A Page Rules URL like:
example.com/*/downloads/*.txt
becomes a filter expression such as:
http.request.full_uri wildcard "http*://example.com/*/downloads/*.txt*"
Cloudflare is continuously improving its platform to deliver more powerful and scalable tools for managing your configurations. To help you take full advantage of these improvements, we recommend using modern Rules features for new implementations. These products address the limitations of Page Rules while providing greater flexibility, scalability, and ease of use.
For a quick start, explore the one-click templates available in the Cloudflare dashboard in Rules > Overview. These templates simplify common configurations like redirects, rewrites and header modifications, making setup faster and easier.
To make the transition seamless, Cloudflare will handle the migration of your existing Page Rules automatically. This process is planned for late 2025 or beyond, with no action required on your part. You will receive advance notification before any changes are made.
If you wish to explore the benefits of modern Rules features sooner, you can begin adopting them today. Doing so allows you to:
To assist with this process, we provide you with a comprehensive mapping between Page Rules settings and modern Rules products in this guide.
Cloudflare Page Rules has several fundamental limitations, such as triggering solely based on URL patterns and being limited to 125 rules per zone for performance reasons. These rules are also complex to debug when multiple page rules apply to the same incoming request.
In 2022, we announced in our blog post The future of Page Rules ↗ that Page Rules would be replaced with a suite of dedicated products, each built to be best-of-breed and put more power into the hands of our users. The new Rules products — Configuration Rules, Compression Rules, Origin Rules, Redirects, and Transform Rules — are now generally available (GA) and have already been adopted by tens of thousands of Cloudflare customers.
Improvements in modern Rules features include:
The evaluation and execution order of Rules features is different from Page Rules:
Modern Rules use filter expressions instead of URL patterns. These expressions, built with the Rules language, allow greater precision by leveraging fields, functions, and operators.
The following example demonstrates the use of the http.request.full_uri field and the wildcard operator for wildcard matching:
A Page Rules URL like:
example.com/*/downloads/*.txt
becomes a filter expression such as:
http.request.full_uri wildcard "http*://example.com/*/downloads/*.txt*"
Single Redirects and URL Rewrite Rules also offer a simplified view called Wildcard pattern, allowing you to specify URL patterns (http*://example.com/*/downloads/*.txt*) without specifying the full filter expression (http.request.full_uri wildcard "http*://example.com/*/downloads/*.txt*").
http:// or https://) unless explicitly included in the rule. Filter expressions using http.request.full_uri field, however, require matching the full URI, including the protocol scheme. To make your filter expression scheme-agnostic, use http*:// as a wildcard for both http:// and https://.http.request.full_uri field. To ensure query strings do not affect your matching, append a * wildcard at the end of your filter expression, such as .txt*.To help you map existing Page Rules to modern Rules products, this table outlines how Page Rules settings translate to modern Rules and provides examples for common configurations.
Also, to streamline common configurations, the Cloudflare dashboard now includes dozens of one-click templates, available in Rules > Overview. These templates enable you to deploy commonly used features — such as redirects, rewrites, and header modifications — instantly, with pre-filled filter expressions and actions. Explore these templates in the dashboard for a faster setup.
