" ]- Generate binding types with
wrangler types— Never hand-write yourEnvinterface. Let Wrangler generate it from your actual configuration to catch mismatches at compile time. - Stream request and response bodies — Avoid buffering large payloads in memory. Use
TransformStreamandpipeToto stay within the 128 MB memory limit and improve time-to-first-byte. - Use bindings, not REST APIs — Bindings to KV, R2, D1, Queues, and other Cloudflare services are direct, in-process references with no network hop and no authentication overhead.
- Use Queues and Workflows for background work — Move long-running or retriable tasks out of the critical request path. Use Queues for simple fan-out and buffering, and Workflows for multi-step durable processes.
- Enable Workers Logs and Traces — Configure observability before deploying to production so you have data when you need to debug.
- Avoid global mutable state — Workers reuse isolates across requests. Storing request-scoped data in module-level variables causes cross-request data leaks.
- Always
awaitorwaitUntilyour Promises — Floating promises cause silent bugs and dropped work. - Use Web Crypto for secure token generation — Never use
Math.random()for security-sensitive operations.
To learn more, refer to Workers Best Practices.
- Keep your compatibility date current and enable
-
Disclaimer: Please note that v5.0.0-beta.1 is in Beta and we are still testing it for stability.
Full Changelog: v4.3.1...v5.0.0-beta.1 ↗
In this release, you'll see a large number of breaking changes. This is primarily due to a change in OpenAPI definitions, which our libraries are based off of, and codegen updates that we rely on to read those OpenAPI definitions and produce our SDK libraries. As the codegen is always evolving and improving, so are our code bases.
There may be changes that are not captured in this changelog. Feel free to open an issue to report any inaccuracies, and we will make sure it gets into the changelog before the v5.0.0 release.
Most of the breaking changes below are caused by improvements to the accuracy of the base OpenAPI schemas, which sometimes translates to breaking changes in downstream clients that depend on those schemas.
Please ensure you read through the list of changes below and the migration guide before moving to this version - this will help you understand any down or upstream issues it may cause to your environments.
The following resources have breaking changes. See the v5 Migration Guide ↗ for detailed migration instructions.
abusereportsacm.totaltlsapigateway.configurationscloudforceone.threateventsd1.databaseintel.indicatorfeedslogpush.edgeorigintlsclientauth.hostnamesqueues.consumersradar.bgprulesets.rulesschemavalidation.schemassnippetszerotrust.dlpzerotrust.networks
abusereports- Abuse report managementabusereports.mitigations- Abuse report mitigation actionsai.tomarkdown- AI-powered markdown conversionaigateway.dynamicrouting- AI Gateway dynamic routing configurationaigateway.providerconfigs- AI Gateway provider configurationsaisearch- AI-powered search functionalityaisearch.instances- AI Search instance managementaisearch.tokens- AI Search authentication tokensalerting.silences- Alert silence managementbrandprotection.logomatches- Brand protection logo match detectionbrandprotection.logos- Brand protection logo managementbrandprotection.matches- Brand protection match resultsbrandprotection.queries- Brand protection query managementcloudforceone.binarystorage- CloudForce One binary storageconnectivity.directory- Connectivity directory servicesd1.database- D1 database managementdiagnostics.endpointhealthchecks- Endpoint health check diagnosticsfraud- Fraud detection and preventioniam.sso- IAM Single Sign-On configurationloadbalancers.monitorgroups- Load balancer monitor groupsorganizations- Organization managementorganizations.organizationprofile- Organization profile settingsorigintlsclientauth.hostnamecertificates- Origin TLS client auth hostname certificatesorigintlsclientauth.hostnames- Origin TLS client auth hostnamesorigintlsclientauth.zonecertificates- Origin TLS client auth zone certificatespipelines- Data pipeline managementpipelines.sinks- Pipeline sink configurationspipelines.streams- Pipeline stream configurationsqueues.subscriptions- Queue subscription managementr2datacatalog- R2 Data Catalog integrationr2datacatalog.credentials- R2 Data Catalog credentialsr2datacatalog.maintenanceconfigs- R2 Data Catalog maintenance configurationsr2datacatalog.namespaces- R2 Data Catalog namespacesradar.bots- Radar bot analyticsradar.ct- Radar certificate transparency dataradar.geolocations- Radar geolocation datarealtimekit.activesession- Real-time Kit active session managementrealtimekit.analytics- Real-time Kit analyticsrealtimekit.apps- Real-time Kit application managementrealtimekit.livestreams- Real-time Kit live streamingrealtimekit.meetings- Real-time Kit meeting managementrealtimekit.presets- Real-time Kit preset configurationsrealtimekit.recordings- Real-time Kit recording managementrealtimekit.sessions- Real-time Kit session managementrealtimekit.webhooks- Real-time Kit webhook configurationstokenvalidation.configuration- Token validation configurationtokenvalidation.rules- Token validation rulesworkers.beta- Workers beta features
edit()update()
list()
create()get()update()
scan_list()scan_review()scan_trigger()
create()delete()list()
get()
list()
summary()timeseries()timeseries_groups()
changes()snapshot()
delete()
create()delete()edit()get()list()
- Type inference improvements: Allow Pyright to properly infer TypedDict types within SequenceNotStr
- Type completeness: Add missing types to method arguments and response models
- Pydantic compatibility: Ensure compatibility with Pydantic versions prior to 2.8.0 when using additional fields
- Multipart form data: Correctly handle sending multipart/form-data requests with JSON data
- Header handling: Do not send headers with default values set to omit
- GET request headers: Don't send Content-Type header on GET requests
- Response body model accuracy: Broad improvements to the correctness of models
- Discriminated unions: Correctly handle nested discriminated unions in response parsing
- Extra field types: Parse extra field types correctly
- Empty metadata: Ignore empty metadata fields during parsing
- Singularization rules: Update resource name singularization rules for better consistency
-
We're excited to announce GLM-4.7-Flash on Workers AI, a fast and efficient text generation model optimized for multilingual dialogue and instruction-following tasks, along with the brand-new @cloudflare/tanstack-ai ↗ package and workers-ai-provider v3.1.1 ↗.
You can now run AI agents entirely on Cloudflare. With GLM-4.7-Flash's multi-turn tool calling support, plus full compatibility with TanStack AI and the Vercel AI SDK, you have everything you need to build agentic applications that run completely at the edge.
@cf/zai-org/glm-4.7-flashis a multilingual model with a 131,072 token context window, making it ideal for long-form content generation, complex reasoning tasks, and multilingual applications.Key Features and Use Cases:
- Multi-turn Tool Calling for Agents: Build AI agents that can call functions and tools across multiple conversation turns
- Multilingual Support: Built to handle content generation in multiple languages effectively
- Large Context Window: 131,072 tokens for long-form writing, complex reasoning, and processing long documents
- Fast Inference: Optimized for low-latency responses in chatbots and virtual assistants
- Instruction Following: Excellent at following complex instructions for code generation and structured tasks
Use GLM-4.7-Flash through the Workers AI binding (
env.AI.run()), the REST API at/runor/v1/chat/completions, AI Gateway, or via workers-ai-provider for the Vercel AI SDK.Pricing is available on the model page or pricing page.
We've released
@cloudflare/tanstack-ai, a new package that brings Workers AI and AI Gateway support to TanStack AI ↗. This provides a framework-agnostic alternative for developers who prefer TanStack's approach to building AI applications.Workers AI adapters support four configuration modes — plain binding (
env.AI), plain REST, AI Gateway binding (env.AI.gateway(id)), and AI Gateway REST — across all capabilities:- Chat (
createWorkersAiChat) — Streaming chat completions with tool calling, structured output, and reasoning text streaming. - Image generation (
createWorkersAiImage) — Text-to-image models. - Transcription (
createWorkersAiTranscription) — Speech-to-text. - Text-to-speech (
createWorkersAiTts) — Audio generation. - Summarization (
createWorkersAiSummarize) — Text summarization.
AI Gateway adapters route requests from third-party providers — OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Grok, and OpenRouter — through Cloudflare AI Gateway for caching, rate limiting, and unified billing.
To get started:
Terminal window npm install @cloudflare/tanstack-ai @tanstack/aiThe Workers AI provider for the Vercel AI SDK ↗ now supports three new capabilities beyond chat and image generation:
- Transcription (
provider.transcription(model)) — Speech-to-text with automatic handling of model-specific input formats across binding and REST paths. - Text-to-speech (
provider.speech(model)) — Audio generation with support for voice and speed options. - Reranking (
provider.reranking(model)) — Document reranking for RAG pipelines and search result ordering.
