Patterns
This page lists and defines common patterns for implementing AI agents, based on Anthropic's patterns for building effective agents ↗.
Code samples use the AI SDK ↗, running in Durable Objects.
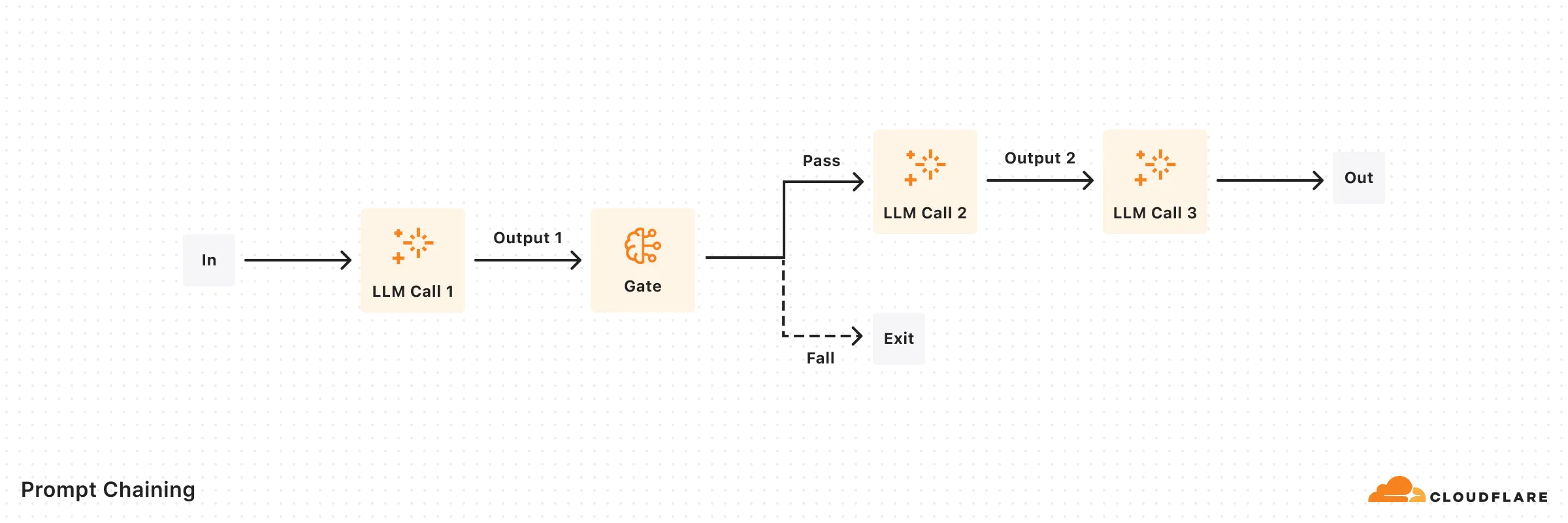
Decomposes tasks into a sequence of steps, where each LLM call processes the output of the previous one.
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";import { generateText, generateObject } from "ai";import { z } from "zod";
export default async function generateMarketingCopy(input: string) { const model = openai("gpt-4o");
// First step: Generate marketing copy const { text: copy } = await generateText({ model, prompt: `Write persuasive marketing copy for: ${input}. Focus on benefits and emotional appeal.`, });
// Perform quality check on copy const { object: qualityMetrics } = await generateObject({ model, schema: z.object({ hasCallToAction: z.boolean(), emotionalAppeal: z.number().min(1).max(10), clarity: z.number().min(1).max(10), }), prompt: `Evaluate this marketing copy for: 1. Presence of call to action (true/false) 2. Emotional appeal (1-10) 3. Clarity (1-10)
Copy to evaluate: ${copy}`, });
// If quality check fails, regenerate with more specific instructions if ( !qualityMetrics.hasCallToAction || qualityMetrics.emotionalAppeal < 7 || qualityMetrics.clarity < 7 ) { const { text: improvedCopy } = await generateText({ model, prompt: `Rewrite this marketing copy with: ${!qualityMetrics.hasCallToAction ? "- A clear call to action" : ""} ${qualityMetrics.emotionalAppeal < 7 ? "- Stronger emotional appeal" : ""} ${qualityMetrics.clarity < 7 ? "- Improved clarity and directness" : ""}
Original copy: ${copy}`, }); return { copy: improvedCopy, qualityMetrics }; }
return { copy, qualityMetrics };}Classifies input and directs it to specialized followup tasks, allowing for separation of concerns.

