Getting started
This guide will instruct you through setting up and deploying your first Realtime Agents project. You will use Workers, the Realtime Agents SDK, a Workers AI binding, and a large language model (LLM) to deploy your first AI-powered application on the Cloudflare global network.
- Sign up for a Cloudflare account ↗.
- Install
Node.js↗.
Node.js version manager
Use a Node version manager like Volta ↗ or nvm ↗ to avoid permission issues and change Node.js versions. Wrangler, discussed later in this guide, requires a Node version of 16.17.0 or later.
You will create a new Worker project using the create-cloudflare CLI (C3). C3 ↗ is a command-line tool designed to help you set up and deploy new applications to Cloudflare.
Create a new project named hello-agent by running:
npm create cloudflare@latest -- hello-agentyarn create cloudflare hello-agentpnpm create cloudflare@latest hello-agentRunning npm create cloudflare@latest will prompt you to install the create-cloudflare package ↗, and lead you through setup. C3 will also install Wrangler, the Cloudflare Developer Platform CLI.
For setup, select the following options:
- For What would you like to start with?, choose
Hello World example. - For Which template would you like to use?, choose
Worker only. - For Which language do you want to use?, choose
TypeScript. - For Do you want to use git for version control?, choose
Yes. - For Do you want to deploy your application?, choose
No(we will be making some changes before deploying).
This will create a new hello-agent directory. Your new hello-agent directory will include:
- A
"Hello World"Worker atsrc/index.ts. - A
wrangler.jsoncconfiguration file.
Go to your application directory:
cd hello-agentnpm i @cloudflare/realtime-agentsYou must create an AI binding for your Worker to connect to Workers AI. Bindings allow your Workers to interact with resources, like Workers AI, on the Cloudflare Developer Platform.
To bind Workers AI to your Worker, add the following to the end of your Wrangler file:
{ "ai": { "binding": "AI" }}[ai]binding = "AI"Your binding is available in your Worker code on env.AI.
Update the index.ts file in your hello-agent application directory with the following code:
import { DeepgramSTT, TextComponent, RealtimeKitTransport, ElevenLabsTTS, RealtimeAgent,} from "@cloudflare/realtime-agents";
class MyTextProcessor extends TextComponent { env;
constructor(env) { super(); this.env = env; }
async onTranscript(text, reply) { const { response } = await this.env.AI.run( "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct", { prompt: text, }, ); reply(response); }}
export class MyAgent extends RealtimeAgent { constructor(ctx, env) { super(ctx, env); }
async init(agentId, meetingId, authToken, workerUrl, accountId, apiToken) { // Construct your text processor for generating responses to text const textProcessor = new MyTextProcessor(this.env); // Construct a Meeting object to join the RTK meeting const rtkTransport = new RealtimeKitTransport(meetingId, authToken);
// Construct a pipeline to take in meeting audio, transcribe it using // Deepgram, and pass our generated responses through ElevenLabs to // be spoken in the meeting await this.initPipeline( [ rtkTransport, new DeepgramSTT(this.env.DEEPGRAM_API_KEY), textProcessor, new ElevenLabsTTS(this.env.ELEVENLABS_API_KEY), rtkTransport, ], agentId, workerUrl, accountId, apiToken, );
const { meeting } = rtkTransport;
// The RTK meeting object is accessible to us, so we can register handlers // on various events like participant joins/leaves, chat, etc. // This is optional meeting.participants.joined.on("participantJoined", (participant) => { textProcessor.speak(`Participant Joined ${participant.name}`); }); meeting.participants.joined.on("participantLeft", (participant) => { textProcessor.speak(`Participant Left ${participant.name}`); });
// Make sure to actually join the meeting after registering all handlers await meeting.join(); }
async deinit() { // Add any other cleanup logic required await this.deinitPipeline(); }}
export default { async fetch(request, env, _ctx) { const url = new URL(request.url); const meetingId = url.searchParams.get("meetingId"); if (!meetingId) { return new Response(null, { status: 400 }); }
const agentId = meetingId; const agent = env.MY_AGENT.idFromName(meetingId); const stub = env.MY_AGENT.get(agent); // The fetch method is implemented for handling internal pipeline logic if (url.pathname.startsWith("/agentsInternal")) { return stub.fetch(request); }
// Your logic continues here switch (url.pathname) { case "/init": // This is the authToken for joining a meeting, it can be passed // in query parameters as well if needed const authHeader = request.headers.get("Authorization"); if (!authHeader) { return new Response(null, { status: 401 }); }
// We just need the part after `Bearer ` await stub.init( agentId, meetingId, authHeader.split(" ")[1], url.host, env.ACCOUNT_ID, env.API_TOKEN, );
return new Response(null, { status: 200 }); case "/deinit": await stub.deinit(); return new Response(null, { status: 200 }); }