TypeScript import { createWorkersAI } from "workers-ai-provider";import {experimental_transcribe,experimental_generateSpeech,rerank,} from "ai";const workersai = createWorkersAI({ binding: env.AI });const transcript = await experimental_transcribe({model: workersai.transcription("@cf/openai/whisper-large-v3-turbo"),audio: audioData,mediaType: "audio/wav",});const speech = await experimental_generateSpeech({model: workersai.speech("@cf/deepgram/aura-1"),text: "Hello world",voice: "asteria",});const ranked = await rerank({model: workersai.reranking("@cf/baai/bge-reranker-base"),query: "What is machine learning?",documents: ["ML is a branch of AI.", "The weather is sunny."],});This release also includes a comprehensive reliability overhaul (v3.0.5):
- Fixed streaming — Responses now stream token-by-token instead of buffering all chunks, using a proper
TransformStreampipeline with backpressure. - Fixed tool calling — Resolved issues with tool call ID sanitization, conversation history preservation, and a heuristic that silently fell back to non-streaming mode when tools were defined.
- Premature stream termination detection — Streams that end unexpectedly now report
finishReason: "error"instead of silently reporting"stop". - AI Search support — Added
createAISearchas the canonical export (renamed from AutoRAG).createAutoRAGstill works with a deprecation warning.
To upgrade:
Terminal window npm install workers-ai-provider@latest ai
-
Workers VPC now supports Cloudflare Origin CA certificates when connecting to your private services over HTTPS. Previously, Workers VPC only trusted certificates issued by publicly trusted certificate authorities (for example, Let's Encrypt, DigiCert).
With this change, you can use free Cloudflare Origin CA certificates on your origin servers within private networks and connect to them from Workers VPC using the
httpsscheme. This is useful for encrypting traffic between the tunnel and your service without needing to provision certificates from a public CA.For more information, refer to Supported TLS certificates.
-
Cloudflare's network now supports real-time content conversion at the source, for enabled zones using content negotiation ↗ headers. When AI systems request pages from any website that uses Cloudflare and has Markdown for Agents enabled, they can express the preference for
text/markdownin the request: our network will automatically and efficiently convert the HTML to markdown, when possible, on the fly.Here is a curl example with the
Acceptnegotiation header requesting this page from our developer documentation:Terminal window curl https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/reference/markdown-for-agents/ \-H "Accept: text/markdown"The response to this request is now formatted in markdown:
HTTP/2 200date: Wed, 11 Feb 2026 11:44:48 GMTcontent-type: text/markdown; charset=utf-8content-length: 2899vary: acceptx-markdown-tokens: 725content-signal: ai-train=yes, search=yes, ai-input=yes---title: Markdown for Agents · Cloudflare Agents docs---## What is Markdown for AgentsMarkdown has quickly become the lingua franca for agents and AI systemsas a whole. The format’s explicit structure makes it ideal for AI processing,ultimately resulting in better results while minimizing token waste....Refer to our developer documentation and our blog announcement ↗ for more details.
-
Radar now includes content type insights for AI bot and crawler traffic. The new
content_typedimension and filter shows the distribution of content types returned to AI crawlers, grouped by MIME type category.The content type dimension and filter are available via the following API endpoints:
Content type categories:
- HTML - Web pages (
text/html) - Images - All image formats (
image/*) - JSON - JSON data and API responses (
application/json,*+json) - JavaScript - Scripts (
application/javascript,text/javascript) - CSS - Stylesheets (
text/css) - Plain Text - Unformatted text (
text/plain) - Fonts - Web fonts (
font/*,application/font-*) - XML - XML documents and feeds (
text/xml,application/xml,application/rss+xml,application/atom+xml) - YAML - Configuration files (
text/yaml,application/yaml) - Video - Video content and streaming (
video/*,application/ogg,*mpegurl) - Audio - Audio content (
audio/*) - Markdown - Markdown documents (
text/markdown) - Documents - PDFs, Office documents, ePub, CSV (
application/pdf,application/msword,text/csv) - Binary - Executables, archives, WebAssembly (
application/octet-stream,application/zip,application/wasm) - Serialization - Binary API formats (
application/protobuf,application/grpc,application/msgpack) - Other - All other content types
Additionally, individual bot information pages ↗ now display content type distribution for AI crawlers that exist in both the Verified Bots and AI Bots datasets.
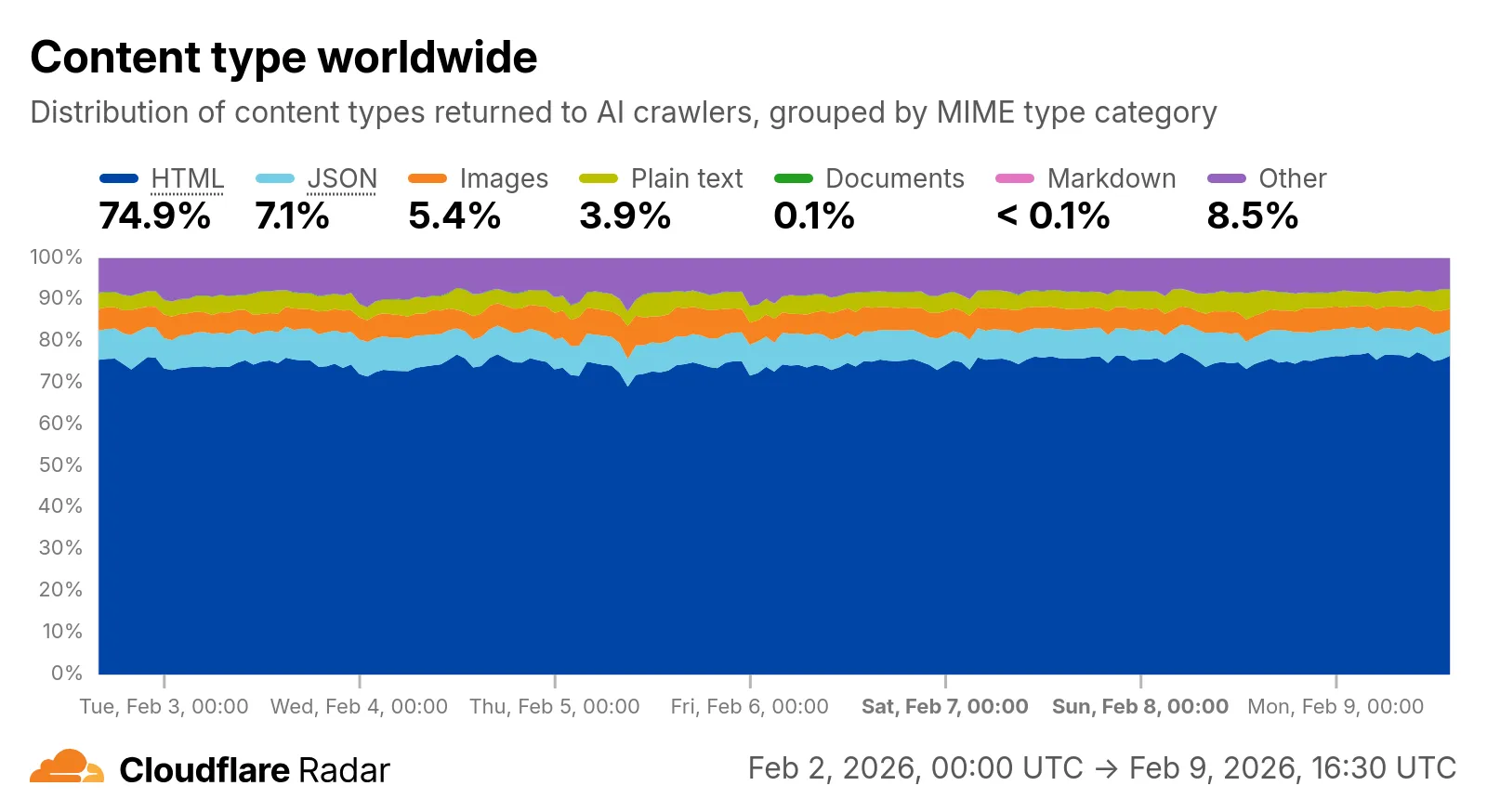
Check out the AI Insights page ↗ to explore the data.
- HTML - Web pages (
-
We have significantly upgraded our Logo Matching capabilities within Brand Protection. While previously limited to approximately 100% matches, users can now detect a wider range of brand assets through a redesigned matching model and UI.
- Configurable match thresholds: Users can set a minimum match score (starting at 75%) when creating a logo query to capture subtle variations or high-quality impersonations.
- Visual match scores: Allow users to see the exact percentage of the match directly in the results table, highlighted with color-coded lozenges to indicate severity.
- Direct logo previews: Available in the Cloudflare dashboard — similar to string matches — to verify infringements at a glance.
- Expose sophisticated impersonators who use slightly altered logos to bypass basic detection filters.
- Faster triage of the most relevant threats immediately using visual indicators, reducing the time spent manually reviewing matches.
Ready to protect your visual identity? Learn more in our Brand Protection documentation.
-
In January 2025, we announced the launch of the new Terraform v5 Provider. We greatly appreciate the proactive engagement and valuable feedback from the Cloudflare community following the v5 release. In response, we have established a consistent and rapid 2-3 week cadence ↗ for releasing targeted improvements, demonstrating our commitment to stability and reliability.