import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { generateObject, generateText } from 'ai';import { z } from 'zod';
async function handleCustomerQuery(query: string) { const model = openai('gpt-4o');
// First step: Classify the query type const { object: classification } = await generateObject({ model, schema: z.object({ reasoning: z.string(), type: z.enum(['general', 'refund', 'technical']), complexity: z.enum(['simple', 'complex']), }), prompt: `Classify this customer query: ${query}
Determine: 1. Query type (general, refund, or technical) 2. Complexity (simple or complex) 3. Brief reasoning for classification`, });
// Route based on classification // Set model and system prompt based on query type and complexity const { text: response } = await generateText({ model: classification.complexity === 'simple' ? openai('gpt-4o-mini') : openai('o1-mini'), system: { general: 'You are an expert customer service agent handling general inquiries.', refund: 'You are a customer service agent specializing in refund requests. Follow company policy and collect necessary information.', technical: 'You are a technical support specialist with deep product knowledge. Focus on clear step-by-step troubleshooting.', }[classification.type], prompt: query, });
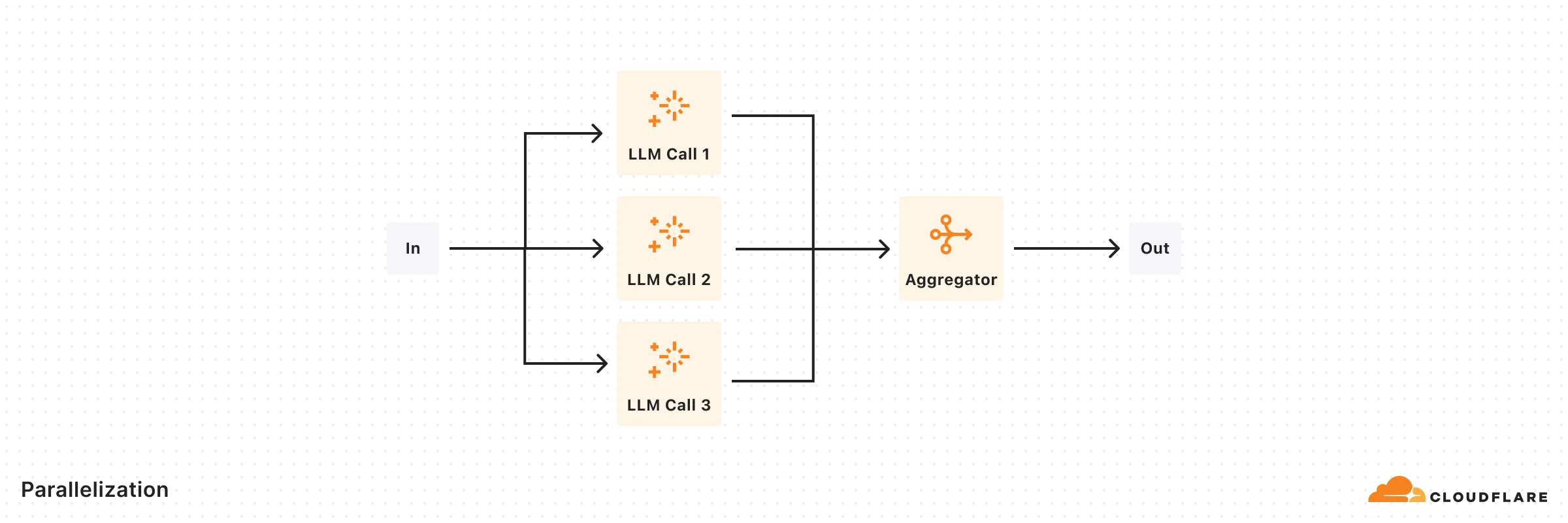
return { response, classification };}Enables simultaneous task processing through sectioning or voting mechanisms.