| Page Rules setting | New implementation uses... | Migration/Replacement instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Always Use HTTPS | Redirect Rules (Single Redirects) | Migrate Always Use HTTPS |
| Browser Cache TTL | Cache Rules | Migrate Browser Cache TTL |
| Browser Integrity Check | Configuration Rules | Migrate Browser Integrity Check |
| Bypass Cache on Cookie | Cache Rules | Migrate Bypass Cache on Cookie |
| Cache By Device Type | Cache Rules | Migrate Cache By Device Type |
| Cache Deception Armor | Cache Rules | Migrate Cache Deception Armor |
| Cache Level | Cache Rules | Migrate Cache Level |
| Cache on Cookie | Cache Rules | Migrate Cache on Cookie |
| Cache TTL by status code | Cache Rules | Migrate Cache TTL by status code |
| Custom Cache Key | Cache Rules | Migrate Custom Cache Key |
| Disable Apps | Configuration Rules | Migrate Disable Apps |
| Disable Performance | N/A (deprecated) | Replace Disable Performance |
| Disable Railgun | N/A (deprecated) | N/A |
| Disable Security | N/A (deprecated) | Replace Disable Security |
| Disable Zaraz | Configuration Rules | Migrate Disable Zaraz |
| Edge Cache TTL | Cache Rules | Migrate Edge Cache TTL |
| Email Obfuscation | Configuration Rules | Migrate Email Obfuscation |
| Forwarding URL | Redirect Rules (Single Redirects) | Migrate Forwarding URL |
| Host Header Override | Origin Rules | Migrate Host Header Override |
| IP Geolocation Header | Transform Rules (Managed Transforms) | Migrate IP Geolocation Header |
| Opportunistic Encryption | Configuration Rules | Migrate Opportunistic Encryption |
| Origin Cache Control | Cache Rules | Migrate Origin Cache Control |
| Origin Error Page Pass-thru | Cache Rules | Migrate Origin Error Page Pass-thru |
| Polish | Configuration Rules | Migrate Polish |
| Query String Sort | Cache Rules | Migrate Query String Sort |
| Resolve Override | Origin Rules | Migrate Resolve Override |
| Respect Strong ETags | Cache Rules | Migrate Respect Strong ETags |
| Response Buffering | N/A (deprecated) | N/A |
| Rocket Loader | Configuration Rules | Migrate Rocket Loader |
| Security Level | Configuration Rules | Migrate Security Level |
| True Client IP Header | Transform Rules (Managed Transforms) | Migrate True Client IP Header |
| SSL | Configuration Rules | Migrate SSL |
| Web Application Firewall | N/A (deprecated) | N/A |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule to perform an automatic redirect from HTTP to HTTPS for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a single redirect to always redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS. You can select the Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS rule template or enter the following rule configuration:
http://*https://${1}Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the redirect you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a single redirect |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Automatic HTTPS Rewrites for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to always rewrite HTTP links to HTTPS for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule adjusting browser cache TTL to one day for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to adjust browser cache TTL for caching resources in the browser to one day for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Browser Integrity Check for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to turn on Browser Integrity Check for protecting against bots and threats for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Bypass Cache on Cookie for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*test_cookieHow to migrate:
Create a cache rule to bypass cache for requests containing cookie test_cookie for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com" AND Cookie contains "test-cookie"(http.host contains "example.com" and http.cookie contains "test-cookie")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Cache By Device Type for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to cache content based on user agent or device type for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Cache Deception Armor for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to protect against cache deception attacks for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on caching of all assets for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to adjust cache level for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on caching for responses that contained cookie test-cookie for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*test-cookieHow to migrate:
Create a cache rule to cache responses containing cookie test_cookie for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com" AND Cookie contains "test-cookie"(http.host contains "example.com" and http.cookie contains "test-cookie")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on caching of every response with status code between 200 and 599 for one day, for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*200-599How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to cache responses with status code between 200 and 599 for one day for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule setting a custom cache key for all query string parameters, for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to set a custom cache key for all query string parameters, for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Cloudflare Apps (deprecated) for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to disable Cloudflare Apps (deprecated) for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
This Page Rules setting turned off Polish and Rocket Loader. You can still turn on or off relevant Cloudflare features one by one using Configuration Rules.
Context:
You configured a Page Rule with Disable Performance (deprecated) for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to replace:
Create a configuration rule to disable Polish and Rocket Loader for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
This Page Rules setting turns off Email Obfuscation, Rate Limiting (previous version), Scrape Shield, URL (Zone) Lockdown, and WAF managed rules (previous version). You can still turn on or off relevant Cloudflare features one by one using Configuration Rules and WAF custom rules.
Context:
You configured a Page Rule with Disable Security (deprecated) for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*This setting turned off a subset of Cloudflare security features: Email Obfuscation, Rate Limiting (previous version), Scrape Shield, URL (Zone) Lockdown, and WAF managed rules (previous version).