With the help of the community, we have a growing number of resources that we have marked as stable ↗, with that list continuing to grow with every release. The most used resources ↗ are on track to be stable by the end of March 2026, when we will also be releasing a new migration tool to help you migrate from v4 to v5 with ease.
This release brings new capabilities for AI Search, enhanced Workers Script placement controls, and numerous bug fixes based on community feedback. We also begun laying foundational work for improving the v4 to v5 migration process. Stay tuned for more details as we approach the March 2026 release timeline.
Thank you for continuing to raise issues. They make our provider stronger and help us build products that reflect your needs.
- ai_search_instance: add data source for querying AI Search instances
- ai_search_token: add data source for querying AI Search tokens
- account: add support for tenant unit management with new
unitfield - account: add automatic mapping from
managed_by.parent_org_idtounit.id - authenticated_origin_pulls_certificate: add data source for querying authenticated origin pull certificates
- authenticated_origin_pulls_hostname_certificate: add data source for querying hostname-specific authenticated origin pull certificates
- authenticated_origin_pulls_settings: add data source for querying authenticated origin pull settings
- workers_kv: add
valuefield to data source to retrieve KV values directly - workers_script: add
scriptfield to data source to retrieve script content - workers_script: add support for
simplerate limit binding - workers_script: add support for targeted placement mode with
placement.targetarray for specifying placement targets (region, hostname, host) - workers_script: add
placement_modeandplacement_statuscomputed fields - zero_trust_dex_test: add data source with filter support for finding specific tests
- zero_trust_dlp_predefined_profile: add
enabled_entriesfield for flexible entry management
- account: map
managed_by.parent_org_idtounit.idin unmarshall and add acceptance tests - authenticated_origin_pulls_certificate: add certificate normalization to prevent drift
- authenticated_origin_pulls: handle array response and implement full lifecycle
- authenticated_origin_pulls_hostname_certificate: fix resource and tests
- cloudforce_one_request_message: use correct
request_idfield instead ofidin API calls - dns_zone_transfers_incoming: use correct
zone_idfield instead ofidin API calls - dns_zone_transfers_outgoing: use correct
zone_idfield instead ofidin API calls - email_routing_settings: use correct
zone_idfield instead ofidin API calls - hyperdrive_config: add proper handling for write-only fields to prevent state drift
- hyperdrive_config: add normalization for empty
mtlsobjects to prevent unnecessary diffs - magic_network_monitoring_rule: use correct
account_idfield instead ofidin API calls - mtls_certificates: fix resource and test
- pages_project: revert build_config to computed optional
- stream_key: use correct
account_idfield instead ofidin API calls - total_tls: use upsert pattern for singleton zone setting
- waiting_room_rules: use correct
waiting_room_idfield instead ofidin API calls - workers_script: add support for placement mode/status
- zero_trust_access_application: update v4 version on migration tests
- zero_trust_device_posture_rule: update tests to match API
- zero_trust_dlp_integration_entry: use correct
entry_idfield instead ofidin API calls - zero_trust_dlp_predefined_entry: use correct
entry_idfield instead ofidin API calls - zero_trust_organization: fix plan issues
- add state upgraders to 95+ resources to lay the foundation for replacing Grit (still under active development)
- certificate_pack: add state migration handler for SDKv2 to Framework conversion
- custom_hostname_fallback_origin: add comprehensive lifecycle test and migration support
- dns_record: add state migration handler for SDKv2 to Framework conversion
- leaked_credential_check: add import functionality and tests
- load_balancer_pool: add state migration handler with detection for v4 vs v5 format
- pages_project: add state migration handlers
- tiered_cache: add state migration handlers
- zero_trust_dlp_predefined_profile: deprecate
entriesfield in favor ofenabled_entries
-
Workers no longer have a limit of 1000 subrequests per invocation, allowing you to make more
fetch()calls or requests to Cloudflare services on every incoming request. This is especially important for long-running Workers requests, such as open websockets on Durable Objects or long-running Workflows, as these could often exceed this limit and error.By default, Workers on paid plans are now limited to 10,000 subrequests per invocation, but this limit can be increased up to 10 million by setting the new
subrequestslimit in your Wrangler configuration file.{"limits": {"subrequests": 50000,},}[limits]subrequests = 50_000Workers on the free plan remain limited to 50 external subrequests and 1000 subrequests to Cloudflare services per invocation.
To protect against runaway code or unexpected costs, you can also set a lower limit for both subrequests and CPU usage.
{"limits": {"subrequests": 10,"cpu_ms": 1000,},}[limits]subrequests = 10cpu_ms = 1_000For more information, refer to the Wrangler configuration documentation for limits and subrequest limits.
-
The Cloudflare Vite plugin now integrates seamlessly @vitejs/plugin-rsc ↗, the official Vite plugin for React Server Components ↗.
A
childEnvironmentsoption has been added to the plugin config to enable using multiple environments within a single Worker. The parent environment can then import modules from a child environment in order to access a separate module graph. For a typical RSC use case, the plugin might be configured as in the following example:vite.config.ts export default defineConfig({plugins: [cloudflare({viteEnvironment: {name: "rsc",childEnvironments: ["ssr"],},}),],});@vitejs/plugin-rscprovides the lower level functionality that frameworks, such as React Router ↗, build upon. The GitHub repository includes a basic Cloudflare example ↗.
-
This week’s release changes the rule action from BLOCK to Disabled for Anomaly:Header:User-Agent - Fake Google Bot.
Ruleset Rule ID Legacy Rule ID Description Previous Action New Action Comments Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A Anomaly:Header:User-Agent - Fake Google Bot Enabled Disabled We are changing the action for this rule from BLOCK to Disabled
-
Announcement Date Release Date Release Behavior Legacy Rule ID Rule ID Description Comments 2026-02-10 2026-02-16 Log N/A Zimbra - Local File Inclusion - CVE:CVE-2025-68645 This is a new detection. 2026-02-10 2026-02-16 Log N/A Vite - WASM Import Path Traversal - CVE:CVE-2025-31125 This is a new detection.
-
The latest release of the Agents SDK ↗ brings readonly connections, MCP protocol and security improvements, x402 payment protocol v2 migration, and the ability to customize OAuth for MCP server connections.
Agents can now restrict WebSocket clients to read-only access, preventing them from modifying agent state. This is useful for dashboards, spectator views, or any scenario where clients should observe but not mutate.
New hooks:
shouldConnectionBeReadonly,setConnectionReadonly,isConnectionReadonly. Readonly connections block both client-sidesetState()and mutating@callable()methods, and the readonly flag survives hibernation.JavaScript class MyAgent extends Agent {shouldConnectionBeReadonly(connection) {// Make spectators readonlyreturn connection.url.includes("spectator");}}TypeScript class MyAgent extends Agent {shouldConnectionBeReadonly(connection) {// Make spectators readonlyreturn connection.url.includes("spectator");}}The new
createMcpOAuthProvidermethod on theAgentclass allows subclasses to override the default OAuth provider used when connecting to MCP servers. This enables custom authentication strategies such as pre-registered client credentials or mTLS, beyond the built-in dynamic client registration.JavaScript class MyAgent extends Agent {createMcpOAuthProvider(callbackUrl) {return new MyCustomOAuthProvider(this.ctx.storage, this.name, callbackUrl);}}TypeScript class MyAgent extends Agent {createMcpOAuthProvider(callbackUrl: string): AgentMcpOAuthProvider {return new MyCustomOAuthProvider(this.ctx.storage, this.name, callbackUrl);}}Upgraded the MCP SDK to 1.26.0 to prevent cross-client response leakage. Stateless MCP Servers should now create a new
McpServerinstance per request instead of sharing a single instance. A guard is added in this version of the MCP SDK which will prevent connection to a Server instance that has already been connected to a transport. Developers will need to modify their code if they declare theirMcpServerinstance as a global variable.Added
callbackPathoption toaddMcpServerto prevent instance name leakage in MCP OAuth callback URLs. WhensendIdentityOnConnectisfalse,callbackPathis now required — the default callback URL would expose the instance name, undermining the security intent. Also fixes callback request detection to match via thestateparameter instead of a loose/callbackURL substring check, enabling custom callback paths.onStateChangedis a drop-in rename ofonStateUpdate(same signature, same behavior).onStateUpdatestill works but emits a one-time console warning per class.validateStateChangerejections now propagate aCF_AGENT_STATE_ERRORmessage back to the client.Migrated the x402 MCP payment integration from the legacy
x402package to@x402/coreand@x402/evmv2.Breaking changes for x402 users:
- Peer dependencies changed: replace
x402with@x402/coreand@x402/evm PaymentRequirementstype now uses v2 fields (e.g.amountinstead ofmaxAmountRequired)X402ClientConfig.accounttype changed fromviem.AccounttoClientEvmSigner(structurally compatible withprivateKeyToAccount())
Terminal window npm uninstall x402npm install @x402/core @x402/evmNetwork identifiers now accept both legacy names and CAIP-2 format:
TypeScript // Legacy name (auto-converted){network: "base-sepolia",}// CAIP-2 format (preferred){network: "eip155:84532",}Other x402 changes:
X402ClientConfig.networkis now optional — the client auto-selects from available payment requirements- Server-side lazy initialization: facilitator connection is deferred until the first paid tool invocation
- Payment tokens support both v2 (
PAYMENT-SIGNATURE) and v1 (X-PAYMENT) HTTP headers - Added
normalizeNetworkexport for converting legacy network names to CAIP-2 format - Re-exports
PaymentRequirements,PaymentRequired,Network,FacilitatorConfig, andClientEvmSignerfromagents/x402
- Fix
useAgentandAgentClientcrashing when usingbasePathrouting - CORS handling delegated to partyserver's native support (simpler, more reliable)
- Client-side
onStateUpdateErrorcallback for handling rejected state updates
To update to the latest version:
Terminal window npm i agents@latest - Peer dependencies changed: replace
-
The Sandbox SDK ↗ now supports PTY (pseudo-terminal) passthrough, enabling browser-based terminal UIs to connect to sandbox shells via WebSocket.