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { generateText, generateObject } from 'ai';import { z } from 'zod';
// Example: Parallel code review with multiple specialized reviewersasync function parallelCodeReview(code: string) { const model = openai('gpt-4o');
// Run parallel reviews const [securityReview, performanceReview, maintainabilityReview] = await Promise.all([ generateObject({ model, system: 'You are an expert in code security. Focus on identifying security vulnerabilities, injection risks, and authentication issues.', schema: z.object({ vulnerabilities: z.array(z.string()), riskLevel: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']), suggestions: z.array(z.string()), }), prompt: `Review this code: ${code}`, }),
generateObject({ model, system: 'You are an expert in code performance. Focus on identifying performance bottlenecks, memory leaks, and optimization opportunities.', schema: z.object({ issues: z.array(z.string()), impact: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']), optimizations: z.array(z.string()), }), prompt: `Review this code: ${code}`, }),
generateObject({ model, system: 'You are an expert in code quality. Focus on code structure, readability, and adherence to best practices.', schema: z.object({ concerns: z.array(z.string()), qualityScore: z.number().min(1).max(10), recommendations: z.array(z.string()), }), prompt: `Review this code: ${code}`, }), ]);
const reviews = [ { ...securityReview.object, type: 'security' }, { ...performanceReview.object, type: 'performance' }, { ...maintainabilityReview.object, type: 'maintainability' }, ];
// Aggregate results using another model instance const { text: summary } = await generateText({ model, system: 'You are a technical lead summarizing multiple code reviews.', prompt: `Synthesize these code review results into a concise summary with key actions: ${JSON.stringify(reviews, null, 2)}`, });
return { reviews, summary };}A central LLM dynamically breaks down tasks, delegates to Worker LLMs, and synthesizes results.

import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { generateObject } from 'ai';import { z } from 'zod';
async function implementFeature(featureRequest: string) { // Orchestrator: Plan the implementation const { object: implementationPlan } = await generateObject({ model: openai('o1'), schema: z.object({ files: z.array( z.object({ purpose: z.string(), filePath: z.string(), changeType: z.enum(['create', 'modify', 'delete']), }), ), estimatedComplexity: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']), }), system: 'You are a senior software architect planning feature implementations.', prompt: `Analyze this feature request and create an implementation plan: ${featureRequest}`, });
