Placement
By default, Workers and Pages Functions run in a data center closest to where the request was received. If your Worker makes requests to back-end infrastructure such as databases or APIs, it may be more performant to run that Worker closer to your back-end than the end user.
{ "placement": { // Use one of the following options (mutually exclusive): "mode": "smart", // Cloudflare automatically places your Worker closest to the upstream with the most requests "region": "gcp:us-east4", // Explicit cloud region to run your Worker closest to - e.g. "gcp:us-east4" or "aws:us-east-1" "host": "db.example.com:5432", // A host to probe (TCP/layer 4) - e.g. a database host - and place your Worker closest to "hostname": "api.example.com", // A hostname to probe (HTTP/layer 7) - e.g. an API endpoint - and place your Worker closest to },}[placement]mode = "smart"region = "gcp:us-east4"host = "db.example.com:5432"hostname = "api.example.com"Placement can reduce the overall latency of a Worker request by minimizing roundtrip latency of requests between your Worker and back-end services. You can achieve single-digit millisecond latency to databases, APIs, and other services running in legacy cloud infrastructure.
| Option | Best for | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Smart | Multiple back-end services, or unknown infrastructure locations | mode = "smart" |
| Region | Single back-end service in a known cloud region | region |
| Host | Single back-end service not in a major cloud provider | host or hostname |
Consider a user in Sydney, Australia accessing an application running on Workers. This application makes multiple round trips to a database in Frankfurt, Germany.
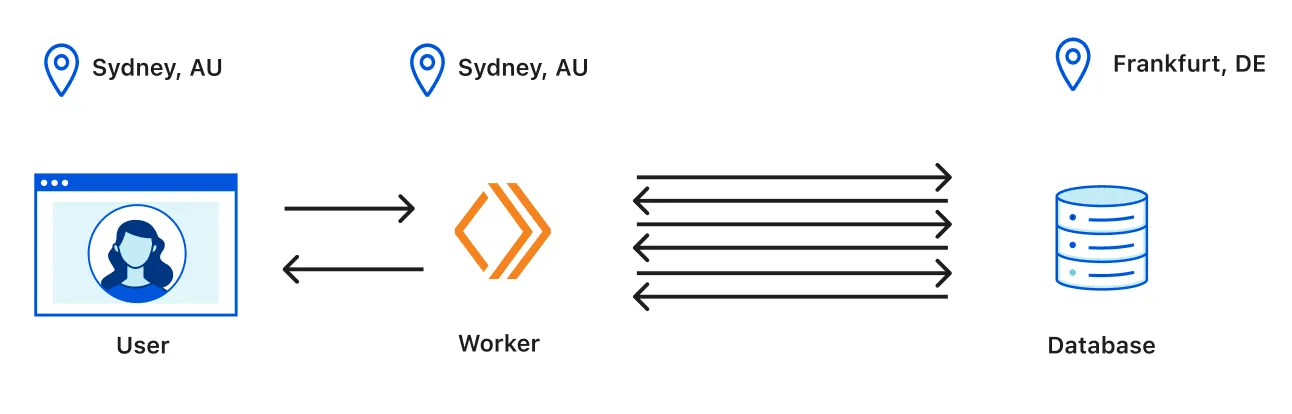
The latency from multiple round trips between Sydney and Frankfurt adds up. By placing the Worker near the database, Cloudflare reduces the total request duration.
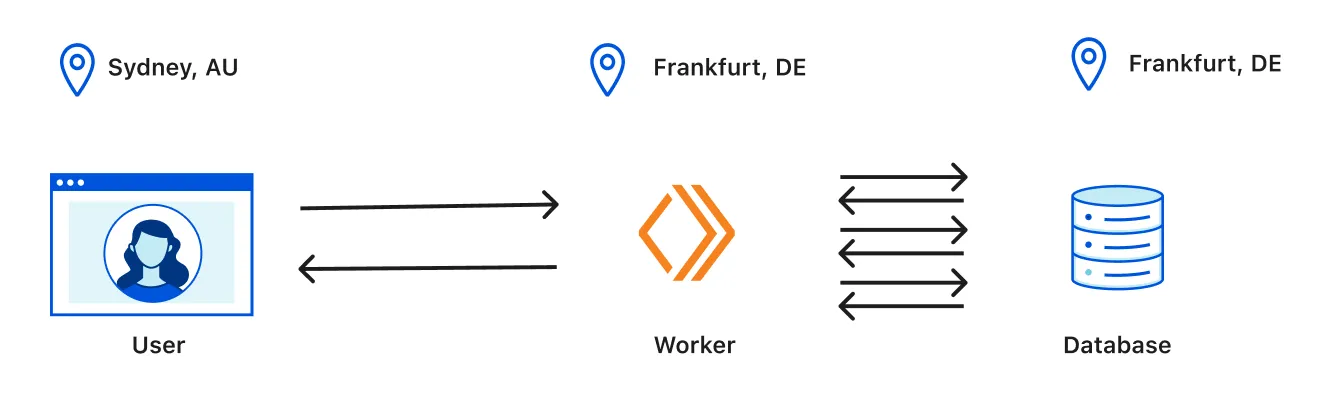
Smart Placement automatically analyzes your Worker's traffic patterns and places it in an optimal location. Use Smart Placement when:
- Your Worker connects to multiple back-end services
- You do not know the exact location of your infrastructure
- Your back-end services are distributed or replicated
Smart Placement is enabled on a per-Worker basis. Once enabled, it analyzes the request duration of the Worker in different Cloudflare locations on a regular basis.