The new
terminal()method proxies a WebSocket upgrade to the container's PTY endpoint, with output buffering for replay on reconnect.JavaScript // Worker: proxy WebSocket to container terminalreturn sandbox.terminal(request, { cols: 80, rows: 24 });TypeScript // Worker: proxy WebSocket to container terminalreturn sandbox.terminal(request, { cols: 80, rows: 24 });Each session can have its own terminal with an isolated working directory and environment, so users can run separate shells side-by-side in the same container.
JavaScript // Multiple isolated terminals in the same sandboxconst dev = await sandbox.getSession("dev");return dev.terminal(request);TypeScript // Multiple isolated terminals in the same sandboxconst dev = await sandbox.getSession("dev");return dev.terminal(request);The new
@cloudflare/sandbox/xtermexport provides aSandboxAddonfor xterm.js ↗ with automatic reconnection (exponential backoff + jitter), buffered output replay, and resize forwarding.JavaScript import { SandboxAddon } from "@cloudflare/sandbox/xterm";const addon = new SandboxAddon({getWebSocketUrl: ({ sandboxId, origin }) =>`${origin}/ws/terminal?id=${sandboxId}`,onStateChange: (state, error) => updateUI(state),});terminal.loadAddon(addon);addon.connect({ sandboxId: "my-sandbox" });TypeScript import { SandboxAddon } from "@cloudflare/sandbox/xterm";const addon = new SandboxAddon({getWebSocketUrl: ({ sandboxId, origin }) =>`${origin}/ws/terminal?id=${sandboxId}`,onStateChange: (state, error) => updateUI(state),});terminal.loadAddon(addon);addon.connect({ sandboxId: "my-sandbox" });To update to the latest version:
Terminal window npm i @cloudflare/sandbox@latest
-
AI Crawl Control metrics have been enhanced with new views, improved filtering, and better data visualization.
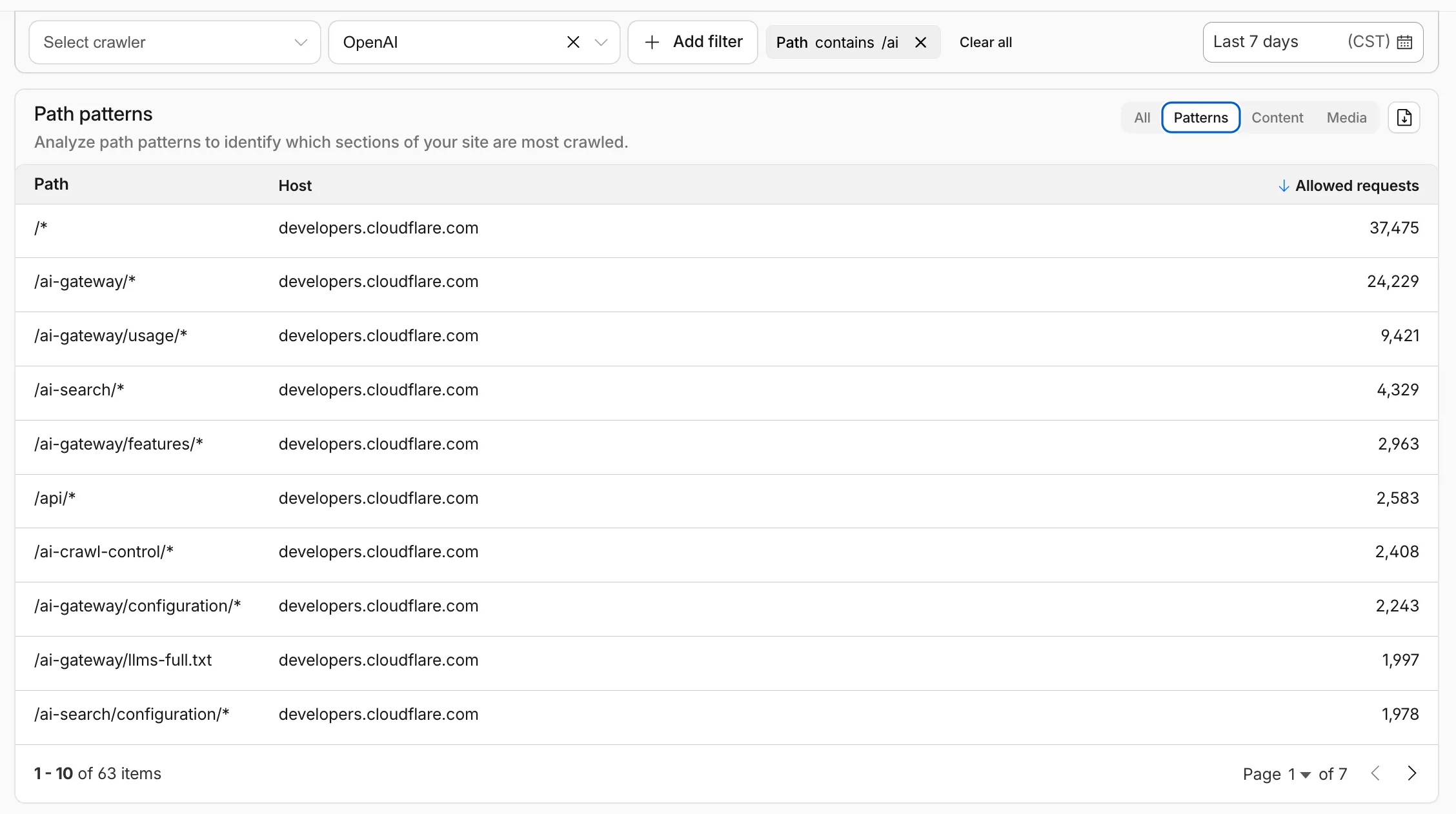
Path pattern grouping
- In the Metrics tab > Most popular paths table, use the new Patterns tab that groups requests by URI pattern (
/blog/*,/api/v1/*,/docs/*) to identify which site areas crawlers target most. Refer to the screenshot above.
Enhanced referral analytics
- Destination patterns show which site areas receive AI-driven referral traffic.
- In the Metrics tab, a new Referrals over time chart shows trends by operator or source.
Data transfer metrics
- In the Metrics tab > Allowed requests over time chart, toggle Bytes to show bandwidth consumption.
- In the Crawlers tab, a new Bytes Transferred column shows bandwidth per crawler.
Image exports
- Export charts and tables as images for reports and presentations.
Learn more about analyzing AI traffic.
- In the Metrics tab > Most popular paths table, use the new Patterns tab that groups requests by URI pattern (
-
Get your content updates into AI Search faster and avoid a full rescan when you do not need it.
Updated a file or need to retry one that errored? When you know exactly which file changed, you can now reindex it directly instead of rescanning your entire data source.
Go to Overview > Indexed Items and select the sync icon next to any file to reindex it immediately.

By default, AI Search crawls all sitemaps listed in your
robots.txt, up to the maximum files per index limit. If your site has multiple sitemaps but you only want to index a specific set, you can now specify a single sitemap URL to limit what the crawler visits.For example, if your
robots.txtlists bothblog-sitemap.xmlanddocs-sitemap.xml, you can specify justhttps://example.com/docs-sitemap.xmlto index only your documentation.Configure your selection anytime in Settings > Parsing options > Specific sitemaps, then trigger a sync to apply the changes.

Learn more about indexing controls and website crawling configuration.
-
R2 SQL now supports five approximate aggregation functions for fast analysis of large datasets. These functions trade minor precision for improved performance on high-cardinality data.
APPROX_PERCENTILE_CONT(column, percentile)— Returns the approximate value at a given percentile (0.0 to 1.0). Works on integer and decimal columns.APPROX_PERCENTILE_CONT_WITH_WEIGHT(column, weight, percentile)— Weighted percentile calculation where each row contributes proportionally to its weight column value.APPROX_MEDIAN(column)— Returns the approximate median. Equivalent toAPPROX_PERCENTILE_CONT(column, 0.5).APPROX_DISTINCT(column)— Returns the approximate number of distinct values. Works on any column type.APPROX_TOP_K(column, k)— Returns thekmost frequent values with their counts as a JSON array.