How to replace:
Create a configuration rule to turn off one or more security features:
If required, create a WAF exception to skip one or more rules of WAF managed rulesets for requests coming from IP addresses in an allowlist.
Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the rules you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Zaraz for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to turn off Zaraz for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule adjusting Edge Cache TTL for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to adjust edge cache TTL for caching resources on Cloudflare edge to one day, for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Email Obfuscation for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to turn off Email Obfuscation for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Example #1: Redirect www to root domain
Context:
You configured a Page Rule permanently redirecting www.example.com to example.com on all URI paths:
www.example.com/*https://example.com/$1How to migrate:
Create a single redirect to permanently redirect requests from https://www.example.com to https://example.com. You can select the Redirect from WWW to Root rule template or enter the following rule configuration:
https://www.example.com/*https://example.com/${1}Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the redirect you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
Notes about the rule equivalence
The provided example using Single Redirects is not an exact match for the previously existing Page Rule in the same example.
The exact equivalent would need to match both HTTP and HTTPS incoming requests, which you could achieve using a wildcard pattern like the following (notice the extra * after http):
http*://www.example.com/*This would require you to also change the Target URL to use the second wildcard capture group instead of the first one (corresponding to the text captured by second * in the wildcard pattern above):
https://example.com/${2}| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a single redirect |
|---|---|
 |  |
Example #2: Redirect all pages under old path to new path
Context:
You configured a Page Rule permanently redirecting example.com/old-path to example.com/new-path:
example.com/old-path/*https://example.com/new-path/$1How to migrate:
Create a single redirect to permanently redirect requests for example.com/old-path to example.com/new-path:
https://example.com/old-path/*https://example.com/new-path/${1}Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the redirect you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
Notes about the rule equivalence
The provided example using Single Redirects is not an exact match for the previously existing Page Rule in the same example.
The exact equivalent would need to match both HTTP and HTTPS incoming requests, which you could achieve using a wildcard pattern like the following (notice the extra * after http):
http*://example.com/old-path/*This would require you to also change the Target URL to use the second wildcard capture group instead of the first one (corresponding to the text captured by second * in the wildcard pattern above):
https://example.com/new-path/${2}| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a single redirect |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule changing the Host HTTP header to example.saas-provider.com, for all requests addressed at any subdomain of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*example.saas-provider.comHow to migrate:
Create an origin rule changing the Host header to example.saas-provider.com for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")example.saas-provider.comTurn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the origin rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to an origin rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule adding a CF-IPCountry HTTP header, for all requests addressed at any subdomain of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
CF-IPCountry and other location headers to all requests.| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a Managed Transform |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Opportunistic Encryption for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to turn off Opportunistic Encryption for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Origin Cache Control for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to determine edge cache behavior for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Origin Error Page Pass-thru for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to determine edge cache behavior for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Polish for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to turn off Polish for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on Query String Sort for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to sort query string parameters for caching purposes, for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule changing the origin to example.saas-provider.com, for all requests addressed at any subdomain of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*example.saas-provider.comHow to migrate:
Create an origin rule overriding the origin to example.saas-provider.com for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")example.saas-provider.comTurn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the origin rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to an origin rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning on byte-for-byte equivalency checks for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a cache rule to respect strong ETags for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the cache rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a cache rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule turning off Rocket Loader for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to turn off Rocket Loader for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
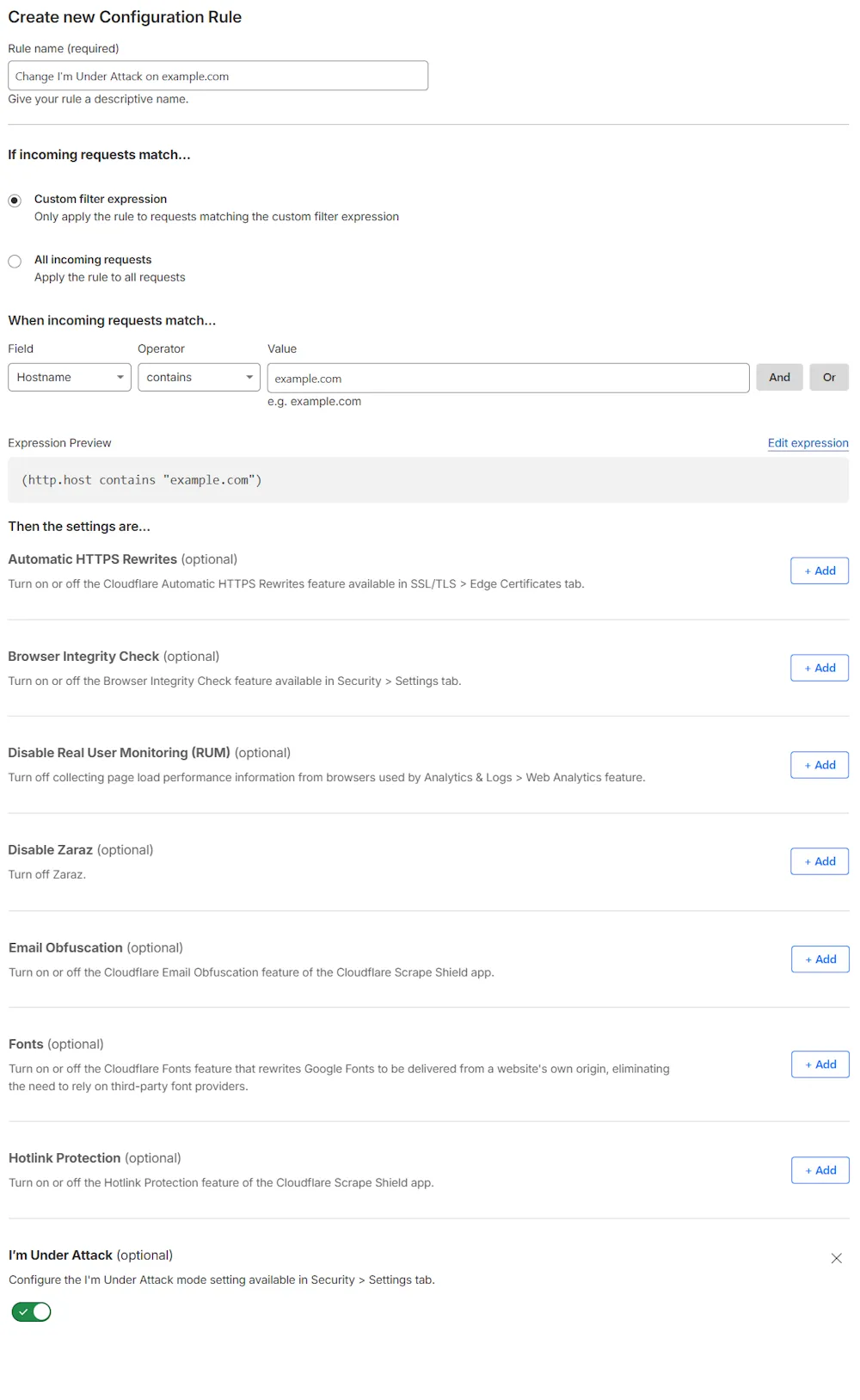
Context:
You configured a Page Rule setting Security Level to I'm Under Attack for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to set Security Level to I'm Under Attack, for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule adding a True-Client-IP HTTP header for all requests addressed at any subdomain of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
True-Client-IP header to all requests.| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a Managed Transform |
|---|---|
 |  |
Context:
You configured a Page Rule setting SSL to Strict for all subdomains of example.com and the example.com domain itself:
*example.com/*How to migrate:
Create a configuration rule to set SSL to Strict, for any hostname containing example.com:
Hostname contains "example.com"(http.host contains "example.com")Turn off your existing Page Rule and validate the behavior of the configuration rule you created.
If your tests succeed, delete the existing Page Rule.
| Page Rules configuration | Migrate to a configuration rule |
|---|---|
 |  |
The following Page Rules settings will not be migrated to other types of rules:
All other Page Rules settings will be migrated during 2025.
If you have feedback to share, refer to our Community thread ↗.