return new Response(null, { status: 404 }); },};import { DeepgramSTT, TextComponent, RealtimeKitTransport, ElevenLabsTTS, RealtimeAgent } from '@cloudflare/realtime-agents';
class MyTextProcessor extends TextComponent { env: Env;
constructor(env: Env) { super(); this.env = env; }
async onTranscript(text: string, reply: (text: string) => void) { const { response } = await this.env.AI.run('@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct', { prompt: text, }); reply(response!); }}
export class MyAgent extends RealtimeAgent<Env> { constructor(ctx: DurableObjectState, env: Env) { super(ctx, env); }
async init(agentId: string, meetingId: string, authToken: string, workerUrl: string, accountId: string, apiToken: string) { // Construct your text processor for generating responses to text const textProcessor = new MyTextProcessor(this.env); // Construct a Meeting object to join the RTK meeting const rtkTransport = new RealtimeKitTransport(meetingId, authToken);
// Construct a pipeline to take in meeting audio, transcribe it using // Deepgram, and pass our generated responses through ElevenLabs to // be spoken in the meeting await this.initPipeline( [ rtkTransport, new DeepgramSTT(this.env.DEEPGRAM_API_KEY), textProcessor, new ElevenLabsTTS(this.env.ELEVENLABS_API_KEY), rtkTransport, ], agentId, workerUrl, accountId, apiToken, );
const { meeting } = rtkTransport;
// The RTK meeting object is accessible to us, so we can register handlers // on various events like participant joins/leaves, chat, etc. // This is optional meeting.participants.joined.on('participantJoined', (participant) => { textProcessor.speak(`Participant Joined ${participant.name}`); }); meeting.participants.joined.on('participantLeft', (participant) => { textProcessor.speak(`Participant Left ${participant.name}`); });
// Make sure to actually join the meeting after registering all handlers await meeting.join(); }
async deinit() { // Add any other cleanup logic required await this.deinitPipeline(); }}
export default { async fetch(request, env, _ctx): Promise<Response> { const url = new URL(request.url); const meetingId = url.searchParams.get('meetingId'); if (!meetingId) { return new Response(null, { status: 400 }); }
const agentId = meetingId; const agent = env.MY_AGENT.idFromName(meetingId); const stub = env.MY_AGENT.get(agent); // The fetch method is implemented for handling internal pipeline logic if (url.pathname.startsWith('/agentsInternal')) { return stub.fetch(request); }
// Your logic continues here switch (url.pathname) { case '/init': // This is the authToken for joining a meeting, it can be passed // in query parameters as well if needed const authHeader = request.headers.get('Authorization'); if (!authHeader) { return new Response(null, { status: 401 }); }
// We just need the part after `Bearer ` await stub.init(agentId, meetingId, authHeader.split(' ')[1], url.host, env.ACCOUNT_ID, env.API_TOKEN);
return new Response(null, { status: 200 }); case '/deinit': await stub.deinit(); return new Response(null, { status: 200 }); }
return new Response(null, { status: 404 }); },} satisfies ExportedHandler<Env>;The Realtime Agents SDK provides several elements that work together to create an end-to-end pipeline
-
RealtimeKitTransport: Represents a RealtimeKit meeting that will be joined by the agent -
DeepgramSTT: Takes in meeting audio and provides transcripts powered by Deepgram -
TextComponent: A concrete implementation for this element needs to be provided by the user as it is responsible for processing the text generated in the meeting and sending back responses. We have implemented it in theMyTextProcessorclass -
ElevenLabsTTS: Converts the generated responses to audio to be spoken in the meeting
We use all of these elements together to create a simple chatbot-like pipeline. As a pre-requisite, we require the meeting ID to be joined along with an authorization token for joining the meeting, which is passed during the worker invocation. Additionally, our class must extend RealtimeAgent as it contains certain internal logic to handle interactions with our pipeline backend
In wrangler.jsonc, append the following fields to enable the Node.js Compatibility ↗ flag and create our Durable Object:
"compatibility_flags": ["nodejs_compat"], "migrations": [ { "new_sqlite_classes": ["MyAgent"], "tag": "v1", }, ], "durable_objects": { "bindings": [ { "class_name": "MyAgent", "name": "MY_AGENT", }, ], },You must also setup a few secrets ↗:
ACCOUNT_ID: Your Cloudflare account IDAPI_TOKEN: Cloudflare API token scoped forAdminaccess toRealtimeELEVENLABS_API_KEY,DEEPGRAM_API_KEY: ElevenLabs & Deepgram API keys
Before deploying your AI Worker globally, log in with your Cloudflare account by running:
npx wrangler loginYou will be directed to a web page asking you to log in to the Cloudflare dashboard. After you have logged in, you will be asked if Wrangler can make changes to your Cloudflare account. Scroll down and select Allow to continue.