All functions support
WHEREfilters. All exceptAPPROX_TOP_KsupportGROUP BY.-- Percentile analysis on revenue dataSELECT approx_percentile_cont(total_amount, 0.25),approx_percentile_cont(total_amount, 0.5),approx_percentile_cont(total_amount, 0.75)FROM my_namespace.sales_data-- Median per departmentSELECT department, approx_median(total_amount)FROM my_namespace.sales_dataGROUP BY department-- Approximate distinct customers by regionSELECT region, approx_distinct(customer_id)FROM my_namespace.sales_dataGROUP BY region-- Top 5 most frequent departmentsSELECT approx_top_k(department, 5)FROM my_namespace.sales_data-- Combine approximate and standard aggregationsSELECT COUNT(*),AVG(total_amount),approx_percentile_cont(total_amount, 0.5),approx_distinct(customer_id)FROM my_namespace.sales_dataWHERE region = 'North'For the full syntax and additional examples, refer to the SQL reference.
-
The Workers Observability dashboard ↗ has some major updates to make it easier to debug your application's issues and share findings with your team.

You can now:
- Create visualizations — Build charts from your Worker data directly in a Worker's Observability tab
- Export data as JSON or CSV — Download logs and traces for offline analysis or to share with teammates
- Share events and traces — Generate direct URLs to specific events, invocations, and traces that open standalone pages with full context
- Customize table columns — Improved field picker to add, remove, and reorder columns in the events table
- Expandable event details — Expand events inline to view full details without leaving the table
- Keyboard shortcuts — Navigate the dashboard with hotkey support

These updates are now live in the Cloudflare dashboard, both in a Worker's Observability tab and in the account-level Observability dashboard for a unified experience. To get started, go to Workers & Pages > select your Worker > Observability.
-
New reference documentation is now available for AI Crawl Control:
- GraphQL API reference — Query examples for crawler requests, top paths, referral traffic, and data transfer. Includes key filters for detection IDs, user agents, and referrer domains.
- Bot reference — Detection IDs and user agents for major AI crawlers from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Meta, and others.
- Worker templates — Deploy the x402 Payment-Gated Proxy to monetize crawler access or charge bots while letting humans through free.
-
Cloudflare Queues is now part of the Workers free plan, offering guaranteed message delivery across up to 10,000 queues to either Cloudflare Workers or HTTP pull consumers. Every Cloudflare account now includes 10,000 operations per day across reads, writes, and deletes. For more details on how each operation is defined, refer to Queues pricing ↗.
All features of the existing Queues functionality are available on the free plan, including unlimited event subscriptions. Note that the maximum retention period on the free tier, however, is 24 hours rather than 14 days.
If you are new to Cloudflare Queues, follow this guide ↗ or try one of our tutorials to get started.
-
Cloudflare Workflows now automatically generates visual diagrams from your code
Your Workflow is parsed to provide a visual map of the Workflow structure, allowing you to:
- Understand how steps connect and execute
- Visualize loops and nested logic
- Follow branching paths for conditional logic

You can collapse loops and nested logic to see the high-level flow, or expand them to see every step.
Workflow diagrams are available in beta for all JavaScript and TypeScript Workflows. Find your Workflows in the Cloudflare dashboard ↗ to see their diagrams.
-
The latest release of the Agents SDK ↗ brings first-class support for Cloudflare Workflows, synchronous state management, and new scheduling capabilities.
Agents excel at real-time communication and state management. Workflows excel at durable execution. Together, they enable powerful patterns where Agents handle WebSocket connections while Workflows handle long-running tasks, retries, and human-in-the-loop flows.
Use the new
AgentWorkflowclass to define workflows with typed access to your Agent:JavaScript import { AgentWorkflow } from "agents/workflows";export class ProcessingWorkflow extends AgentWorkflow {async run(event, step) {// Call Agent methods via RPCawait this.agent.updateStatus(event.payload.taskId, "processing");// Non-durable: progress reporting to clientsawait this.reportProgress({ step: "process", percent: 0.5 });this.broadcastToClients({ type: "update", taskId: event.payload.taskId });// Durable via step: idempotent, won't repeat on retryawait step.mergeAgentState({ taskProgress: 0.5 });const result = await step.do("process", async () => {return processData(event.payload.data);});await step.reportComplete(result);return result;}}TypeScript import { AgentWorkflow } from "agents/workflows";import type { AgentWorkflowEvent, AgentWorkflowStep } from "agents/workflows";export class ProcessingWorkflow extends AgentWorkflow<MyAgent, TaskParams> {async run(event: AgentWorkflowEvent<TaskParams>, step: AgentWorkflowStep) {// Call Agent methods via RPCawait this.agent.updateStatus(event.payload.taskId, "processing");// Non-durable: progress reporting to clientsawait this.reportProgress({ step: "process", percent: 0.5 });this.broadcastToClients({ type: "update", taskId: event.payload.taskId });// Durable via step: idempotent, won't repeat on retryawait step.mergeAgentState({ taskProgress: 0.5 });const result = await step.do("process", async () => {return processData(event.payload.data);});await step.reportComplete(result);return result;}}Start workflows from your Agent with
runWorkflow()and handle lifecycle events:JavaScript export class MyAgent extends Agent {async startTask(taskId, data) {const instanceId = await this.runWorkflow("PROCESSING_WORKFLOW", {taskId,data,});return { instanceId };}async onWorkflowProgress(workflowName, instanceId, progress) {this.broadcast(JSON.stringify({ type: "progress", progress }));}async onWorkflowComplete(workflowName, instanceId, result) {console.log(`Workflow ${instanceId} completed`);}async onWorkflowError(workflowName, instanceId, error) {console.error(`Workflow ${instanceId} failed:`, error);}}TypeScript export class MyAgent extends Agent {async startTask(taskId: string, data: string) {const instanceId = await this.runWorkflow("PROCESSING_WORKFLOW", {taskId,data,});return { instanceId };}async onWorkflowProgress(workflowName: string,instanceId: string,progress: unknown,) {this.broadcast(JSON.stringify({ type: "progress", progress }));}async onWorkflowComplete(workflowName: string,instanceId: string,result?: unknown,) {console.log(`Workflow ${instanceId} completed`);}async onWorkflowError(workflowName: string,instanceId: string,error: unknown,) {console.error(`Workflow ${instanceId} failed:`, error);}}Key workflow methods on your Agent:
runWorkflow(workflowName, params, options?)— Start a workflow with optional metadatagetWorkflow(workflowId)/getWorkflows(criteria?)— Query workflows with cursor-based paginationapproveWorkflow(workflowId)/rejectWorkflow(workflowId)— Human-in-the-loop approval flowspauseWorkflow(),resumeWorkflow(),terminateWorkflow()— Workflow control
State updates are now synchronous with a new
validateStateChange()validation hook:JavaScript export class MyAgent extends Agent {validateStateChange(oldState, newState) {// Return false to reject the changeif (newState.count < 0) return false;// Return modified state to transformreturn { ...newState, lastUpdated: Date.now() };}}TypeScript export class MyAgent extends Agent<Env, State> {validateStateChange(oldState: State, newState: State): State | false {// Return false to reject the changeif (newState.count < 0) return false;// Return modified state to transformreturn { ...newState, lastUpdated: Date.now() };}}The new
scheduleEvery()method enables fixed-interval recurring tasks with built-in overlap prevention:JavaScript // Run every 5 minutesawait this.scheduleEvery("syncData", 5 * 60 * 1000, { source: "api" });TypeScript // Run every 5 minutesawait this.scheduleEvery("syncData", 5 * 60 * 1000, { source: "api" });- Client-side RPC timeout — Set timeouts on callable method invocations
StreamingResponse.error(message)— Graceful stream error signalinggetCallableMethods()— Introspection API for discovering callable methods- Connection close handling — Pending calls are automatically rejected on disconnect
JavaScript await agent.call("method", [args], {timeout: 5000,stream: { onChunk, onDone, onError },});TypeScript await agent.call("method", [args], {timeout: 5000,stream: { onChunk, onDone, onError },});Secure email reply routing — Email replies are now secured with HMAC-SHA256 signed headers, preventing unauthorized routing of emails to agent instances.
Routing improvements:
basePathoption to bypass default URL construction for custom routing- Server-sent identity — Agents send
nameandagenttype on connect - New
onIdentityandonIdentityChangecallbacks on the client
JavaScript const agent = useAgent({basePath: "user",onIdentity: (name, agentType) => console.log(`Connected to ${name}`),});TypeScript const agent = useAgent({basePath: "user",onIdentity: (name, agentType) => console.log(`Connected to ${name}`),});To update to the latest version:
Terminal window npm i agents@latestFor the complete Workflows API reference and patterns, see Run Workflows.