For each candidate location, Smart Placement considers the Worker's performance and the network latency added by forwarding the request. If a candidate location is significantly faster, the request is forwarded there. Otherwise, the Worker runs in the default location closest to the request.
Smart Placement only considers locations where the Worker has previously run. It cannot place your Worker in a location that does not normally receive traffic.
- Smart Placement only affects the execution of fetch event handlers. It does not affect RPC methods or named entrypoints.
- Workers without a fetch event handler are ignored by Smart Placement.
- Static assets are always served from the location nearest to the incoming request. If your code retrieves assets via the static assets binding, assets are served from the location where your Worker runs.
Smart Placement is available on all Workers plans.
Add the following to your Wrangler configuration file:
{ "placement": { "mode": "smart", },}[placement]mode = "smart"Smart Placement may take up to 15 minutes to analyze your Worker after deployment.
-
Go to Workers & Pages.
Go to Workers & Pages -
Select your Worker.
-
Go to Settings > General.
-
Under Placement, select Smart.
Smart Placement requires consistent traffic to the Worker from multiple locations to make a placement decision. The analysis process may take up to 15 minutes.
Query your Worker's placement status through the Workers API:
curl -X GET https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/workers/services/$WORKER_NAME \-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \-H "Content-Type: application/json" | jq .Possible placement states:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| (not present) | The Worker has not been analyzed yet. It runs in the default location closest to the request. |
SUCCESS | The Worker was analyzed and will be optimized by Smart Placement. |
INSUFFICIENT_INVOCATIONS | The Worker has not received enough requests from multiple locations to make a placement decision. |
UNSUPPORTED_APPLICATION | Smart Placement made the Worker slower and reverted the placement. This state is rare (fewer than 1% of Workers). |
Once Smart Placement is enabled, data about request duration is collected. Request duration is measured at the data center closest to the end user. By default, 1% of requests are not routed with Smart Placement to serve as a baseline for comparison.
View your Worker's request duration analytics to measure the impact of Smart Placement.
Cloudflare adds a cf-placement header to all requests when placement is enabled. Use this header to check whether a request was routed with Smart Placement and where the Worker processed the request.
The header value includes a placement type and an airport code indicating the data center location:
remote-LHR— The request was routed using Smart Placement to a data center near London.local-EWR— The request was not routed using Smart Placement. The Worker ran in the default location near Newark.
Placement Hints let you explicitly specify where your Worker runs. Use Placement Hints when:
- You know the exact location of your back-end infrastructure
- Your Worker connects to a single database, API, or service
- Your infrastructure is single-homed (not replicated or anycasted)
Examples include a primary database, a virtual machine, or a Kubernetes cluster in a specific region. Reducing round-trip latency from 20 to 30 milliseconds per query to 1 to 3 milliseconds improves response times.
If your infrastructure runs in AWS, GCP, or Azure, set the placement.region property using the format {provider}:{region}:
{ "placement": { "region": "aws:us-east-1", // Explicit cloud region to run your Worker closest to - e.g. "gcp:us-east4" or "aws:us-east-1" },}[placement]region = "aws:us-east-1"Cloudflare maps your specified cloud region to the data center with the lowest latency to that region. Cloudflare automatically adjusts placement to account for network maintenance or changes, so you do not need to specify failover regions.
If your infrastructure is not in a major cloud provider, you can specify an endpoint for Cloudflare to probe. Cloudflare will triangulate the position of your external host and place Workers in a nearby region.
Set placement.host to identify a layer 4 service. Cloudflare uses TCP CONNECT checks to measure latency and selects the best data center.
