---
title: Overview · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Cloudflare's AI Gateway allows you to gain visibility and control
over your AI apps. By connecting your apps to AI Gateway, you can gather
insights on how people are using your application with analytics and logging
and then control how your application scales with features such as caching,
rate limiting, as well as request retries, model fallback, and more. Better
yet - it only takes one line of code to get started.
lastUpdated: 2026-02-18T19:10:24.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
tags: AI
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/index.md
---
Observe and control your AI applications.
Available on all plans
Cloudflare's AI Gateway allows you to gain visibility and control over your AI apps. By connecting your apps to AI Gateway, you can gather insights on how people are using your application with analytics and logging and then control how your application scales with features such as caching, rate limiting, as well as request retries, model fallback, and more. Better yet - it only takes one line of code to get started.
Check out the [Get started guide](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/) to learn how to configure your applications with AI Gateway.
## Features
### Analytics
View metrics such as the number of requests, tokens, and the cost it takes to run your application.
[View Analytics](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/)
### Logging
Gain insight on requests and errors.
[View Logging](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/)
### Caching
Serve requests directly from Cloudflare's cache instead of the original model provider for faster requests and cost savings.
[Use Caching](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/)
### Rate limiting
Control how your application scales by limiting the number of requests your application receives.
[Use Rate limiting](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/rate-limiting/)
### Request retry and fallback
Improve resilience by defining request retry and model fallbacks in case of an error.
[Use Request retry and fallback](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/)
### Your favorite providers
Workers AI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, OpenAI, Replicate, and more work with AI Gateway.
[Use Your favorite providers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/)
***
## Related products
**[Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/)**
Run machine learning models, powered by serverless GPUs, on Cloudflare’s global network.
**[Vectorize](https://developers.cloudflare.com/vectorize/)**
Build full-stack AI applications with Vectorize, Cloudflare's vector database. Adding Vectorize enables you to perform tasks such as semantic search, recommendations, anomaly detection or can be used to provide context and memory to an LLM.
## More resources
[Developer Discord](https://discord.cloudflare.com)
Connect with the Workers community on Discord to ask questions, show what you are building, and discuss the platform with other developers.
[Use cases](https://developers.cloudflare.com/use-cases/ai/)
Learn how you can build and deploy ambitious AI applications to Cloudflare's global network.
[@CloudflareDev](https://x.com/cloudflaredev)
Follow @CloudflareDev on Twitter to learn about product announcements, and what is new in Cloudflare Workers.
---
title: 404 - Page Not Found · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/404/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/404/index.md
---
# 404
Check the URL, try using our [search](https://developers.cloudflare.com/search/) or try our LLM-friendly [llms.txt directory](https://developers.cloudflare.com/llms.txt).
---
title: AI Assistant · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
lastUpdated: 2024-10-30T16:07:34.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/ai/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/ai/index.md
---
---
title: REST API reference · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
lastUpdated: 2024-12-18T13:12:05.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/api-reference/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/api-reference/index.md
---
---
title: Changelog · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Subscribe to RSS
lastUpdated: 2025-05-09T15:42:57.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/changelog/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/changelog/index.md
---
[Subscribe to RSS](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/changelog/index.xml)
## 2025-11-21
Unified Billing now supports opt-in Zero Data Retention. This ensures supported upstream AI providers (eg [OpenAI ZDR](https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/your-data#zero-data-retention)) do not retain request and response data.
## 2025-11-14
* Supports adding OpenAI compatible [Custom Providers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-providers/) for inferencing with AI providers that are not natively supported by AI Gateway
* Cost and usage tracking for voice models
* You can now use Workers AI via AI Gateway with no additional configuration. Previously, this required generating / passing additional Workers AI tokens.
## 2025-11-06
**Unified Billing**
* [Unified Billing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/unified-billing/) is now in open beta. Connect multiple AI providers (e.g. OpenAI, Anthropic) without any additional setup and pay through a single Cloudflare invoice. To use it, purchase credits in the Cloudflare Dashboard and spend them across providers via AI Gateway.
## 2025-11-03
New supported providers
* [Baseten](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/baseten/)
* [Ideogram](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/ideogram/)
* [Deepgram](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepgram/)
## 2025-10-29
* Add support for pipecat model on Workers AI
* Fix OpenAI realtime websocket authentication.
## 2025-10-24
* Added cost tracking and observability support for async video generation requests for OpenAI Sora 2 and Google AI Studio Veo 3.
* `cf-aig-eventId` and `cf-aig-log-id` headers are now returned on all requests including failed requests
## 2025-10-14
The Model playground is now available in the AI Gateway Cloudflare Dashboard, allowing you to request and compare model behaviour across all models supported by AI Gateway.
## 2025-10-07
* Add support for [Deepgram on Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/#deepgram-workers-ai) using Websocket transport.
* Added [Parallel](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/parallel/) as a provider.
## 2025-09-24
**OTEL Tracing**
Added OpenTelemetry (OTEL) tracing export for better observability and debugging of AI Gateway requests.
## 2025-09-21
* Added support for [Fal AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/fal/) provider.
* You can now set up custom Stripe usage reporting, and report usage and costs for your users directly to Stripe from AI Gateway.
* Fixed incorrectly geoblocked requests for certain regions.
## 2025-09-19
* New API endpoint (`/compat/v1/models`) for listing available models along with their costs.
* Unified API now supports Google Vertex AI providers and all their models.
* BYOK support for requests using WebSocket transport.
## 2025-08-28
**Data Loss Prevention**
[Data loss prevention](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/) capabilities are now available to scan both incoming prompts and outgoing AI responses for sensitive information, ensuring your AI applications maintain security and compliance standards.
## 2025-08-25
**Dynamic routing**
Introduced [Dynamic routing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/) that lets you visually or via JSON define flexible request flows that segment users, enforce quotas, and choose models with fallbacks—without changing application code.
## 2025-08-21
**Bring your own keys (BYOK)**
Introduced [Bring your own keys (BYOK)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/) allowing you to save your AI provider keys securely with Cloudflare Secret Store and manage them through the Cloudflare dashboard.
## 2025-06-18
**New GA providers**
We have moved the following providers out of beta and into GA:
* [Cartesia](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cartesia/)
* [Cerebras](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cerebras/)
* [DeepSeek](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepseek/)
* [ElevenLabs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/elevenlabs/)
* [OpenRouter](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openrouter/)
## 2025-05-28
**OpenAI Compatibility**
* Introduced a new [OpenAI-compatible chat completions endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) to simplify switching between different AI providers without major code modifications.
## 2025-04-22
* Increased Max Number of Gateways per account: Raised the maximum number of gateways per account from 10 to 20 for paid users. This gives you greater flexibility in managing your applications as you build and scale.
* Streaming WebSocket Bug Fix: Resolved an issue affecting streaming responses over [WebSockets](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/websockets-api/). This fix ensures more reliable and consistent streaming behavior across all supported AI providers.
* Increased Timeout Limits: Extended the default timeout for AI Gateway requests beyond the previous 100-second limit. This enhancement improves support for long-running requests.
## 2025-04-02
**Cache Key Calculation Changes**
* We have updated how [cache](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/) keys are calculated. As a result, new cache entries will be created, and you may experience more cache misses than usual during this transition. Please monitor your traffic and performance, and let us know if you encounter any issues.
## 2025-03-18
**WebSockets**
* Added [WebSockets API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/websockets-api/) to provide a persistent connection for AI interactions, eliminating repeated handshakes and reducing latency.
## 2025-02-26
**Guardrails**
* Added [Guardrails](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/) help deploy AI applications safely by intercepting and evaluating both user prompts and model responses for harmful content.
## 2025-02-19
**Updated Log Storage Settings**
* Introduced customizable log storage settings, enabling users to:
* Define the maximum number of logs stored per gateway.
* Choose how logs are handled when the storage limit is reached:
* **On** - Automatically delete the oldest logs to ensure new logs are always saved.
* **Off** - Stop saving new logs when the storage limit is reached.
## 2025-02-06
**Added request handling**
* Added [request handling options](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/) to help manage AI provider interactions effectively, ensuring your applications remain responsive and reliable.
## 2025-02-05
**New AI Gateway providers**
* **Configuration**: Added [ElevenLabs](https://elevenlabs.io/), [Cartesia](https://docs.cartesia.ai/), and [Cerebras](https://inference-docs.cerebras.ai/) as new providers.
## 2025-01-02
**DeepSeek**
* **Configuration**: Added [DeepSeek](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepseek/) as a new provider.
## 2024-12-17
**AI Gateway Dashboard**
* Updated dashboard to view performance, costs, and stats across all gateways.
## 2024-12-13
**Bug Fixes**
* **Bug Fixes**: Fixed Anthropic errors being cached.
* **Bug Fixes**: Fixed `env.AI.run()` requests using authenticated gateways returning authentication error.
## 2024-11-28
**OpenRouter**
* **Configuration**: Added [OpenRouter](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openrouter/) as a new provider.
## 2024-11-19
**WebSockets API**
* **Configuration**: Added [WebSockets API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/websockets-api/) which provides a single persistent connection, enabling continuous communication.
## 2024-11-19
**Authentication**
* **Configuration**: Added [Authentication](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/) which adds security by requiring a valid authorization token for each request.
## 2024-10-28
**Grok**
* **Providers**: Added [Grok](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/grok/) as a new provider.
## 2024-10-17
**Vercel SDK**
Added [Vercel AI SDK](https://sdk.vercel.ai/). The SDK supports many different AI providers, tools for streaming completions, and more.
## 2024-09-26
**Persistent logs**
* **Logs**: AI Gateway now has [logs that persist](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/index), giving you the flexibility to store them for your preferred duration.
## 2024-09-26
**Logpush**
* **Logs**: Securely export logs to an external storage location using [Logpush](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/logpush).
## 2024-09-26
**Pricing**
* **Pricing**: Added [pricing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing/) for storing logs persistently.