-
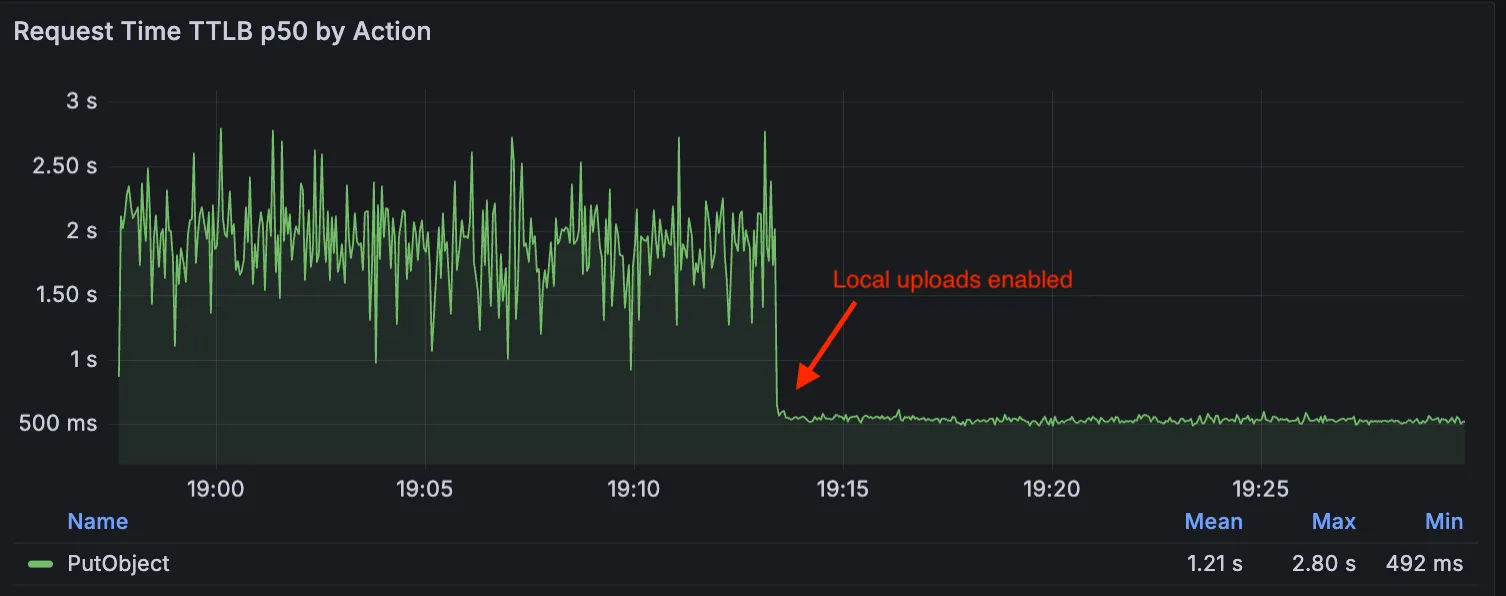
Local Uploads is now available in open beta. Enable it on your R2 bucket to improve upload performance when clients upload data from a different region than your bucket. With Local Uploads enabled, object data is written to storage infrastructure near the client, then asynchronously replicated to your bucket. The object is immediately accessible and remains strongly consistent throughout. Refer to How R2 works for details on how data is written to your bucket.
In our tests, we observed up to 75% reduction in Time to Last Byte (TTLB) for upload requests when Local Uploads is enabled.
This feature is ideal when:
- Your users are globally distributed
- Upload performance and reliability is critical to your application
- You want to optimize write performance without changing your bucket's primary location
To enable Local Uploads on your bucket, find Local Uploads in your bucket settings in the Cloudflare Dashboard ↗, or run:
Terminal window npx wrangler r2 bucket local-uploads enable <BUCKET_NAME>Enabling Local Uploads on a bucket is seamless: existing uploads will complete as expected and there’s no interruption to traffic. There is no additional cost to enable Local Uploads. Upload requests incur the standard Class A operation costs same as upload requests made without Local Uploads.
For more information, refer to Local Uploads.
-
Identifying threat actors can be challenging, because naming conventions often vary across the security industry. To simplify your research, Cloudflare Threat Events now include an Also known as field, providing a list of common aliases and industry-standard names for the groups we track.
This new field is available in both the Cloudflare dashboard and via the API. In the dashboard, you can view these aliases by expanding the event details side panel (under the Attacker field) or by adding it as a column in your configurable table view.
- Easily map Cloudflare-tracked actors to the naming conventions used by other vendors without manual cross-referencing.
- Quickly identify if a detected threat actor matches a group your team is already monitoring via other intelligence feeds.
For more information on how to access this data, refer to the Threat Events API documentation ↗.
-
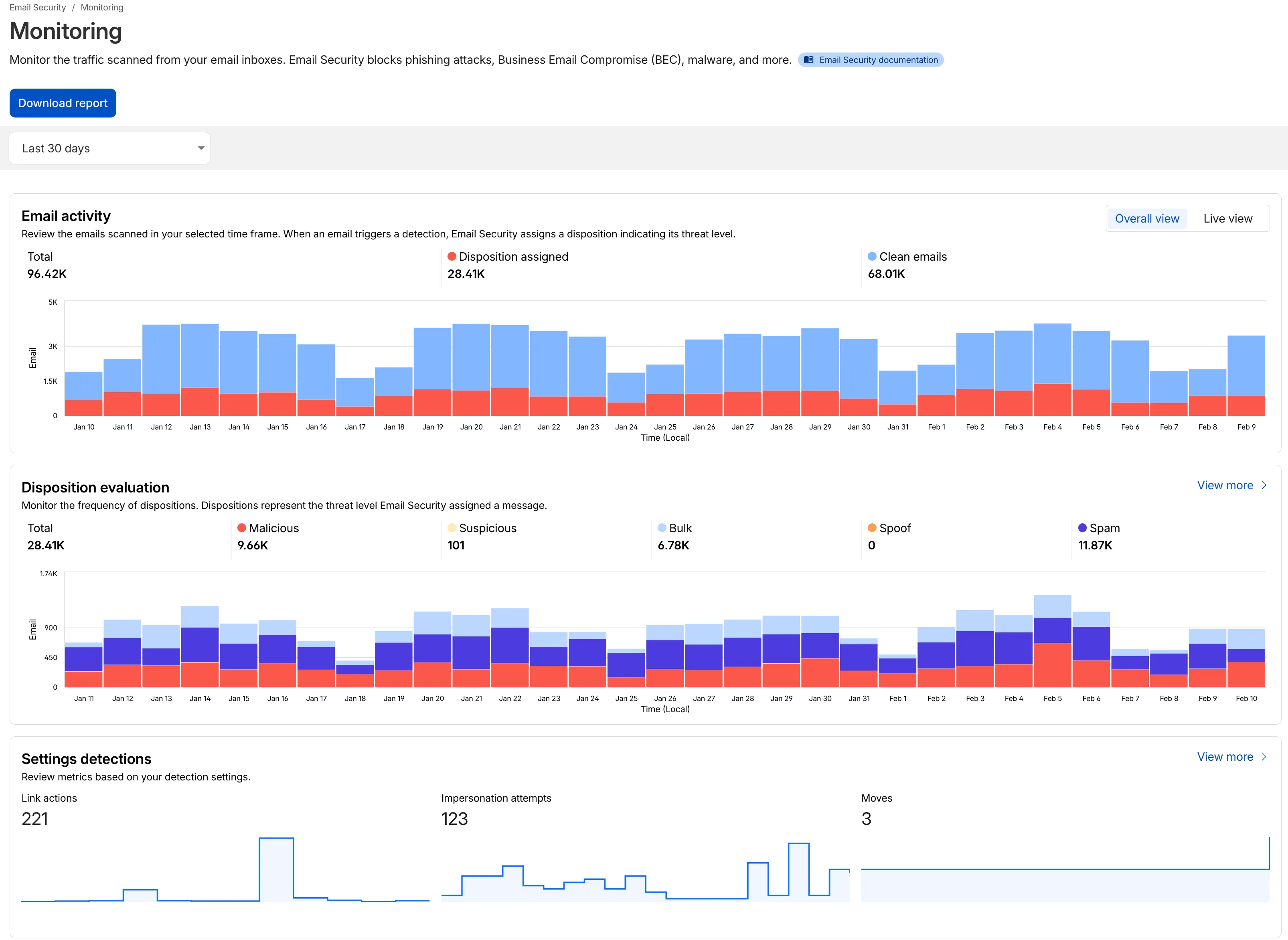
We have updated the Monitoring page to provide a more streamlined and insightful experience for administrators, improving both data visualization and dashboard accessibility.
- Enhanced Visual Layout: Optimized contrast and the introduction of stacked bar charts for clearer data visualization and trend analysis.
- Improved Accessibility & Usability:
- Widget Search: Added search functionality to multiple widgets, including Policies, Submitters, and Impersonation.