Finally, deploy your Worker to make your project accessible on the Internet. To deploy your Worker, run:
npx wrangler deployhttps://hello-agent.<YOUR_SUBDOMAIN>.workers.devFinally, to invoke the worker, we need to generate a RealtimeKit token from the dashboard ↗:
- Go to the
Meetingstab and click onCreate Meeting:
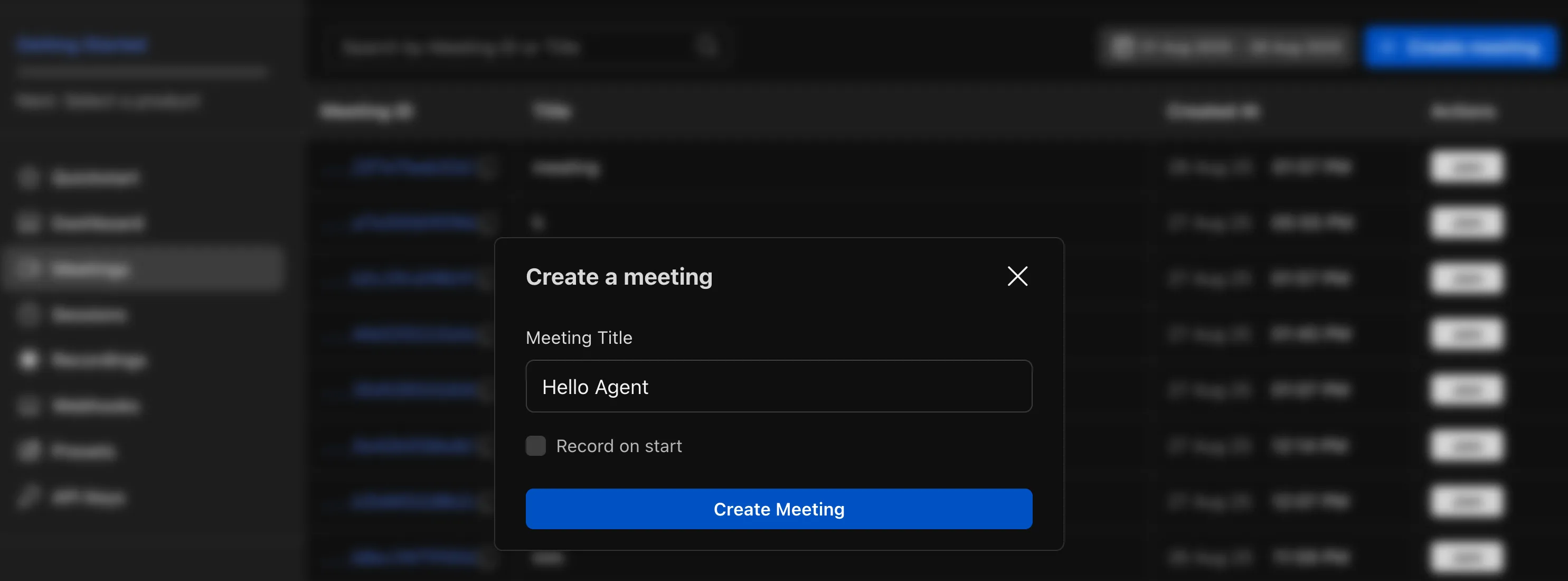
- Click on
Joinnext to the meeting and generate the RealtimeKit link. This contains themeetingId(bbbb2fac-953c-4239-9ba8-75ba912d76fc) and theauthTokento be passed in the final step:
https://demo.realtime.cloudflare.com/v2/meeting?id=bbbb2fac-953c-4239-9ba8-75ba912d76fc&authToken=ey...

- Repeat the same
Joinflow to join the meeting yourself before adding in the Agent
Finally, invoke the worker to make the agent join a meeting:
curl -X POST https://hello-agent.<YOUR_SUBDOMAIN>.workers.dev/init?meetingId=<REALTIME_KIT_MEETING_ID> -H "Authorization: Bearer <REALTIME_KIT_AUTH_TOKEN>"- Cloudflare Developers community on Discord ↗ - Submit feature requests, report bugs, and share your feedback directly with the Cloudflare team by joining the Cloudflare Discord server.