## 2024-09-26
**Evaluations**
* **Configurations**: Use AI Gateway’s [Evaluations](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations) to make informed decisions on how to optimize your AI application.
## 2024-09-10
**Custom costs**
* **Configuration**: AI Gateway now allows you to set custom costs at the request level [custom costs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/) to requests, accurately reflect your unique pricing, overriding the default or public model costs.
## 2024-08-02
**Mistral AI**
* **Providers**: Added [Mistral AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/mistral/) as a new provider.
## 2024-07-23
**Google AI Studio**
* **Providers**: Added [Google AI Studio](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/) as a new provider.
## 2024-07-10
**Custom metadata**
AI Gateway now supports adding [custom metadata](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-metadata/) to requests, improving tracking and analysis of incoming requests.
## 2024-07-09
**Logs**
[Logs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/#logging) are now available for the last 24 hours.
## 2024-06-24
**Custom cache key headers**
AI Gateway now supports [custom cache key headers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#custom-cache-key-cf-aig-cache-key).
## 2024-06-18
**Access an AI Gateway through a Worker**
Workers AI now natively supports [AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/#worker).
## 2024-05-22
**AI Gateway is now GA**
AI Gateway is moving from beta to GA.
## 2024-05-16
* **Providers**: Added [Cohere](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cohere/) and [Groq](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/groq/) as new providers.
## 2024-05-09
* Added new endpoints to the [REST API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/).
## 2024-03-26
* [LLM Side Channel vulnerability fixed](https://blog.cloudflare.com/ai-side-channel-attack-mitigated)
* **Providers**: Added Anthropic, Google Vertex, Perplexity as providers.
## 2023-10-26
* **Real-time Logs**: Logs are now real-time, showing logs for the last hour. If you have a need for persistent logs, please let the team know on Discord. We are building out a persistent logs feature for those who want to store their logs for longer.
* **Providers**: Azure OpenAI is now supported as a provider!
* **Docs**: Added Azure OpenAI example.
* **Bug Fixes**: Errors with costs and tokens should be fixed.
## 2023-10-09
* **Logs**: Logs will now be limited to the last 24h. If you have a use case that requires more logging, please reach out to the team on Discord.
* **Dashboard**: Logs now refresh automatically.
* **Docs**: Fixed Workers AI example in docs and dash.
* **Caching**: Embedding requests are now cacheable. Rate limit will not apply for cached requests.
* **Bug Fixes**: Identical requests to different providers are not wrongly served from cache anymore. Streaming now works as expected, including for the Universal endpoint.
* **Known Issues**: There's currently a bug with costs that we are investigating.
---
title: Configuration · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Configure your AI Gateway with multiple options and customizations.
lastUpdated: 2025-05-28T19:49:34.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/index.md
---
Configure your AI Gateway with multiple options and customizations.
* [BYOK (Store Keys)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/)
* [Custom costs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/)
* [Custom Providers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-providers/)
* [Manage gateways](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/manage-gateway/)
* [Request handling](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/)
* [Fallbacks](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/fallbacks/)
* [Authenticated Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/)
---
title: Architectures · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Learn how you can use AI Gateway within your existing architecture.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-13T13:40:40.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/demos/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/demos/index.md
---
Learn how you can use AI Gateway within your existing architecture.
## Reference architectures
Explore the following reference architectures that use AI Gateway:
[Fullstack applications](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/serverless/fullstack-application/)
[A practical example of how these services come together in a real fullstack application architecture.](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/serverless/fullstack-application/)
[Multi-vendor AI observability and control](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/ai/ai-multivendor-observability-control/)
[By shifting features such as rate limiting, caching, and error handling to the proxy layer, organizations can apply unified configurations across services and inference service providers.](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/ai/ai-multivendor-observability-control/)
[AI Vibe Coding Platform](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/ai/ai-vibe-coding-platform/)
[Cloudflare's low-latency, fully serverless compute platform, Workers offers powerful capabilities to enable A/B testing using a server-side implementation.](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/ai/ai-vibe-coding-platform/)
---
title: Evaluations · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Understanding your application's performance is essential for
optimization. Developers often have different priorities, and finding the
optimal solution involves balancing key factors such as cost, latency, and
accuracy. Some prioritize low-latency responses, while others focus on
accuracy or cost-efficiency.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/index.md
---
Understanding your application's performance is essential for optimization. Developers often have different priorities, and finding the optimal solution involves balancing key factors such as cost, latency, and accuracy. Some prioritize low-latency responses, while others focus on accuracy or cost-efficiency.
AI Gateway's Evaluations provide the data needed to make informed decisions on how to optimize your AI application. Whether it is adjusting the model, provider, or prompt, this feature delivers insights into key metrics around performance, speed, and cost. It empowers developers to better understand their application's behavior, ensuring improved accuracy, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Evaluations use datasets which are collections of logs stored for analysis. You can create datasets by applying filters in the Logs tab, which help narrow down specific logs for evaluation.
Our first step toward comprehensive AI evaluations starts with human feedback (currently in open beta). We will continue to build and expand AI Gateway with additional evaluators.
[Learn how to set up an evaluation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/set-up-evaluations/) including creating datasets, selecting evaluators, and running the evaluation process.
---
title: Features · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: AI Gateway provides a comprehensive set of features to help you
build, deploy, and manage AI applications with confidence. From performance
optimization to security and observability, these features work together to
create a robust AI infrastructure.
lastUpdated: 2025-09-02T18:45:30.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/index.md
---
AI Gateway provides a comprehensive set of features to help you build, deploy, and manage AI applications with confidence. From performance optimization to security and observability, these features work together to create a robust AI infrastructure.
## Core Features
### Performance & Cost Optimization
### Caching
Serve identical requests directly from Cloudflare's global cache, reducing latency by up to 90% and significantly cutting costs by avoiding repeated API calls to AI providers.
**Key benefits:**
* Reduced response times for repeated queries
* Lower API costs through cache hits
* Configurable TTL and per-request cache control
* Works across all supported AI providers
[Use Caching](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/)
### Rate Limiting
Control application scaling and protect against abuse with flexible rate limiting options. Set limits based on requests per time window with sliding or fixed window techniques.
**Key benefits:**
* Prevent API quota exhaustion
* Control costs and usage patterns
* Configurable per gateway or per request
* Multiple rate limiting techniques available
[Use Rate Limiting](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/rate-limiting/)
### Dynamic Routing
Create sophisticated request routing flows without code changes. Route requests based on user segments, geography, content analysis, or A/B testing requirements through a visual interface.
**Key benefits:**
* Visual flow-based configuration
* User-based and geographic routing
* A/B testing and fractional traffic splitting
* Context-aware routing based on request content
* Dynamic rate limiting with automatic fallbacks
[Use Dynamic Routing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/)
### Security & Safety
### Guardrails
Deploy AI applications safely with real-time content moderation. Automatically detect and block harmful content in both user prompts and model responses across all providers.
**Key benefits:**
* Consistent moderation across all AI providers
* Real-time prompt and response evaluation
* Configurable content categories and actions
* Compliance and audit capabilities
* Enhanced user safety and trust
[Use Guardrails](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/)
### Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Protect your organization from inadvertent exposure of sensitive data through AI interactions. Scan prompts and responses for PII, financial data, and other sensitive information.
**Key benefits:**
* Real-time scanning of AI prompts and responses
* Detection of PII, financial, healthcare, and custom data patterns
* Configurable actions: flag or block sensitive content
* Integration with Cloudflare's enterprise DLP solution
* Compliance support for GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS
[Use Data Loss Prevention (DLP)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/)
### Authentication
Secure your AI Gateway with token-based authentication. Control access to your gateways and protect against unauthorized usage.
**Key benefits:**
* Token-based access control
* Configurable per gateway
* Integration with Cloudflare's security infrastructure
* Audit trail for access attempts
[Use Authentication](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/)
### Bring Your Own Keys (BYOK)
Securely store and manage AI provider API keys in Cloudflare's encrypted infrastructure. Remove hardcoded keys from your applications while maintaining full control.
**Key benefits:**
* Encrypted key storage at rest and in transit
* Centralized key management across providers
* Easy key rotation without code changes
* Support for 20+ AI providers
* Enhanced security and compliance
[Use Bring Your Own Keys (BYOK)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/)
### Observability & Analytics
### Analytics
Gain deep insights into your AI application usage with comprehensive analytics. Track requests, tokens, costs, errors, and performance across all providers.
**Key benefits:**
* Real-time usage metrics and trends
* Cost tracking and estimation across providers
* Error monitoring and troubleshooting
* Cache hit rates and performance insights
* GraphQL API for custom dashboards
[Use Analytics](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/)
### Logging
Capture detailed logs of all AI requests and responses for debugging, compliance, and analysis. Configure log retention and export options.
**Key benefits:**
* Complete request/response logging
* Configurable log retention policies
* Export capabilities via Logpush
* Custom metadata support
* Compliance and audit support
[Use Logging](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/)
### Custom Metadata
Enrich your logs and analytics with custom metadata. Tag requests with user IDs, team information, or any custom data for enhanced filtering and analysis.
**Key benefits:**
* Enhanced request tracking and filtering
* User and team-based analytics
* Custom business logic integration
* Improved debugging and troubleshooting
[Use Custom Metadata](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/custom-metadata/)
### Advanced Configuration
### Custom Costs
Override default pricing with your negotiated rates or custom cost models. Apply custom costs at the request level for accurate cost tracking.