- Actionable UI: All available actions are now accessible via dedicated buttons.
- State Indicators: Improved UI states to clearly communicate loading, empty datasets, and error conditions.
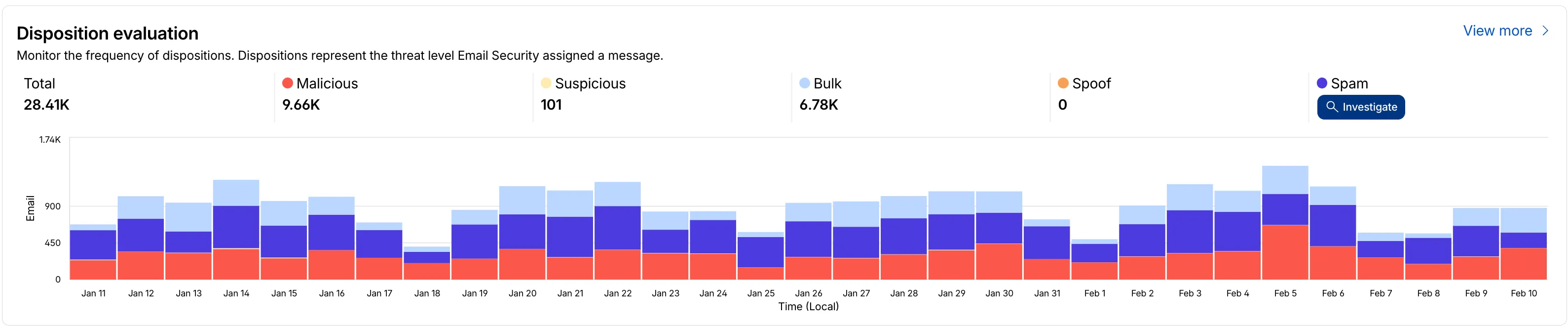
- Granular Data Breakdowns: New views for dispositions by month, malicious email details, link actions, and impersonations.

This applies to all Email Security packages:
- Advantage
- Enterprise
- Enterprise + PhishGuard
- Enhanced Visual Layout: Optimized contrast and the introduction of stacked bar charts for clearer data visualization and trend analysis.
-
This week’s release introduces new detections for CVE-2025-64459 and CVE-2025-24893.
Key Findings
- CVE-2025-64459: Django versions prior to 5.1.14, 5.2.8, and 4.2.26 are vulnerable to SQL injection via crafted dictionaries passed to QuerySet methods and the
Q()class. - CVE-2025-24893: XWiki allows unauthenticated remote code execution through crafted requests to the SolrSearch endpoint, affecting the entire installation.
Ruleset Rule ID Legacy Rule ID Description Previous Action New Action Comments Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A XWiki - Remote Code Execution - CVE:CVE-2025-24893 2 Log Block This is a new detection. Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A Django SQLI - CVE:CVE-2025-64459 Log Block This is a new detection. Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A NoSQL, MongoDB - SQLi - Comparison - 2 Block Block Rule metadata description refined. Detection unchanged. - CVE-2025-64459: Django versions prior to 5.1.14, 5.2.8, and 4.2.26 are vulnerable to SQL injection via crafted dictionaries passed to QuerySet methods and the
-
The minimum
cacheTtlparameter for Workers KV has been reduced from 60 seconds to 30 seconds. This change applies to bothget()andgetWithMetadata()methods.This reduction allows you to maintain more up-to-date cached data and have finer-grained control over cache behavior. Applications requiring faster data refresh rates can now configure cache durations as low as 30 seconds instead of the previous 60-second minimum.
The
cacheTtlparameter defines how long a KV result is cached at the global network location it is accessed from:JavaScript // Read with custom cache TTLconst value = await env.NAMESPACE.get("my-key", {cacheTtl: 30, // Cache for minimum 30 seconds (previously 60)});// getWithMetadata also supports the reduced cache TTLconst valueWithMetadata = await env.NAMESPACE.getWithMetadata("my-key", {cacheTtl: 30, // Cache for minimum 30 seconds});The default cache TTL remains unchanged at 60 seconds. Upgrade to the latest version of Wrangler to be able to use 30 seconds
cacheTtl.This change affects all KV read operations using the binding API. For more information, consult the Workers KV cache TTL documentation.
-
Magic WAN and Magic Transit customers can use the Cloudflare dashboard to configure and manage BGP peering between their networks and their Magic routing table when using IPsec and GRE tunnel on-ramps (beta).
Using BGP peering allows customers to:
- Automate the process of adding or removing networks and subnets.
- Take advantage of failure detection and session recovery features.
With this functionality, customers can:
- Establish an eBGP session between their devices and the Magic WAN / Magic Transit service when connected via IPsec and GRE tunnel on-ramps.
- Secure the session by MD5 authentication to prevent misconfigurations.
- Exchange routes dynamically between their devices and their Magic routing table.
For configuration details, refer to:
-
We have partnered with Black Forest Labs (BFL) again to bring their optimized FLUX.2 [klein] 9B model to Workers AI. This distilled model offers enhanced quality compared to the 4B variant, while maintaining cost-effective pricing. With a fixed 4-step inference process, Klein 9B is ideal for rapid prototyping and real-time applications where both speed and quality matter.
Read the BFL blog ↗ to learn more about the model itself, or try it out yourself on our multi modal playground ↗.
Pricing documentation is available on the model page or pricing page.
The model hosted on Workers AI is optimized for speed with a fixed 4-step inference process and supports up to 4 image inputs. Since this is a distilled model, the
stepsparameter is fixed at 4 and cannot be adjusted. Like FLUX.2 [dev] and FLUX.2 [klein] 4B, this image model uses multipart form data inputs, even if you just have a prompt.With the REST API, the multipart form data input looks like this:
Terminal window curl --request POST \--url 'https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/{ACCOUNT}/ai/run/@cf/black-forest-labs/flux-2-klein-9b' \--header 'Authorization: Bearer {TOKEN}' \--header 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data' \--form 'prompt=a sunset at the alps' \--form width=1024 \--form height=1024With the Workers AI binding, you can use it as such:
JavaScript const form = new FormData();form.append("prompt", "a sunset with a dog");form.append("width", "1024");form.append("height", "1024");// FormData doesn't expose its serialized body or boundary. Passing it to a// Request (or Response) constructor serializes it and generates the Content-Type// header with the boundary, which is required for the server to parse the multipart fields.const formResponse = new Response(form);const formStream = formResponse.body;const formContentType = formResponse.headers.get('content-type');const resp = await env.AI.run("@cf/black-forest-labs/flux-2-klein-9b", {multipart: {body: formStream,contentType: formContentType,},});The parameters you can send to the model are detailed here:
JSON Schema for Model
Required Parametersprompt(string) - Text description of the image to generate
Optional Parameters
input_image_0(string) - Binary imageinput_image_1(string) - Binary imageinput_image_2(string) - Binary imageinput_image_3(string) - Binary imageguidance(float) - Guidance scale for generation. Higher values follow the prompt more closelywidth(integer) - Width of the image, default1024Range: 256-1920height(integer) - Height of the image, default768Range: 256-1920seed(integer) - Seed for reproducibility
Note: Since this is a distilled model, the
stepsparameter is fixed at 4 and cannot be adjusted.The FLUX.2 klein-9b model supports generating images based on reference images, just like FLUX.2 [dev] and FLUX.2 [klein] 4B. You can use this feature to apply the style of one image to another, add a new character to an image, or iterate on past generated images. You would use it with the same multipart form data structure, with the input images in binary. The model supports up to 4 input images.
For the prompt, you can reference the images based on the index, like
take the subject of image 1 and style it like image 0or even use natural language likeplace the dog beside the woman.You must name the input parameter as
input_image_0,input_image_1,input_image_2,input_image_3for it to work correctly. All input images must be smaller than 512x512.Terminal window curl --request POST \--url 'https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/{ACCOUNT}/ai/run/@cf/black-forest-labs/flux-2-klein-9b' \--header 'Authorization: Bearer {TOKEN}' \--header 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data' \--form 'prompt=take the subject of image 1 and style it like image 0' \--form input_image_0=@/Users/johndoe/Desktop/icedoutkeanu.png \--form input_image_1=@/Users/johndoe/Desktop/me.png \--form width=1024 \--form height=1024Through Workers AI Binding:
JavaScript //helper function to convert ReadableStream to Blobasync function streamToBlob(stream: ReadableStream, contentType: string): Promise<Blob> {const reader = stream.getReader();const chunks = [];while (true) {const { done, value } = await reader.read();if (done) break;chunks.push(value);}return new Blob(chunks, { type: contentType });}const image0 = await fetch("http://image-url");const image1 = await fetch("http://image-url");const form = new FormData();const image_blob0 = await streamToBlob(image0.body, "image/png");const image_blob1 = await streamToBlob(image1.body, "image/png");form.append('input_image_0', image_blob0)form.append('input_image_1', image_blob1)form.append('prompt', 'take the subject of image 1 and style it like image 0')// FormData doesn't expose its serialized body or boundary. Passing it to a// Request (or Response) constructor serializes it and generates the Content-Type// header with the boundary, which is required for the server to parse the multipart fields.const formResponse = new Response(form);const formStream = formResponse.body;const formContentType = formResponse.headers.get('content-type');const resp = await env.AI.run("@cf/black-forest-labs/flux-2-klein-9b", {multipart: {body: formStream,contentType: formContentType}})
-
A new Beta release for the Windows WARP client is now available on the beta releases downloads page.