// Workers: Execute the planned changes const fileChanges = await Promise.all( implementationPlan.files.map(async file => { // Each worker is specialized for the type of change const workerSystemPrompt = { create: 'You are an expert at implementing new files following best practices and project patterns.', modify: 'You are an expert at modifying existing code while maintaining consistency and avoiding regressions.', delete: 'You are an expert at safely removing code while ensuring no breaking changes.', }[file.changeType];
const { object: change } = await generateObject({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), schema: z.object({ explanation: z.string(), code: z.string(), }), system: workerSystemPrompt, prompt: `Implement the changes for ${file.filePath} to support: ${file.purpose}
Consider the overall feature context: ${featureRequest}`, });
return { file, implementation: change, }; }), );
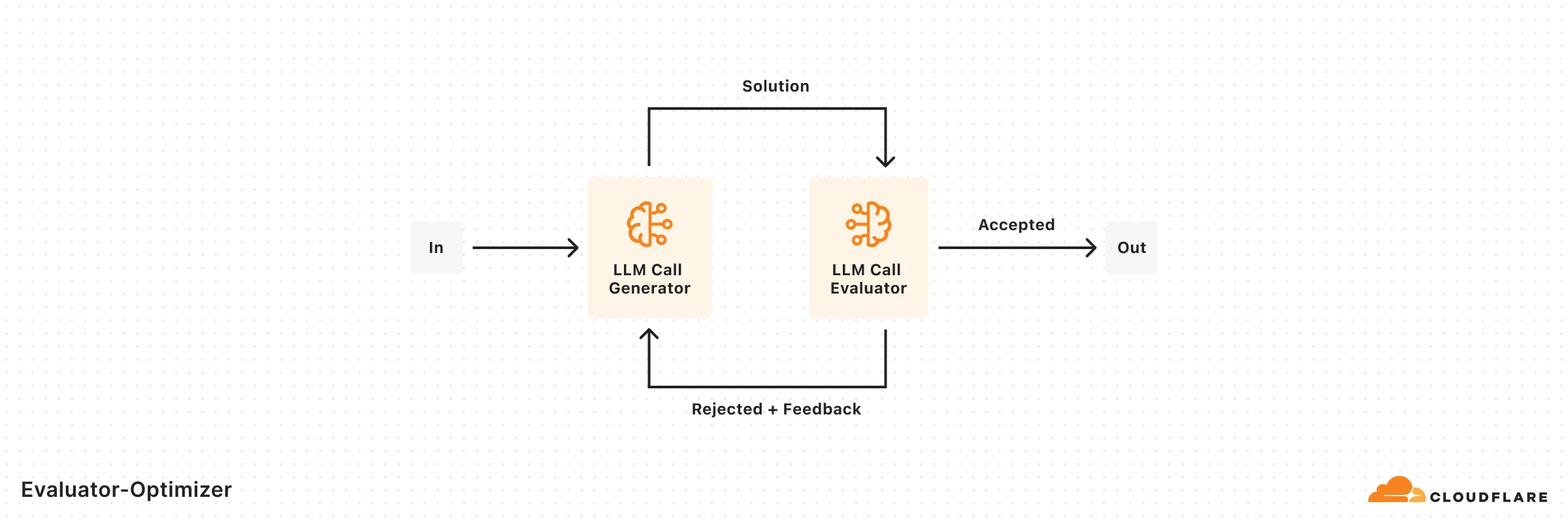
return { plan: implementationPlan, changes: fileChanges, };}One LLM generates responses while another provides evaluation and feedback in a loop.
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { generateText, generateObject } from 'ai';import { z } from 'zod';
async function translateWithFeedback(text: string, targetLanguage: string) { let currentTranslation = ''; let iterations = 0; const MAX_ITERATIONS = 3;
// Initial translation const { text: translation } = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o-mini'), // use small model for first attempt system: 'You are an expert literary translator.', prompt: `Translate this text to ${targetLanguage}, preserving tone and cultural nuances: ${text}`, });
currentTranslation = translation;
// Evaluation-optimization loop while (iterations < MAX_ITERATIONS) { // Evaluate current translation const { object: evaluation } = await generateObject({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), // use a larger model to evaluate schema: z.object({ qualityScore: z.number().min(1).max(10), preservesTone: z.boolean(), preservesNuance: z.boolean(), culturallyAccurate: z.boolean(), specificIssues: z.array(z.string()), improvementSuggestions: z.array(z.string()), }), system: 'You are an expert in evaluating literary translations.', prompt: `Evaluate this translation:
Original: ${text} Translation: ${currentTranslation}
Consider: 1. Overall quality 2. Preservation of tone 3. Preservation of nuance 4. Cultural accuracy`, });
// Check if quality meets threshold if ( evaluation.qualityScore >= 8 && evaluation.preservesTone && evaluation.preservesNuance && evaluation.culturallyAccurate ) { break; }
// Generate improved translation based on feedback const { text: improvedTranslation } = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), // use a larger model system: 'You are an expert literary translator.', prompt: `Improve this translation based on the following feedback: ${evaluation.specificIssues.join('\n')} ${evaluation.improvementSuggestions.join('\n')}
Original: ${text} Current Translation: ${currentTranslation}`, });
currentTranslation = improvedTranslation; iterations++; }
return { finalTranslation: currentTranslation, iterationsRequired: iterations, };}