**Key benefits:**
* Accurate cost tracking with negotiated rates
* Per-request cost customization
* Better budget planning and forecasting
* Support for enterprise pricing agreements
[Use Custom Costs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/)
## Feature Comparison by Use Case
| Use Case | Recommended Features |
| - | - |
| **Cost Optimization** | Caching, Rate Limiting, Custom Costs |
| **High Availability** | Fallbacks using Dynamic Routing |
| **Security & Compliance** | Guardrails, DLP, Authentication, BYOK, Logging |
| **Performance Monitoring** | Analytics, Logging, Custom Metadata |
| **A/B Testing** | Dynamic Routing, Custom Metadata, Analytics |
## Getting Started with Features
1. **Start with the basics**: Enable [Caching](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/) and [Analytics](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/) for immediate benefits
2. **Add reliability**: Configure Fallbacks and Rate Limiting using [Dynamic routing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/)
3. **Enhance security**: Implement [Guardrails](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/), [DLP](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/), and [Authentication](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/)
***
*All features work seamlessly together and across all 20+ supported AI providers. Get started with [AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/) to begin using these features in your applications.*
---
title: Getting started · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: In this guide, you will learn how to create and use your first AI Gateway.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-21T09:55:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/index.md
---
In this guide, you will learn how to create and use your first AI Gateway.
* Dashboard
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select **Create Gateway**.
4. Enter your **Gateway name**. Note: Gateway name has a 64 character limit.
5. Select **Create**.
* API
To set up an AI Gateway using the API:
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
2. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
3. Using that API token and Account ID, send a [`POST` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/) to the Cloudflare API.
### Authenticated gateway 🔒
When you enable authentication on a gateway, each request is required to include a valid Cloudflare API token, adding an extra layer of security. We recommend using an authenticated gateway to prevent unauthorized access. [Learn more](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/).
## Provider Authentication
Authenticate with your upstream AI provider using one of the following options:
* **Unified Billing:** Use the AI Gateway billing to pay for and authenticate your inference requests. Refer to [Unified Billing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/unified-billing/).
* **BYOK (Store Keys):** Store your own provider API Keys with Cloudflare, and AI Gateway will include them at runtime. Refer to [BYOK](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/).
* **Request headers:** Include your provider API Key in the request headers as you normally would (for example, `Authorization: Bearer `).
## Integration Options
### Unified API Endpoint
OpenAI Compatible Recommended
The easiest way to get started with AI Gateway is through our OpenAI-compatible `/chat/completions` endpoint. This allows you to use existing OpenAI SDKs and tools with minimal code changes while gaining access to multiple AI providers.
`https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_name}/compat/chat/completions`
**Key benefits:**
* Drop-in replacement for OpenAI API, works with existing OpenAI SDKs and other OpenAI compliant clients
* Switch between providers by changing the `model` parameter
* Dynamic Routing - Define complex routing scenarios requiring conditional logic, conduct A/B tests, set rate / budget limits, etc
#### Example:
Make a request to
 OpenAI
using
OpenAI JS SDK
with
Stored Key (BYOK)
Refer to [Unified API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) to learn more about OpenAI compatibility.
### Provider-specific endpoints
For direct integration with specific AI providers, use dedicated endpoints that maintain the original provider's API schema while adding AI Gateway features.
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/{provider}
```
**Available providers:**
* [OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/) - GPT models and embeddings
* [Anthropic](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/) - Claude models
* [Google AI Studio](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/) - Gemini models
* [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/) - Cloudflare's inference platform
* [AWS Bedrock](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/bedrock/) - Amazon's managed AI service
* [Azure OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/azureopenai/) - Microsoft's OpenAI service
* [and more...](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/)
## Next steps
* Learn more about [caching](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/) for faster requests and cost savings and [rate limiting](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/rate-limiting/) to control how your application scales.
* Explore how to specify model or provider [fallbacks, ratelimits, A/B tests](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/) for resiliency.
* Learn how to use low-cost, open source models on [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/) - our AI inference service.
---
title: Header Glossary · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: AI Gateway supports a variety of headers to help you configure,
customize, and manage your API requests. This page provides a complete list of
all supported headers, along with a short description
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/glossary/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/glossary/index.md
---
AI Gateway supports a variety of headers to help you configure, customize, and manage your API requests. This page provides a complete list of all supported headers, along with a short description
| Term | Definition |
| - | - |
| cf-aig-backoff | Header to customize the backoff type for [request retries](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/#request-retries) of a request. |
| cf-aig-cache-key | The [cf-aig-cache-key-aig-cache-key](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#custom-cache-key-cf-aig-cache-key) let you override the default cache key in order to precisely set the cacheability setting for any resource. |
| cf-aig-cache-status | [Status indicator for caching](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#default-configuration), showing if a request was served from cache. |
| cf-aig-cache-ttl | Specifies the [cache time-to-live for responses](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#cache-ttl-cf-aig-cache-ttl). |
| cf-aig-collect-log | The [cf-aig-collect-log](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/#collect-logs-cf-aig-collect-log) header allows you to bypass the default log setting for the gateway. |
| cf-aig-custom-cost | Allows the [customization of request cost](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/#custom-cost) to reflect user-defined parameters. |
| cf-aig-event-id | [cf-aig-event-id](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-api/#3-retrieve-the-cf-aig-log-id) is a unique identifier for an event, used to trace specific events through the system. |
| cf-aig-log-id | The [cf-aig-log-id](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-api/#3-retrieve-the-cf-aig-log-id) is a unique identifier for the specific log entry to which you want to add feedback. |
| cf-aig-max-attempts | Header to customize the number of max attempts for [request retries](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/#request-retries) of a request. |
| cf-aig-metadata | [Custom metadata](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-metadata/)allows you to tag requests with user IDs or other identifiers, enabling better tracking and analysis of your requests. |
| cf-aig-request-timeout | Header to trigger a fallback provider based on a [predetermined response time](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/fallbacks/#request-timeouts) (measured in milliseconds). |
| cf-aig-retry-delay | Header to customize the retry delay for [request retries](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/#request-retries) of a request. |
| cf-aig-skip-cache | Header to [bypass caching for a specific request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#skip-cache-cf-aig-skip-cache). |
| cf-aig-step | [cf-aig-step](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/fallbacks/#response-headercf-aig-step) identifies the processing step in the AI Gateway flow for better tracking and debugging. |
| cf-cache-ttl | Deprecated: This header is replaced by `cf-aig-cache-ttl`. It specifies cache time-to-live. |
| cf-skip-cache | Deprecated: This header is replaced by `cf-aig-skip-cache`. It bypasses caching for a specific request. |
## Configuration hierarchy
Settings in AI Gateway can be configured at three levels: **Provider**, **Request**, and **Gateway**. Since the same settings can be configured in multiple locations, the following hierarchy determines which value is applied:
1. **Provider-level headers**: Relevant only when using the [Universal Endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/), these headers take precedence over all other configurations.
2. **Request-level headers**: Apply if no provider-level headers are set.
3. **Gateway-level settings**: Act as the default if no headers are set at the provider or request levels.
This hierarchy ensures consistent behavior, prioritizing the most specific configurations. Use provider-level and request-level headers for more fine-tuned control, and gateway settings for general defaults.
---
title: Integrations · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
lastUpdated: 2025-05-09T15:42:57.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/index.md
---
---
title: MCP server · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
lastUpdated: 2025-10-09T17:32:08.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/mcp-server/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/mcp-server/index.md
---
---
title: Observability · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Observability is the practice of instrumenting systems to collect
metrics, and logs enabling better monitoring, troubleshooting, and
optimization of applications.
lastUpdated: 2025-05-09T15:42:57.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/index.md
---
Observability is the practice of instrumenting systems to collect metrics, and logs enabling better monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization of applications.
* [Analytics](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/)
* [Costs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/costs/)
* [Custom metadata](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/custom-metadata/)
* [OpenTelemetry](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/otel-integration/)
* [Logging](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/)
---
title: Platform · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
lastUpdated: 2025-05-09T15:42:57.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/index.md
---
* [Audit logs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/audit-logs/)
* [Limits](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/limits/)
* [Pricing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing/)
---
title: Tutorials · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: View tutorials to help you get started with AI Gateway.
lastUpdated: 2025-05-09T15:42:57.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/index.md
---
View tutorials to help you get started with AI Gateway.
## Docs
| Name | Last Updated | Difficulty |
| - | - | - |
| [AI Gateway Binding Methods](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/worker-binding-methods/) | 11 months ago | |
| [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/aig-workers-ai-binding/) | over 1 year ago | |
| [Create your first AI Gateway using Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/create-first-aig-workers/) | over 1 year ago | Beginner |
| [Deploy a Worker that connects to OpenAI via AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/deploy-aig-worker/) | over 2 years ago | Beginner |
## Videos
Cloudflare Workflows | Introduction (Part 1 of 3)
In this video, we introduce Cloudflare Workflows, the Newest Developer Platform Primitive at Cloudflare.
Cloudflare Workflows | Batching and Monitoring Your Durable Execution (Part 2 of 3)
Workflows exposes metrics such as execution, error rates, steps, and total duration!
Welcome to the Cloudflare Developer Channel
Welcome to the Cloudflare Developers YouTube channel. We've got tutorials and working demos and everything you need to level up your projects. Whether you're working on your next big thing or just dorking around with some side projects, we've got you covered! So why don't you come hang out, subscribe to our developer channel and together we'll build something awesome. You're gonna love it.
Optimize your AI App & fine-tune models (AI Gateway, R2)
In this workshop, Kristian Freeman, Cloudflare Developer Advocate, shows how to optimize your existing AI applications with Cloudflare AI Gateway, and how to finetune OpenAI models using R2.
How to use Cloudflare AI models and inference in Python with Jupyter Notebooks
Cloudflare Workers AI provides a ton of AI models and inference capabilities. In this video, we will explore how to make use of Cloudflare’s AI model catalog using a Python Jupyter Notebook.
---
title: Using AI Gateway · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/index.md
---
##
---
title: Authenticated Gateway · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Add security by requiring a valid authorization token for each request.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-07T18:26:33.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/index.md
---
Using an Authenticated Gateway in AI Gateway adds security by requiring a valid authorization token for each request. This feature is especially useful when storing logs, as it prevents unauthorized access and protects against invalid requests that can inflate log storage usage and make it harder to find the data you need. With Authenticated Gateway enabled, only requests with the correct token are processed.
Note
We recommend enabling Authenticated Gateway when opting to store logs with AI Gateway.