{ "placement": { "host": "my_database_host.com:5432", // A host to probe (TCP/layer 4) - e.g. a database host - and place your Worker closest to },}[placement]host = "my_database_host.com:5432"Set placement.hostname to identify a layer 7 service. Cloudflare uses HTTP HEAD checks to measure latency and selects the best data center.
{ "placement": { "hostname": "my_api_server.com", // A hostname to probe (HTTP/layer 7) - e.g. an API endpoint - and place your Worker closest to },}[placement]hostname = "my_api_server.com"Probes are sent from public IP ranges, not Cloudflare IP ranges. Cloudflare rechecks service location at regular intervals. These probes locate single-homed resources and do not work correctly for broadcast, anycast, multicast, or replicated resources.
Placement Hints support Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure region identifiers:
| Provider | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| AWS | aws:{region} | aws:us-east-1, aws:us-west-2, aws:eu-central-1 |
| GCP | gcp:{region} | gcp:us-east4, gcp:europe-west1, gcp:asia-east1 |
| Azure | azure:{region} | azure:westeurope, azure:eastus, azure:southeastasia |
For a full list of region codes, refer to AWS regions ↗, GCP regions ↗, or Azure regions ↗.
Workers placement behaves in similar fashion when either Smart Placement or Placement Hints are used. The following behavior applies to both.
The following limitations apply to both Smart Placement and Placement Hints:
- Placement only affects the execution of fetch event handlers. It does not affect RPC methods or named entrypoints.
- Workers without a fetch event handler are ignored by placement.
- Static assets are always served from the location nearest to the incoming request. If your code retrieves assets via the static assets binding, assets are served from the location where your Worker runs.
Cloudflare adds a cf-placement header to all requests when placement is enabled. Use this header to check whether a request was routed with placement and where the Worker processed the request.
The header value includes a placement type and an airport code indicating the data center location:
remote-LHR— The request was routed using Smart Placement to a data center near London.local-EWR— The request was not routed using Smart Placement. The Worker ran in the default location near Newark.
If you are building full-stack applications on Workers, split your edge logic (authentication, routing) and back-end logic (database queries, API calls) into separate Workers. Use Service Bindings to connect them with type-safe RPC.
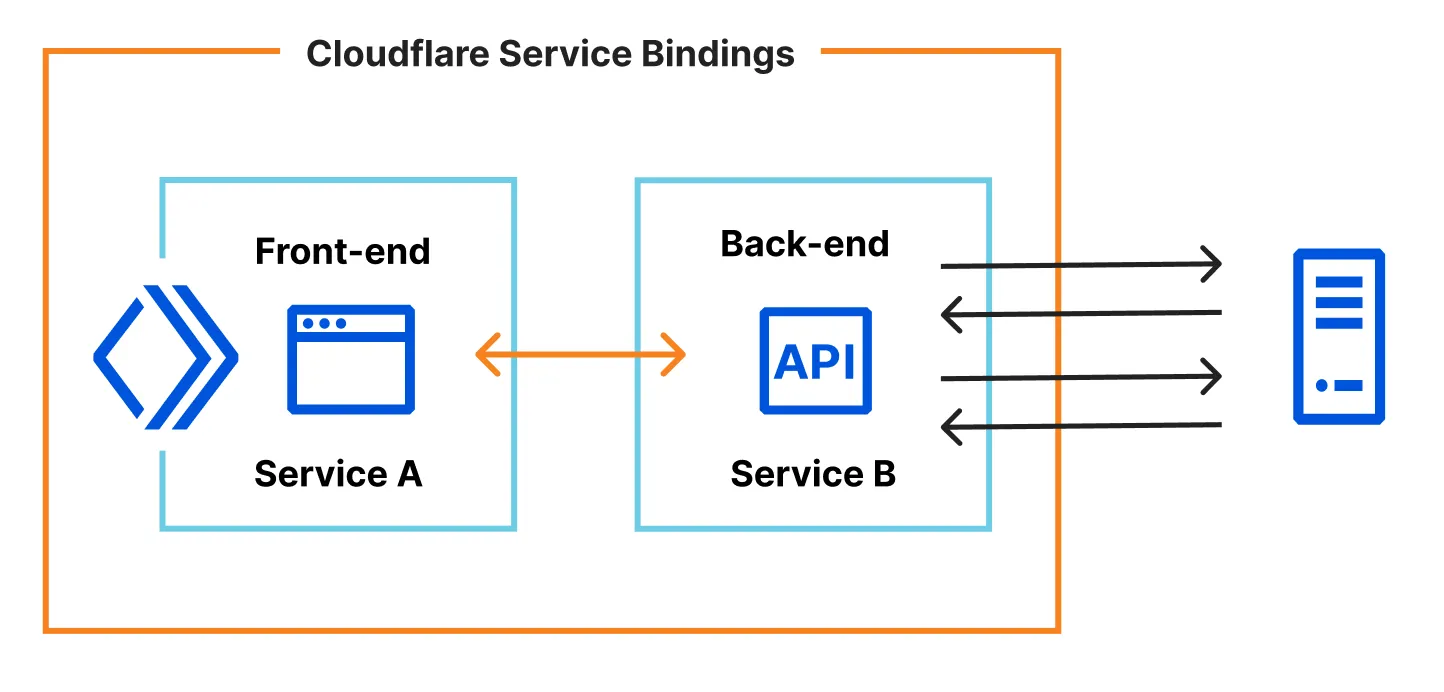
Enable placement on your back-end Worker to invoke it close to your database, while the edge Worker handles authentication close to the user.