This release contains minor fixes, improvements, and new features.
Changes and improvements
- Improvements to multi-user mode. Fixed an issue where when switching from a pre-login registration to a user registration, Mobile Device Management (MDM) configuration association could be lost.
- Added a new feature to manage NetBIOS over TCP/IP functionality on the Windows client. NetBIOS over TCP/IP on the Windows client is now disabled by default and can be enabled in device profile settings.
- Fixed an issue causing failure of the local network exclusion feature when configured with a timeout of
0. - Improvement for the Windows client certificate posture check to ensure logged results are from checks that run once users log in.
- Improvement for more accurate reporting of device colocation information in the Cloudflare One dashboard.
Known issues
For Windows 11 24H2 users, Microsoft has confirmed a regression that may lead to performance issues like mouse lag, audio cracking, or other slowdowns. Cloudflare recommends users experiencing these issues upgrade to a minimum Windows 11 24H2 KB5062553 or higher for resolution.
Devices with KB5055523 installed may receive a warning about
Win32/ClickFix.ABAbeing present in the installer. To resolve this false positive, update Microsoft Security Intelligence to version 1.429.19.0 or later.DNS resolution may be broken when the following conditions are all true:
- WARP is in Secure Web Gateway without DNS filtering (tunnel-only) mode.
- A custom DNS server address is configured on the primary network adapter.
- The custom DNS server address on the primary network adapter is changed while WARP is connected.
To work around this issue, reconnect the WARP client by toggling off and back on.
-
A new Beta release for the macOS WARP client is now available on the beta releases downloads page.
This release contains minor fixes and improvements.
Changes and improvements
- Fixed an issue causing failure of the local network exclusion feature when configured with a timeout of
0. - Improvement for more accurate reporting of device colocation information in the Cloudflare One dashboard.
- Fixed an issue causing failure of the local network exclusion feature when configured with a timeout of
-
Cloudflare source IPs are the IP addresses used by Cloudflare services (such as Load Balancing, Gateway, and Browser Isolation) when sending traffic to your private networks.
For customers using legacy mode routing, traffic to private networks is sourced from public Cloudflare IPs, which may cause IP conflicts. For customers using Unified Routing mode (beta), traffic to private networks is sourced from dedicated, non-Internet-routable private IPv4 range to ensure:
- Symmetric routing over private network connections
- Proper firewall state preservation
- Private traffic stays on secure paths
Key details:
- IPv4: Sourced from
100.64.0.0/12by default, configurable to any/12CIDR - IPv6: Sourced from
2606:4700:cf1:5000::/64(not configurable) - Affected connectors: GRE, IPsec, CNI, WARP Connector, and WARP Client (Cloudflare Tunnel is not affected)
Configuring Cloudflare source IPs requires Unified Routing (beta) and the
Cloudflare One Networks Writepermission.For configuration details, refer to Configure Cloudflare source IPs.
-
You can now set the timezone in the Cloudflare dashboard as Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) or your browser or system's timezone.
Unless otherwise specified in the user interface, all dates and times in the Cloudflare dashboard are now displayed in the selected timezone.
You can change the timezone setting from the user profile dropdown.

The page will reload to apply the new timezone setting.
-
You can now control how Cloudflare buffers HTTP request and response bodies using two new settings in Configuration Rules.
Controls how Cloudflare buffers HTTP request bodies before forwarding them to your origin server:
Mode Behavior Standard (default) Cloudflare can inspect a prefix of the request body for enabled functionality such as WAF and Bot Management. Full Buffers the entire request body before sending to origin. None No buffering — the request body streams directly to origin without inspection. Controls how Cloudflare buffers HTTP response bodies before forwarding them to the client:
Mode Behavior Standard (default) Cloudflare can inspect a prefix of the response body for enabled functionality. None No buffering — the response body streams directly to the client without inspection. {"action": "set_config","action_parameters": {"request_body_buffering": "standard","response_body_buffering": "none"}}For more information, refer to Configuration Rules.
-
This week’s release introduces new detections for denial-of-service attempts targeting React CVE-2026-23864 (https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2026-23864 ↗).
Key Findings
- CVE-2026-23864 (https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2026-23864 ↗) affects
react-server-dom-parcel,react-server-dom-turbopack, andreact-server-dom-webpackpackages. - Attackers can send crafted HTTP requests to Server Function endpoints, causing server crashes, out-of-memory exceptions, or excessive CPU usage.
Ruleset Rule ID Legacy Rule ID Description Previous Action New Action Comments Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A React Server - DOS - CVE:CVE-2026-23864 - 1 N/A Block This is a new detection. Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A React Server - DOS - CVE:CVE-2026-23864 - 2 N/A Block This is a new detection. Cloudflare Managed Ruleset N/A React Server - DOS - CVE:CVE-2026-23864 - 3 N/A Block This is a new detection. - CVE-2026-23864 (https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2026-23864 ↗) affects
-
In an effort to improve overall user security, users without 2FA will be prompted upon login to enroll in email 2FA. This will improve user security posture while minimizing friction. Users without email 2FA enabled will see a prompt to secure their account with additional factors upon logging in. Enrolling in 2FA remains optional, but strongly encouraged as it is the best way to prevent account takeovers.
We also made changes to existing 2FA screens to improve the user experience. Now we have distinct experiences for each 2FA factor type, reflective of the way that factor works.
-
Paid plans can now have up to 100,000 files per Pages site, increased from the previous limit of 20,000 files.
To enable this increased limit, set the environment variable
PAGES_WRANGLER_MAJOR_VERSION=4in your Pages project settings.The Free plan remains at 20,000 files per site.
For more details, refer to the Pages limits documentation.
-
You can now store up to 10 million vectors in a single Vectorize index, doubling the previous limit of 5 million vectors. This enables larger-scale semantic search, recommendation systems, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications without splitting data across multiple indexes.
Vectorize continues to support indexes with up to 1,536 dimensions per vector at 32-bit precision. Refer to the Vectorize limits documentation for complete details.
-
Cloudflare Rulesets now includes
encode_base64()andsha256()functions, enabling you to generate signed request headers directly in rule expressions. These functions support common patterns like constructing a canonical string from request attributes, computing a SHA256 digest, and Base64-encoding the result.
Function Description Availability encode_base64(input, flags)Encodes a string to Base64 format. Optional flagsparameter:ufor URL-safe encoding,pfor padding (adds=characters to make the output length a multiple of 4, as required by some systems). By default, output is standard Base64 without padding.All plans (in header transform rules) sha256(input)Computes a SHA256 hash of the input string. Requires enablement
Encode a string to Base64 format:
encode_base64("hello world")Returns:
aGVsbG8gd29ybGQEncode a string to Base64 format with padding:
encode_base64("hello world", "p")Returns:
aGVsbG8gd29ybGQ=Perform a URL-safe Base64 encoding of a string:
encode_base64("hello world", "u")Returns:
aGVsbG8gd29ybGQCompute the SHA256 hash of a secret token:
sha256("my-token")Returns a hash that your origin can validate to authenticate requests.
Compute the SHA256 hash of a string and encode the result to Base64 format:
encode_base64(sha256("my-token"))Combines hashing and encoding for systems that expect Base64-encoded signatures.
For more information, refer to the Functions reference.
-
You can now configure Workers to run close to infrastructure in legacy cloud regions to minimize latency to existing services and databases. This is most useful when your Worker makes multiple round trips.
To set a placement hint, set the
placement.regionproperty in your Wrangler configuration file:{"placement": {"region": "aws:us-east-1",},}[placement]region = "aws:us-east-1"Placement hints support Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure region identifiers. Workers run in the Cloudflare data center ↗ with the lowest latency to the specified cloud region.
If your existing infrastructure is not in these cloud providers, expose it to placement probes with
placement.hostfor layer 4 checks orplacement.hostnamefor layer 7 checks. These probes are designed to locate single-homed infrastructure and are not suitable for anycasted or multicasted resources.{"placement": {"host": "my_database_host.com:5432",},}[placement]host = "my_database_host.com:5432"{"placement": {"hostname": "my_api_server.com",},}[placement]hostname = "my_api_server.com"This is an extension of Smart Placement, which automatically places your Workers closer to back-end APIs based on measured latency. When you do not know the location of your back-end APIs or have multiple back-end APIs, set
mode: "smart":{"placement": {"mode": "smart",},}[placement]mode = "smart"
No recent entries for this product.
Search all changelog entries →