If Authenticated Gateway is enabled but a request does not include the required `cf-aig-authorization` header, the request will fail. This setting ensures that only verified requests pass through the gateway. To bypass the need for the `cf-aig-authorization` header, make sure to disable Authenticated Gateway.
## Setting up Authenticated Gateway using the Dashboard
1. Go to the Settings for the specific gateway you want to enable authentication for.
2. Select **Create authentication token** to generate a custom token with the required `Run` permissions. Be sure to securely save this token, as it will not be displayed again.
3. Include the `cf-aig-authorization` header with your API token in each request for this gateway.
4. Return to the settings page and toggle on Authenticated Gateway.
## Example requests with OpenAI
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer OPENAI_TOKEN' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{"model": "gpt-5-mini", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is Cloudflare?"}]}'
```
Using the OpenAI SDK:
```javascript
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
baseURL: "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/account-id/gateway/openai",
defaultHeaders: {
"cf-aig-authorization": `Bearer {token}`,
},
});
```
## Example requests with the Vercel AI SDK
```javascript
import { createOpenAI } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const openai = createOpenAI({
baseURL: "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/account-id/gateway/openai",
headers: {
"cf-aig-authorization": `Bearer {token}`,
},
});
```
## Expected behavior
Note
When an AI Gateway is accessed from a Cloudflare Worker using a **binding**, the `cf-aig-authorization` header does not need to be manually included.\
Requests made through bindings are **pre-authenticated** within the associated Cloudflare account.
The following table outlines gateway behavior based on the authentication settings and header status:
| Authentication Setting | Header Info | Gateway State | Response |
| - | - | - | - |
| On | Header present | Authenticated gateway | Request succeeds |
| On | No header | Error | Request fails due to missing authorization |
| Off | Header present | Unauthenticated gateway | Request succeeds |
| Off | No header | Unauthenticated gateway | Request succeeds |
---
title: BYOK (Store Keys) · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Bring your own keys (BYOK) is a feature in Cloudflare AI Gateway
that allows you to securely store your AI provider API keys directly in the
Cloudflare dashboard. Instead of including API keys in every request to your
AI models, you can configure them once in the dashboard, and reference them in
your gateway configuration.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-14T14:49:24.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/index.md
---
## Introduction
Bring your own keys (BYOK) is a feature in Cloudflare AI Gateway that allows you to securely store your AI provider API keys directly in the Cloudflare dashboard. Instead of including API keys in every request to your AI models, you can configure them once in the dashboard, and reference them in your gateway configuration.
The keys are stored securely with [Secrets Store](https://developers.cloudflare.com/secrets-store/) and allows for:
* Secure storage and limit exposure
* Easier key rotation
* Rate limit, budget limit and other restrictions with [Dynamic Routes](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/)
## Setting up BYOK
### Prerequisites
* Ensure your gateway is [authenticated](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/).
* Ensure you have appropriate [permissions](https://developers.cloudflare.com/secrets-store/access-control/) to create and deploy secrets on Secrets Store.
### Configure API keys
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select your gateway or create a new one.
4. Go to the **Provider Keys** section.
5. Click **Add API Key**.
6. Select your AI provider from the dropdown.
7. Enter your API key and optionally provide a description.
8. Click **Save**.
### Update your applications
Once you've configured your API keys in the dashboard:
1. **Remove API keys from your code**: Delete any hardcoded API keys or environment variables.
2. **Update request headers**: Remove provider authorization headers from your requests. Note that you still need to pass `cf-aig-authorization`.
3. **Test your integration**: Verify that requests work without including API keys.
## Example
With BYOK enabled, your workflow changes from:
1. **Traditional approach**: Include API key in every request header
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
-H 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "gpt-4", "messages": [...]}'
```
2. **BYOK approach**: Configure key once in dashboard, make requests without exposing keys
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
-H 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "gpt-4", "messages": [...]}'
```
## Managing API keys
### Viewing configured keys
In the AI Gateway dashboard, you can:
* View all configured API keys by provider
* See when each key was last used
* Check the status of each key (active, expired, invalid)
### Rotating keys
To rotate an API key:
1. Generate a new API key from your AI provider
2. In the Cloudflare dashboard, edit the existing key entry
3. Replace the old key with the new one
4. Save the changes
Your applications will immediately start using the new key without any code changes or downtime.
### Revoking access
To remove an API key:
1. In the AI Gateway dashboard, find the key you want to remove
2. Click the **Delete** button
3. Confirm the deletion
Impact of key deletion
Deleting an API key will immediately stop all requests that depend on it. Make sure to update your applications or configure alternative keys before deletion.
## Multiple keys per provider
AI Gateway supports storing multiple API keys for the same provider. This allows you to:
* Use different keys for different use cases (for example, development vs production)
* Gradually migrate between keys during rotation
### Key aliases
Each API key can be assigned an alias to identify it. When you add a key, you can specify a custom alias, or the system will use `default` as the alias.
When making requests, AI Gateway uses the key with the `default` alias by default. To use a different key, include the `cf-aig-byok-alias` header with the alias of the key you want to use.
### Example: Using a specific key alias
If you have multiple OpenAI keys configured with different aliases (for example, `default`, `production`, and `testing`), you can specify which one to use:
```bash
# Uses the key with alias "default" (no header needed)
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
-H 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "gpt-4", "messages": [...]}'
```
```bash
# Uses the key with alias "production"
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
-H 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
-H 'cf-aig-byok-alias: production' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "gpt-4", "messages": [...]}'
```
```bash
# Uses the key with alias "testing"
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
-H 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
-H 'cf-aig-byok-alias: testing' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "gpt-4", "messages": [...]}'
```
---
title: Custom costs · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Override default or public model costs on a per-request basis.
lastUpdated: 2025-03-05T12:30:57.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/index.md
---
AI Gateway allows you to set custom costs at the request level. By using this feature, the cost metrics can accurately reflect your unique pricing, overriding the default or public model costs.
Note
Custom costs will only apply to requests that pass tokens in their response. Requests without token information will not have costs calculated.
## Custom cost
To add custom costs to your API requests, use the `cf-aig-custom-cost` header. This header enables you to specify the cost per token for both input (tokens sent) and output (tokens received).
* **per\_token\_in**: The negotiated input token cost (per token).
* **per\_token\_out**: The negotiated output token cost (per token).
There is no limit to the number of decimal places you can include, ensuring precise cost calculations, regardless of how small the values are.
Custom costs will appear in the logs with an underline, making it easy to identify when custom pricing has been applied.
In this example, if you have a negotiated price of $1 per million input tokens and $2 per million output tokens, include the `cf-aig-custom-cost` header as shown below.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-custom-cost: {"per_token_in":0.000001,"per_token_out":0.000002}' \
--data ' {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "When is Cloudflare’s Birthday Week?"
}
]
}'
```
Note
If a response is served from cache (cache hit), the cost is always `0`, even if you specified a custom cost. Custom costs only apply when the request reaches the model provider.
---
title: Custom Providers · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Create and manage custom AI providers for your account.
lastUpdated: 2026-02-17T16:17:11.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-providers/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-providers/index.md
---
## Overview
Custom Providers allow you to integrate AI providers that are not natively supported by AI Gateway. This feature enables you to use AI Gateway's observability, caching, rate limiting, and other features with any AI provider that has an HTTPS API endpoint.
## Use cases
* **Internal AI models**: Connect to your organization's self-hosted AI models
* **Regional providers**: Integrate with AI providers specific to your region
* **Specialized models**: Use domain-specific AI services not available through standard providers
* **Custom endpoints**: Route requests to your own AI infrastructure
## Before you begin
### Prerequisites
* An active Cloudflare account with AI Gateway access
* A valid API key from your custom AI provider
* The HTTPS base URL for your provider's API
### Authentication
The API endpoints for creating, reading, updating, or deleting custom providers require authentication. You need to create a Cloudflare API token with the appropriate permissions.
To create an API token:
1. Go to the [Cloudflare dashboard API tokens page](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=:account/api-tokens)
2. Click **Create Token**
3. Select **Custom Token** and add the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
4. Click **Continue to summary** and then **Create Token**
5. Copy the token - you'll use it in the `Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN` header
## Create a custom provider
* API
To create a new custom provider using the API:
1. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/) and Account Tag.
2. Send a `POST` request to create a new custom provider:
```bash
curl -X POST "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "My Custom Provider",
"slug": "some-provider",
"base_url": "https://api.myprovider.com",
"description": "Custom AI provider for internal models",
"enable": true
}'
```
**Required fields:**
* `name` (string): Display name for your provider
* `slug` (string): Unique identifier (alphanumeric with hyphens). Must be unique within your account.
* `base_url` (string): HTTPS URL for your provider's API endpoint. Must start with `https://`.
**Optional fields:**
* `description` (string): Description of the provider
* `link` (string): URL to provider documentation
* `enable` (boolean): Whether the provider is active (default: `false`)
* `beta` (boolean): Mark as beta feature (default: `false`)
* `curl_example` (string): Example cURL command for using the provider
* `js_example` (string): Example JavaScript code for using the provider
**Response:**
```json
{
"success": true,
"result": {
"id": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
"account_id": "abc123def456",
"account_tag": "my-account",
"name": "My Custom Provider",
"slug": "some-provider",
"base_url": "https://api.myprovider.com",
"description": "Custom AI provider for internal models",
"enable": true,
"beta": false,
"logo": "Base64 encoded SVG logo",
"link": null,
"curl_example": null,
"js_example": null,
"created_at": 1700000000,
"modified_at": 1700000000
}
}
```
Auto-generated logo
A default SVG logo is automatically generated for each custom provider. The logo is returned as a base64-encoded string.
* Dashboard
To create a new custom provider using the dashboard:
1. Log in to the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) and select your account.
2. Go to [**Compute & AI** > **AI Gateway** > **Custom Providers**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway/custom-providers).