This example shows two Workers:
auth-worker— runs at the edge (no placement), handles authenticationapp-worker— placed near your database, handles data queries
{ "name": "auth-worker", "main": "src/index.ts", "services": [{ "binding": "APP", "service": "app-worker" }],}name = "auth-worker"main = "src/index.ts"
[[services]]binding = "APP"service = "app-worker"import { AppWorker } from "../app-worker/src/index";
interface Env { APP: Service<AppWorker>;}
export default { async fetch(request: Request, env: Env): Promise<Response> { const authHeader = request.headers.get("Authorization"); if (!authHeader?.startsWith("Bearer ")) { return new Response("Unauthorized", { status: 401 }); }
const userId = await validateToken(authHeader.slice(7)); if (!userId) { return new Response("Invalid token", { status: 403 }); }
// Call the placed back-end Worker via RPC const data = await env.APP.getUser(userId); return Response.json(data); },};
async function validateToken(token: string): Promise<string | null> { return token === "valid" ? "user-123" : null;}{ "name": "app-worker", "main": "src/index.ts", "placement": { // Use one of the following options (mutually exclusive): // "mode": "smart", // Cloudflare automatically places your Worker closest to the upstream with the most requests "region": "aws:us-east-1", // Explicit cloud region to run your Worker closest to - e.g. "gcp:us-east4" or "aws:us-east-1" // "host": "db.example.com:5432", // A host to probe (TCP/layer 4) - e.g. a database host - and place your Worker closest to // "hostname": "api.example.com", // A hostname to probe (HTTP/layer 7) - e.g. an API endpoint - and place your Worker closest to },}name = "app-worker"main = "src/index.ts"
[placement]region = "aws:us-east-1"import { WorkerEntrypoint } from "cloudflare:workers";
export default class AppWorker extends WorkerEntrypoint { async fetch() { return new Response(null, { status: 404 }); }
// Each method runs near your database - multiple queries stay fast async getUser(userId: string) { const user = await this.env.DB.prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?") .bind(userId) .first(); return user; }
async getUserListings(userId: string) { // Multiple round-trips to the DB are low-latency when placed nearby const user = await this.env.DB.prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?") .bind(userId) .first(); const listings = await this.env.DB.prepare( "SELECT * FROM listings WHERE owner_id = ?", ) .bind(userId) .all(); const reviews = await this.env.DB.prepare( "SELECT * FROM reviews WHERE listing_id IN (SELECT id FROM listings WHERE owner_id = ?)", ) .bind(userId) .all();
return { user, listings: listings.results, reviews: reviews.results }; }}The auth-worker runs at the edge to reject unauthorized requests quickly. Authenticated requests are forwarded via RPC to app-worker, which runs near your database for fast queries.
Durable Objects provide automatic placement without configuration. Queries to a Durable Object's embedded SQLite database are effectively zero-latency ↗ because compute runs in the same process as the data.
Do as much work as possible within the Durable Object and return a composite result, rather than making multiple round-trips from your Worker:
import { DurableObject } from "cloudflare:workers";
type Session = { id: string; user_id: string; created_at: number };type PromptHistory = { id: string; session_id: string; role: string; content: string;};
export class AgentHistory extends DurableObject { async getSessionContext(sessionId: string) { // All queries execute with zero network latency — compute and data are colocated const session = this.ctx.storage.sql .exec<Session>("SELECT * FROM sessions WHERE id = ?", sessionId) .one(); const prompts = this.ctx.storage.sql .exec<PromptHistory>( "SELECT * FROM prompt_history WHERE session_id = ? ORDER BY created_at", sessionId, ) .toArray();
return { session, prompts }; }}