3. Select **Add Custom Provider**.
4. Enter the following information:
* **Provider Name**: Display name for your provider
* **Provider Slug**: Unique identifier (alphanumeric with hyphens)
* **Base URL**: HTTPS URL for your provider's API endpoint (e.g., `https://api.myprovider.com/v1`)
5. Select **Save** to create your custom provider.
## List custom providers
* API
Retrieve all custom providers with optional filtering and pagination:
```bash
curl "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN"
```
**Query parameters:**
* `page` (number): Page number (default: `1`)
* `per_page` (number): Items per page (default: `20`, max: `100`)
* `enable` (boolean): Filter by enabled status
* `beta` (boolean): Filter by beta status
* `search` (string): Search in id, name, or slug fields
* `order_by` (string): Sort field and direction (default: `"name ASC"`)
**Examples:**
List only enabled providers:
```bash
curl "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers?enable=true" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN"
```
Search for specific providers:
```bash
curl "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers?search=custom" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN"
```
**Response:**
```json
{
"success": true,
"result": [
{
"id": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
"name": "My Custom Provider",
"slug": "some-provider",
"base_url": "https://api.myprovider.com",
"enable": true,
"created_at": 1700000000,
"modified_at": 1700000000
}
],
"result_info": {
"page": 1,
"per_page": 20,
"total_count": 1,
"total_pages": 1
}
}
```
* Dashboard
To view all your custom providers:
1. Log in to the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) and select your account.
2. Go to [**Compute & AI** > **AI Gateway** > **Custom Providers**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway/custom-providers).
3. You will see a list of all your custom providers with their names, slugs, base URLs, and status.
## Get a specific custom provider
* API
Retrieve details for a specific custom provider by its ID:
```bash
curl "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers/{provider_id}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN"
```
**Response:**
```json
{
"success": true,
"result": {
"id": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
"account_id": "abc123def456",
"account_tag": "my-account",
"name": "My Custom Provider",
"slug": "some-provider",
"base_url": "https://api.myprovider.com",
"description": "Custom AI provider for internal models",
"enable": true,
"beta": false,
"logo": "Base64 encoded SVG logo",
"link": "https://docs.myprovider.com",
"curl_example": "curl -X POST https://api.myprovider.com/v1/chat ...",
"js_example": "fetch('https://api.myprovider.com/v1/chat', {...})",
"created_at": 1700000000,
"modified_at": 1700000000
}
}
```
## Update a custom provider
* API
Update an existing custom provider. All fields are optional - only include the fields you want to change:
```bash
curl -X PATCH "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers/{provider_id}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Updated Provider Name",
"enable": true,
"description": "Updated description"
}'
```
**Updatable fields:**
* `name` (string): Provider display name
* `slug` (string): Provider identifier
* `base_url` (string): API endpoint URL (must be HTTPS)
* `description` (string): Provider description
* `link` (string): Documentation URL
* `enable` (boolean): Active status
* `beta` (boolean): Beta flag
* `curl_example` (string): Example cURL command
* `js_example` (string): Example JavaScript code
**Examples:**
Enable a provider:
```bash
curl -X PATCH "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers/{provider_id}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"enable": true}'
```
Update provider URL:
```bash
curl -X PATCH "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers/{provider_id}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"base_url": "https://api.newprovider.com"}'
```
Cache invalidation
Updates to custom providers automatically invalidate any cached entries related to that provider.
* Dashboard
To update an existing custom provider:
1. Log in to the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) and select your account.
2. Go to [**Compute & AI** > **AI Gateway** > **Custom Providers**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway/custom-providers).
3. Find the custom provider you want to update and select **Edit**.
4. Update the fields you want to change (name, slug, base URL, etc.).
5. Select **Save** to apply your changes.
## Delete a custom provider
* API
Delete a custom provider:
```bash
curl -X DELETE "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/custom-providers/{provider_id}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN"
```
**Response:**
```json
{
"success": true,
"result": {
"id": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
"name": "My Custom Provider",
"slug": "some-provider"
}
}
```
Impact of deletion
Deleting a custom provider will immediately stop all requests routed through it. Ensure you have updated your applications before deleting a provider. Cache entries related to the provider will also be invalidated.
* Dashboard
To delete a custom provider:
1. Log in to the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) and select your account.
2. Go to [**Compute & AI** > **AI Gateway** > **Custom Providers**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway/custom-providers).
3. Find the custom provider you want to delete and select **Delete**.
4. Confirm the deletion when prompted.
Impact of deletion
Deleting a custom provider will immediately stop all requests routed through it. Ensure you have updated your applications before deleting a provider.
## Using custom providers with AI Gateway
Once you've created a custom provider, you can route requests through AI Gateway using one of two approaches: the **Unified API** or the **provider-specific endpoint**. When referencing your custom provider with either approach, you must prefix the slug with `custom-`.
Custom provider prefix
All custom provider slugs must be prefixed with `custom-` when making requests through AI Gateway. For example, if your provider slug is `some-provider`, you must use `custom-some-provider` in your requests.
### How URL routing works
When AI Gateway receives a request for a custom provider, it constructs the upstream URL by combining the provider's configured `base_url` with the path that comes after `custom-{slug}/` in the gateway URL.
**The `base_url` field should contain only the root domain** (or domain with a fixed prefix) of the provider's API. Any API-specific path segments (like `/v1/chat/completions`) go in the request URL, not in `base_url`.
The formula is:
```plaintext
Gateway URL: https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-{slug}/{provider-path}
Upstream URL: {base_url}/{provider-path}
```
Everything after `custom-{slug}/` in your request URL is appended directly to the `base_url` to form the final upstream URL. This means `{provider-path}` can include multiple path segments, query parameters, or any path structure your provider requires.
### Choosing between Unified API and provider-specific endpoint
| | Unified API (`/compat`) | Provider-specific endpoint |
| - | - | - |
| **Best for** | Providers with OpenAI-compatible APIs | Providers with any API structure |
| **Request format** | Must follow the OpenAI `/chat/completions` schema | Uses the provider's native request format |
| **Path control** | Fixed to `/compat/chat/completions` | Full control over the upstream path |
| **How to specify the provider** | `model` field: `custom-{slug}/{model-name}` | URL path: `/custom-{slug}/{path}` |
Use the **Unified API** when your custom provider accepts the OpenAI-compatible `/chat/completions` request format. This is the simplest option and works well with OpenAI SDKs.
Use the **provider-specific endpoint** when your custom provider uses a non-standard API path or request format. This gives you full control over both the URL path and the request body sent to the upstream provider.
### Via Unified API
The Unified API sends requests to the provider's chat completions endpoint using the OpenAI-compatible format. Specify the model using the format `custom-{slug}/{model-name}`.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $PROVIDER_API_KEY" \
-H "cf-aig-authorization: Bearer $CF_AIG_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "custom-some-provider/model-name",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
### Via provider-specific endpoint
The provider-specific endpoint gives you full control over the upstream path. Everything after `custom-{slug}/` in the URL is appended to the `base_url`.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-some-provider/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $PROVIDER_API_KEY" \
-H "cf-aig-authorization: Bearer $CF_AIG_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "model-name",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
If `base_url` is `https://api.myprovider.com`, this request is proxied to: `https://api.myprovider.com/v1/chat/completions`
### Examples
The following examples show how to configure `base_url` and construct request URLs for different types of providers.
#### Example 1: OpenAI-compatible provider (standard `/v1/` path)
Many providers follow the OpenAI convention of hosting their API at `{domain}/v1/chat/completions`.
**Configuration:**
* `slug`: `my-openai-compat`
* `base_url`: `https://api.example-provider.com`
**Provider-specific endpoint:**
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-my-openai-compat/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $PROVIDER_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "example-model",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
**URL mapping:**
| Component | Value |
| - | - |
| Gateway URL | `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-my-openai-compat/v1/chat/completions` |
| `base_url` | `https://api.example-provider.com` |
| Provider path | `/v1/chat/completions` |
| Upstream URL | `https://api.example-provider.com/v1/chat/completions` |
Since this provider is OpenAI-compatible, you could also use the Unified API:
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $PROVIDER_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "custom-my-openai-compat/example-model",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
#### Example 2: Provider with a non-standard API path
Some providers use API paths that don't follow the `/v1/` convention. For example, a provider whose chat endpoint is at `https://api.custom-ai.com/api/coding/paas/v4/chat/completions`.
**Configuration:**
* `slug`: `custom-ai`
* `base_url`: `https://api.custom-ai.com`
**Provider-specific endpoint:**
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-custom-ai/api/coding/paas/v4/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $PROVIDER_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "custom-ai-model",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
**URL mapping:**
| Component | Value |
| - | - |
| Gateway URL | `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-custom-ai/api/coding/paas/v4/chat/completions` |
| `base_url` | `https://api.custom-ai.com` |
| Provider path | `/api/coding/paas/v4/chat/completions` |
| Upstream URL | `https://api.custom-ai.com/api/coding/paas/v4/chat/completions` |
Note
For providers with non-standard paths, you must use the provider-specific endpoint. The Unified API only supports the `/chat/completions` path and cannot route to custom API paths.
#### Example 3: Self-hosted model with a path prefix
If you host your own model behind a reverse proxy or on a platform that adds a path prefix, include only the fixed prefix portion in `base_url` if all your endpoints share it. Otherwise, keep `base_url` as just the domain.
**Configuration (domain-only `base_url`):**
* `slug`: `internal-llm`
* `base_url`: `https://ml.internal.example.com`
**Provider-specific endpoint:**
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-internal-llm/serving/models/my-model:predict \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $INTERNAL_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"instances": [{"prompt": "Summarize the following text:"}]
}'
```
**URL mapping:**
| Component | Value |
| - | - |
| Gateway URL | `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-internal-llm/serving/models/my-model:predict` |
| `base_url` | `https://ml.internal.example.com` |
| Provider path | `/serving/models/my-model:predict` |
| Upstream URL | `https://ml.internal.example.com/serving/models/my-model:predict` |
#### Example 4: Provider using OpenAI SDK with a custom base URL
When using the OpenAI SDK to connect to a custom provider through AI Gateway, set the SDK's `base_url` to the gateway's provider-specific endpoint path (up to and including the API version prefix that your provider expects).
**Configuration:**
* `slug`: `alt-provider`
* `base_url`: `https://api.alt-provider.com`
**Python (OpenAI SDK):**
```python
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="your-provider-api-key",
base_url="https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-alt-provider/v1",
default_headers={
"cf-aig-authorization": "Bearer {cf_aig_token}",
},
)
# The SDK appends /chat/completions to the base_url automatically.
# Final upstream URL: https://api.alt-provider.com/v1/chat/completions
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="alt-model-v2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}],
)
```
**URL mapping:**
| Component | Value |
| - | - |
| SDK `base_url` | `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-alt-provider/v1` |
| SDK appends | `/chat/completions` |
| Full gateway URL | `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/custom-alt-provider/v1/chat/completions` |
| Provider `base_url` | `https://api.alt-provider.com` |
| Provider path | `/v1/chat/completions` |
| Upstream URL | `https://api.alt-provider.com/v1/chat/completions` |
## Common errors
### 409 Conflict - Duplicate slug
```json
{
"success": false,
"errors": [
{
"code": 1003,
"message": "A custom provider with this slug already exists",
"path": ["body", "slug"]
}
]
}
```
Each custom provider slug must be unique within your account. Choose a different slug or update the existing provider.
### 404 Not Found
```json
{
"success": false,
"errors": [
{
"code": 1004,
"message": "Custom Provider not found"
}
]
}
```
The specified provider ID does not exist or you don't have access to it. Verify the provider ID and your authentication credentials.
### 400 Bad Request - Invalid base\_url
```json
{
"success": false,
"errors": [
{
"code": 1002,
"message": "base_url must be a valid HTTPS URL starting with https://",
"path": ["body", "base_url"]
}
]
}
```
The `base_url` field must be a valid HTTPS URL. HTTP URLs are not supported for security reasons.
### 404 when making requests to a custom provider
If you receive a 404 from the upstream provider, the most common cause is an incorrect path mapping. Verify that:
1. Your `base_url` is set to the provider's **root domain** (for example, `https://api.provider.com`) rather than including API path segments.
2. Your request URL includes the **full API path** after `custom-{slug}/`. For example, if the upstream endpoint is `https://api.provider.com/api/v2/chat`, your gateway URL should end in `/custom-{slug}/api/v2/chat`.
3. There is no duplicate or missing path segment. A common mistake is including `/v1` in both `base_url` and the request path, resulting in the upstream receiving `/v1/v1/chat/completions`.
## Best practices
1. **Use descriptive slugs**: Choose slugs that clearly identify the provider (e.g., `internal-gpt`, `regional-ai`)
2. **Document your integrations**: Use the `curl_example` and `js_example` fields to provide usage examples
3. **Enable gradually**: Test with `enable: false` before making the provider active
4. **Monitor usage**: Use AI Gateway's analytics to track requests to your custom providers
5. **Secure your endpoints**: Ensure your custom provider's base URL implements proper authentication and authorization
6. **Use BYOK**: Store provider API keys securely using [BYOK](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/) instead of including them in every request
## Limitations
* Custom providers are account-specific and not shared across Cloudflare accounts
* The `base_url` must use HTTPS (HTTP is not supported)
* Provider slugs must be unique within each account
* Cache and rate limiting settings apply globally to the provider, not per-model
## Related resources
* [Get started with AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/)
* [Configure authentication](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/)
* [BYOK (Store Keys)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/)
* [Dynamic routing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/)
* [Caching](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/)
* [Rate limiting](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/rate-limiting/)
---
title: Fallbacks · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Specify model or provider fallbacks with your Universal endpoint to
handle request failures and ensure reliability.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-20T18:25:25.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/fallbacks/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/fallbacks/index.md
---
Specify model or provider fallbacks with your [Universal endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/) to handle request failures and ensure reliability.
Cloudflare can trigger your fallback provider in response to [request errors](#request-failures) or [predetermined request timeouts](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling#request-timeouts). The [response header `cf-aig-step`](#response-headercf-aig-step) indicates which step successfully processed the request.
## Request failures
By default, Cloudflare triggers your fallback if a model request returns an error.
### Example
In the following example, a request first goes to the [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/) Inference API. If the request fails, it falls back to OpenAI. The response header `cf-aig-step` indicates which provider successfully processed the request.
1. Sends a request to Workers AI Inference API.
2. If that request fails, proceeds to OpenAI.
```mermaid
graph TD
A[AI Gateway] --> B[Request to Workers AI Inference API]
B -->|Success| C[Return Response]
B -->|Failure| D[Request to OpenAI API]
D --> E[Return Response]
```
You can add as many fallbacks as you need, just by adding another object in the array.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id} \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '[
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
},
{
"provider": "openai",
"endpoint": "chat/completions",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {open_ai_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"stream": true,
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
}
]'
```
## Response header(cf-aig-step)
When using the [Universal endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/) with fallbacks, the response header `cf-aig-step` indicates which model successfully processed the request by returning the step number. This header provides visibility into whether a fallback was triggered and which model ultimately processed the response.
* `cf-aig-step:0` – The first (primary) model was used successfully.
* `cf-aig-step:1` – The request fell back to the second model.
* `cf-aig-step:2` – The request fell back to the third model.
* Subsequent steps – Each fallback increments the step number by 1.
---
title: Manage gateways · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: You have several different options for managing an AI Gateway.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-20T18:25:25.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/manage-gateway/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/manage-gateway/index.md
---
You have several different options for managing an AI Gateway.
## Create gateway
* Dashboard
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select **Create Gateway**.
4. Enter your **Gateway name**. Note: Gateway name has a 64 character limit.
5. Select **Create**.
* API
To set up an AI Gateway using the API:
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
2. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
3. Using that API token and Account ID, send a [`POST` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/) to the Cloudflare API.
## Edit gateway
* Dashboard
To edit an AI Gateway in the dashboard:
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select your gateway.
4. Go to **Settings** and update as needed.
* API
To edit an AI Gateway, send a [`PUT` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/update/) to the Cloudflare API.
Note
For more details about what settings are available for editing, refer to [Configuration](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/).
## Delete gateway
Deleting your gateway is permanent and can not be undone.
* Dashboard
To delete an AI Gateway in the dashboard:
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select your gateway from the list of available options.
4. Go to **Settings**.
5. For **Delete Gateway**, select **Delete** (and confirm your deletion).
* API
To delete an AI Gateway, send a [`DELETE` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/delete/) to the Cloudflare API.
---
title: Request handling · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Your AI gateway supports different strategies for handling requests
to providers, which allows you to manage AI interactions effectively and
ensure your applications remain responsive and reliable.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/index.md
---
Deprecated
While the request handling features described on this page still work, [Dynamic Routing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/) is now the preferred way to achieve advanced request handling, including timeouts, retries, and fallbacks. Dynamic Routing provides a more powerful and flexible approach with a visual interface for managing complex routing scenarios.
Your AI gateway supports different strategies for handling requests to providers, which allows you to manage AI interactions effectively and ensure your applications remain responsive and reliable.
## Request timeouts
A request timeout allows you to trigger fallbacks or a retry if a provider takes too long to respond.
These timeouts help:
* Improve user experience, by preventing users from waiting too long for a response
* Proactively handle errors, by detecting unresponsive providers and triggering a fallback option
Request timeouts can be set on a Universal Endpoint or directly on a request to any provider.
### Definitions
A timeout is set in milliseconds. Additionally, the timeout is based on when the first part of the response comes back. As long as the first part of the response returns within the specified timeframe - such as when streaming a response - your gateway will wait for the response.
### Configuration
#### Universal Endpoint
If set on a [Universal Endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/), a request timeout specifies the timeout duration for requests and triggers a fallback.
For a Universal Endpoint, configure the timeout value by setting a `requestTimeout` property within the provider-specific `config` object. Each provider can have a different `requestTimeout` value for granular customization.
```bash
curl 'https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '[
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"config": {
"requestTimeout": 1000
},
"query": {
34 collapsed lines
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
},
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct-fast",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
},
"config": {
"requestTimeout": 3000
},
}
]'
```
#### Direct provider
If set on a [provider](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/) request, request timeout specifies the timeout duration for a request and - if exceeded - returns an error.
For a provider-specific endpoint, configure the timeout value by adding a `cf-aig-request-timeout` header.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/workers-ai/@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {cf_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-request-timeout: 5000'
--data '{"prompt": "What is Cloudflare?"}'
```
***
## Request retries
AI Gateway also supports automatic retries for failed requests, with a maximum of five retry attempts.
This feature improves your application's resiliency, ensuring you can recover from temporary issues without manual intervention.
Request timeouts can be set on a Universal Endpoint or directly on a request to any provider.
### Definitions
With request retries, you can adjust a combination of three properties:
* Number of attempts (maximum of 5 tries)
* How long before retrying (in milliseconds, maximum of 5 seconds)
* Backoff method (constant, linear, or exponential)
On the final retry attempt, your gateway will wait until the request completes, regardless of how long it takes.
### Configuration
#### Universal endpoint
If set on a [Universal Endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/), a request retry will automatically retry failed requests up to five times before triggering any configured fallbacks.
For a Universal Endpoint, configure the retry settings with the following properties in the provider-specific `config`:
```json
config:{
maxAttempts?: number;
retryDelay?: number;
backoff?: "constant" | "linear" | "exponential";
}
```
As with the [request timeout](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/request-handling/#universal-endpoint), each provider can have a different retry settings for granular customization.
```bash
curl 'https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '[
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"config": {
"maxAttempts": 2,
"retryDelay": 1000,
"backoff": "constant"
},
39 collapsed lines
"query": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
},
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct-fast",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
},
"config": {
"maxAttempts": 4,
"retryDelay": 1000,
"backoff": "exponential"
},
}
]'
```
#### Direct provider
If set on a [provider](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/) request, a request retry will automatically retry failed requests up to five times. On the final retry attempt, your gateway will wait until the request completes, regardless of how long it takes.
For a provider-specific endpoint, configure the retry settings by adding different header values:
* `cf-aig-max-attempts` (number)
* `cf-aig-retry-delay` (number)
* `cf-aig-backoff` ("constant" | "linear" | "exponential)
---
title: Add Human Feedback using Dashboard · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Human feedback is a valuable metric to assess the performance of
your AI models. By incorporating human feedback, you can gain deeper insights
into how the model's responses are perceived and how well it performs from a
user-centric perspective. This feedback can then be used in evaluations to
calculate performance metrics, driving optimization and ultimately enhancing
the reliability, accuracy, and efficiency of your AI application.
lastUpdated: 2025-09-05T08:34:36.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback/index.md
---
Human feedback is a valuable metric to assess the performance of your AI models. By incorporating human feedback, you can gain deeper insights into how the model's responses are perceived and how well it performs from a user-centric perspective. This feedback can then be used in evaluations to calculate performance metrics, driving optimization and ultimately enhancing the reliability, accuracy, and efficiency of your AI application.
Human feedback measures the performance of your dataset based on direct human input. The metric is calculated as the percentage of positive feedback (thumbs up) given on logs, which are annotated in the Logs tab of the Cloudflare dashboard. This feedback helps refine model performance by considering real-world evaluations of its output.
This tutorial will guide you through the process of adding human feedback to your evaluations in AI Gateway using the Cloudflare dashboard.
On the next guide, you can [learn how to add human feedback via the API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-api/).
## 1. Log in to the dashboard
In the Cloudflare dashboard, go to the **AI Gateway** page.
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
## 2. Access the Logs tab
1. Go to **Logs**.
2. The Logs tab displays all logs associated with your datasets. These logs show key information, including:
* Timestamp: When the interaction occurred.
* Status: Whether the request was successful, cached, or failed.
* Model: The model used in the request.
* Tokens: The number of tokens consumed by the response.
* Cost: The cost based on token usage.
* Duration: The time taken to complete the response.
* Feedback: Where you can provide human feedback on each log.
## 3. Provide human feedback
1. Click on the log entry you want to review. This expands the log, allowing you to see more detailed information.
2. In the expanded log, you can view additional details such as:
* The user prompt.
* The model response.
* HTTP response details.
* Endpoint information.
3. You will see two icons:
* Thumbs up: Indicates positive feedback.
* Thumbs down: Indicates negative feedback.
4. Click either the thumbs up or thumbs down icon based on how you rate the model response for that particular log entry.
## 4. Evaluate human feedback
After providing feedback on your logs, it becomes a part of the evaluation process.
When you run an evaluation (as outlined in the [Set Up Evaluations](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/set-up-evaluations/) guide), the human feedback metric will be calculated based on the percentage of logs that received thumbs-up feedback.
Note
You need to select human feedback as an evaluator to receive its metrics.
## 5. Review results
After running the evaluation, review the results on the Evaluations tab. You will be able to see the performance of the model based on cost, speed, and now human feedback, represented as the percentage of positive feedback (thumbs up).
The human feedback score is displayed as a percentage, showing the distribution of positively rated responses from the database.
For more information on running evaluations, refer to the documentation [Set Up Evaluations](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/set-up-evaluations/).
---
title: Add Human Feedback using API · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: This guide will walk you through the steps of adding human feedback
to an AI Gateway request using the Cloudflare API. You will learn how to
retrieve the relevant request logs, and submit feedback using the API.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-api/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-api/index.md
---
This guide will walk you through the steps of adding human feedback to an AI Gateway request using the Cloudflare API. You will learn how to retrieve the relevant request logs, and submit feedback using the API.
If you prefer to add human feedback via the dashboard, refer to [Add Human Feedback](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback/).
## 1. Create an API Token
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
1. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
2. Using that API token and Account ID, send a [`POST` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/) to the Cloudflare API.
## 2. Retrieve the `cf-aig-log-id`
The `cf-aig-log-id` is a unique identifier for the specific log entry to which you want to add feedback. Below are two methods to obtain this identifier.
### Method 1: Locate the `cf-aig-log-id` in the request response
This method allows you to directly find the `cf-aig-log-id` within the header of the response returned by the AI Gateway. This is the most straightforward approach if you have access to the original API response.
The steps below outline how to do this.
1. **Make a Request to the AI Gateway**: This could be a request your application sends to the AI Gateway. Once the request is made, the response will contain various pieces of metadata.
2. **Check the Response Headers**: The response will include a header named `cf-aig-log-id`. This is the identifier you will need to submit feedback.
In the example below, the `cf-aig-log-id` is `01JADMCQQQBWH3NXZ5GCRN98DP`.
```json
{
"status": "success",
"headers": {
"cf-aig-log-id": "01JADMCQQQBWH3NXZ5GCRN98DP"
},
"data": {
"response": "Sample response data"
}
}
```
### Method 2: Retrieve the `cf-aig-log-id` via API (GET request)
If you do not have the `cf-aig-log-id` in the response body or you need to access it after the fact, you are able to retrieve it by querying the logs using the [Cloudflare API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/subresources/logs/methods/list/).
Send a `GET` request to get a list of logs and then find a specific ID
Required API token permissions
At least one of the following [token permissions](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/reference/permissions/) is required:
* `AI Gateway Write`
* `AI Gateway Read`
```bash
curl "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/gateways/$GATEWAY_ID/logs" \
--request GET \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN"
```
```json
{
"result": [
{
"id": "01JADMCQQQBWH3NXZ5GCRN98DP",
"cached": true,
"created_at": "2019-08-24T14:15:22Z",
"custom_cost": true,
"duration": 0,
"id": "string",
"metadata": "string",
"model": "string",
"model_type": "string",
"path": "string",
"provider": "string",
"request_content_type": "string",
"request_type": "string",
"response_content_type": "string",
"status_code": 0,
"step": 0,
"success": true,
"tokens_in": 0,
"tokens_out": 0
}
]
}
```
### Method 3: Retrieve the `cf-aig-log-id` via a binding
You can also retrieve the `cf-aig-log-id` using a binding, which streamlines the process. Here's how to retrieve the log ID directly:
```js
const resp = await env.AI.run(
"@cf/meta/llama-3-8b-instruct",
{
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
{
gateway: {
id: "my_gateway_id",
},
},
);
const myLogId = env.AI.aiGatewayLogId;
```
Note:
The `aiGatewayLogId` property, will only hold the last inference call log id.
## 3. Submit feedback via PATCH request
Once you have both the API token and the `cf-aig-log-id`, you can send a PATCH request to submit feedback.
Required API token permissions
At least one of the following [token permissions](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/reference/permissions/) is required:
* `AI Gateway Write`
```bash
curl "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/$ACCOUNT_ID/ai-gateway/gateways/$GATEWAY_ID/logs/$ID" \
--request PATCH \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
--json '{
"feedback": 1
}'
```
If you had negative feedback, adjust the body of the request to be `-1`.
```json
{
"feedback": -1
}
```
## 4. Verify the feedback submission
You can verify the feedback submission in two ways:
* **Through the [Cloudflare dashboard ](https://dash.cloudflare.com)**: check the updated feedback on the AI Gateway interface.
* **Through the API**: Send another GET request to retrieve the updated log entry and confirm the feedback has been recorded.
---
title: Add human feedback using Worker Bindings · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: This guide explains how to provide human feedback for AI Gateway
evaluations using Worker bindings.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-bindings/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/add-human-feedback-bindings/index.md
---
This guide explains how to provide human feedback for AI Gateway evaluations using Worker bindings.
## 1. Run an AI Evaluation
Start by sending a prompt to the AI model through your AI Gateway.
```javascript
const resp = await env.AI.run(
"@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
{
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
{
gateway: {
id: "my-gateway",
},
},
);
const myLogId = env.AI.aiGatewayLogId;
```
Let the user interact with or evaluate the AI response. This interaction will inform the feedback you send back to the AI Gateway.
## 2. Send Human Feedback
Use the [`patchLog()`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/worker-binding-methods/#31-patchlog-send-feedback) method to provide feedback for the AI evaluation.
```javascript
await env.AI.gateway("my-gateway").patchLog(myLogId, {
feedback: 1, // all fields are optional; set values that fit your use case
score: 100,
metadata: {
user: "123", // Optional metadata to provide additional context
},
});
```
## Feedback parameters explanation
* `feedback`: is either `-1` for negative or `1` to positive, `0` is considered not evaluated.
* `score`: A number between 0 and 100.
* `metadata`: An object containing additional contextual information.
### patchLog: Send Feedback
The `patchLog` method allows you to send feedback, score, and metadata for a specific log ID. All object properties are optional, so you can include any combination of the parameters:
```javascript
gateway.patchLog("my-log-id", {
feedback: 1,
score: 100,
metadata: {
user: "123",
},
});
```
Returns: `Promise` (Make sure to `await` the request.)
---
title: Caching · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Override caching settings on a per-request basis.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-21T09:55:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/index.md
---
AI Gateway can cache responses from your AI model providers, serving them directly from Cloudflare's cache for identical requests.
## Benefits of Using Caching
* **Reduced Latency:** Serve responses faster to your users by avoiding a round trip to the origin AI provider for repeated requests.
* **Cost Savings:** Minimize the number of paid requests made to your AI provider, especially for frequently accessed or non-dynamic content.
* **Increased Throughput:** Offload repetitive requests from your AI provider, allowing it to handle unique requests more efficiently.
Note
Currently caching is supported only for text and image responses, and it applies only to identical requests.
This configuration benefits use cases with limited prompt options. For example, a support bot that asks "How can I help you?" and lets the user select an answer from a limited set of options works well with the current caching configuration. We plan on adding semantic search for caching in the future to improve cache hit rates.
## Default configuration
* Dashboard
To set the default caching configuration in the dashboard:
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Select **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select **Settings**.
4. Enable **Cache Responses**.
5. Change the default caching to whatever value you prefer.
* API
To set the default caching configuration using the API:
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
1. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
2. Using that API token and Account ID, send a [`POST` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/) to create a new Gateway and include a value for the `cache_ttl`.
This caching behavior will be uniformly applied to all requests that support caching. If you need to modify the cache settings for specific requests, you have the flexibility to override this setting on a per-request basis.
To check whether a response comes from cache or not, **cf-aig-cache-status** will be designated as `HIT` or `MISS`.
## Per-request caching
While your gateway's default cache settings provide a good baseline, you might need more granular control. These situations could include data freshness, content with varying lifespans, or dynamic or personalized responses.
To address these needs, AI Gateway allows you to override default cache behaviors on a per-request basis using specific HTTP headers. This gives you the precision to optimize caching for individual API calls.
The following headers allow you to define this per-request cache behavior:
Note
The following headers have been updated to new names, though the old headers will still function. We recommend updating to the new headers to ensure future compatibility:
`cf-cache-ttl` is now `cf-aig-cache-ttl`
`cf-skip-cache` is now `cf-aig-skip-cache`
### Skip cache (cf-aig-skip-cache)
Skip cache refers to bypassing the cache and fetching the request directly from the original provider, without utilizing any cached copy.
You can use the header **cf-aig-skip-cache** to bypass the cached version of the request.
As an example, when submitting a request to OpenAI, include the header in the following manner:
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-skip-cache: true' \
--data ' {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "how to build a wooden spoon in 3 short steps? give as short as answer as possible"
}
]
}
'
```
### Cache TTL (cf-aig-cache-ttl)
Cache TTL, or Time To Live, is the duration a cached request remains valid before it expires and is refreshed from the original source. You can use **cf-aig-cache-ttl** to set the desired caching duration in seconds. The minimum TTL is 60 seconds and the maximum TTL is one month.
For example, if you set a TTL of one hour, it means that a request is kept in the cache for an hour. Within that hour, an identical request will be served from the cache instead of the original API. After an hour, the cache expires and the request will go to the original API for a fresh response, and that response will repopulate the cache for the next hour.
As an example, when submitting a request to OpenAI, include the header in the following manner:
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-cache-ttl: 3600' \
--data ' {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "how to build a wooden spoon in 3 short steps? give as short as answer as possible"
}
]
}
'
```
### Custom cache key (cf-aig-cache-key)
Custom cache keys let you override the default cache key in order to precisely set the cacheability setting for any resource. To override the default cache key, you can use the header **cf-aig-cache-key**.
When you use the **cf-aig-cache-key** header for the first time, you will receive a response from the provider. Subsequent requests with the same header will return the cached response. If the **cf-aig-cache-ttl** header is used, responses will be cached according to the specified Cache Time To Live. Otherwise, responses will be cached according to the cache settings in the dashboard. If caching is not enabled for the gateway, responses will be cached for 5 minutes by default.
As an example, when submitting a request to OpenAI, include the header in the following manner:
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {openai_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-cache-key: responseA' \
--data ' {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "how to build a wooden spoon in 3 short steps? give as short as answer as possible"
}
]
}
'
```
AI Gateway caching behavior
Cache in AI Gateway is volatile. If two identical requests are sent simultaneously, the first request may not cache in time for the second request to use it, which may result in the second request retrieving data from the original source.
---
title: Set up Evaluations · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: This guide walks you through the process of setting up an
evaluation in AI Gateway. These steps are done in the Cloudflare dashboard.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/set-up-evaluations/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/set-up-evaluations/index.md
---
This guide walks you through the process of setting up an evaluation in AI Gateway. These steps are done in the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/).
## 1. Select or create a dataset
Datasets are collections of logs stored for analysis that can be used in an evaluation. You can create datasets by applying filters in the Logs tab. Datasets will update automatically based on the set filters.
### Set up a dataset from the Logs tab
1. Apply filters to narrow down your logs. Filter options include provider, number of tokens, request status, and more.
2. Select **Create Dataset** to store the filtered logs for future analysis.
You can manage datasets by selecting **Manage datasets** from the Logs tab.
Note
Please keep in mind that datasets currently use `AND` joins, so there can only be one item per filter (for example, one model or one provider). Future updates will allow more flexibility in dataset creation.
### List of available filters
| Filter category | Filter options | Filter by description |
| - | - | - |
| Status | error, status | error type or status. |
| Cache | cached, not cached | based on whether they were cached or not. |
| Provider | specific providers | the selected AI provider. |
| AI Models | specific models | the selected AI model. |
| Cost | less than, greater than | cost, specifying a threshold. |
| Request type | Universal, Workers AI Binding, WebSockets | the type of request. |
| Tokens | Total tokens, Tokens In, Tokens Out | token count (less than or greater than). |
| Duration | less than, greater than | request duration. |
| Feedback | equals, does not equal (thumbs up, thumbs down, no feedback) | feedback type. |
| Metadata Key | equals, does not equal | specific metadata keys. |
| Metadata Value | equals, does not equal | specific metadata values. |
| Log ID | equals, does not equal | a specific Log ID. |
| Event ID | equals, does not equal | a specific Event ID. |
## 2. Select evaluators
After creating a dataset, choose the evaluation parameters:
* Cost: Calculates the average cost of inference requests within the dataset (only for requests with [cost data](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/costs/)).
* Speed: Calculates the average duration of inference requests within the dataset.
* Performance:
* Human feedback: measures performance based on human feedback, calculated by the % of thumbs up on the logs, annotated from the Logs tab.
Note
Additional evaluators will be introduced in future updates to expand performance analysis capabilities.
## 3. Name, review, and run the evaluation
1. Create a unique name for your evaluation to reference it in the dashboard.
2. Review the selected dataset and evaluators.
3. Select **Run** to start the process.
## 4. Review and analyze results
Evaluation results will appear in the Evaluations tab. The results show the status of the evaluation (for example, in progress, completed, or error). Metrics for the selected evaluators will be displayed, excluding any logs with missing fields. You will also see the number of logs used to calculate each metric.
While datasets automatically update based on filters, evaluations do not. You will have to create a new evaluation if you want to evaluate new logs.
Use these insights to optimize based on your application's priorities. Based on the results, you may choose to:
* Change the model or [provider](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/)
* Adjust your prompts
* Explore further optimizations, such as setting up [Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/diagrams/ai/ai-rag/)
---
title: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) for AI Gateway helps protect your
organization from inadvertent exposure of sensitive data through AI
interactions. By integrating with Cloudflare's proven DLP technology, AI
Gateway can scan both incoming prompts and outgoing AI responses for sensitive
information, ensuring your AI applications maintain security and compliance
standards.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-22T21:11:06.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/index.md
---
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) for AI Gateway helps protect your organization from inadvertent exposure of sensitive data through AI interactions. By integrating with Cloudflare's proven DLP technology, AI Gateway can scan both incoming prompts and outgoing AI responses for sensitive information, ensuring your AI applications maintain security and compliance standards.
## How it works
AI Gateway DLP leverages the same powerful detection engines used in [Cloudflare's Data Loss Prevention](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/data-loss-prevention/) solution to scan AI traffic in real-time. The system analyzes both user prompts sent to AI models and responses received from AI providers, identifying sensitive data patterns and taking appropriate protective actions.
## Key benefits
* **Prevent data leakage**: Stop sensitive information from being inadvertently shared with AI providers or exposed in AI responses
* **Maintain compliance**: Help meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS
* **Consistent protection**: Apply the same DLP policies across all AI providers and models
* **Audit visibility**: Comprehensive logging and reporting for security and compliance teams
* **Zero-code integration**: Enable protection without modifying existing AI applications
## Supported AI traffic
AI Gateway DLP can scan:
* **User prompts** - Content submitted to AI models, including text, code, and structured data
* **AI responses** - Output generated by AI models before being returned to users
The system works with all AI providers supported by AI Gateway, providing consistent protection regardless of which models or services you use.
## Integration with Cloudflare DLP
AI Gateway DLP uses the same detection profiles and policies as Cloudflare's enterprise DLP solution. This means:
* **Unified management** - Configure DLP policies once and apply them across web traffic, email, SaaS applications, and AI interactions
* **Consistent detection** - The same sensitive data patterns are detected across all channels
* **Centralized reporting** - All DLP events appear in the same dashboard and logs
* **Shared profiles** - Reuse existing DLP detection profiles for AI traffic
For more information about Cloudflare's DLP capabilities, refer to the [Data Loss Prevention documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/data-loss-prevention/).
## Getting started
To enable DLP for your AI Gateway:
1. [Set up DLP policies](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/set-up-dlp/) for your AI Gateway
2. Configure detection profiles and response actions
3. Monitor DLP events through the Cloudflare dashboard
## Related resources
* [Set up DLP for AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/set-up-dlp/)
* [Cloudflare Data Loss Prevention](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/data-loss-prevention/)
* [AI Gateway Security Features](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/)
* [DLP Detection Profiles](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/data-loss-prevention/dlp-profiles/)
---
title: Dynamic routing · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: "Dynamic routing enables you to create request routing flows
through a visual interface or a JSON-based configuration. Instead of
hard-coding a single model, with Dynamic Routing you compose a small flow that
evaluates conditions, enforces quotas, and chooses models with fallbacks. You
can iterate without touching application code—publish a new route version and
you’re done. With dynamic routing, you can easily implement advanced use cases
such as:"
lastUpdated: 2026-01-10T06:11:22.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/index.md
---
## Introduction
Dynamic routing enables you to create request routing flows through a **visual interface** or a **JSON-based configuration**. Instead of hard-coding a single model, with Dynamic Routing you compose a small flow that evaluates conditions, enforces quotas, and chooses models with fallbacks. You can iterate without touching application code—publish a new route version and you’re done. With dynamic routing, you can easily implement advanced use cases such as:
* Directing different segments (paid/not-paid user) to different models
* Restricting each user/project/team with budget/rate limits
* A/B and gradual rollouts
while making it accessible to both developers and non-technical team members.
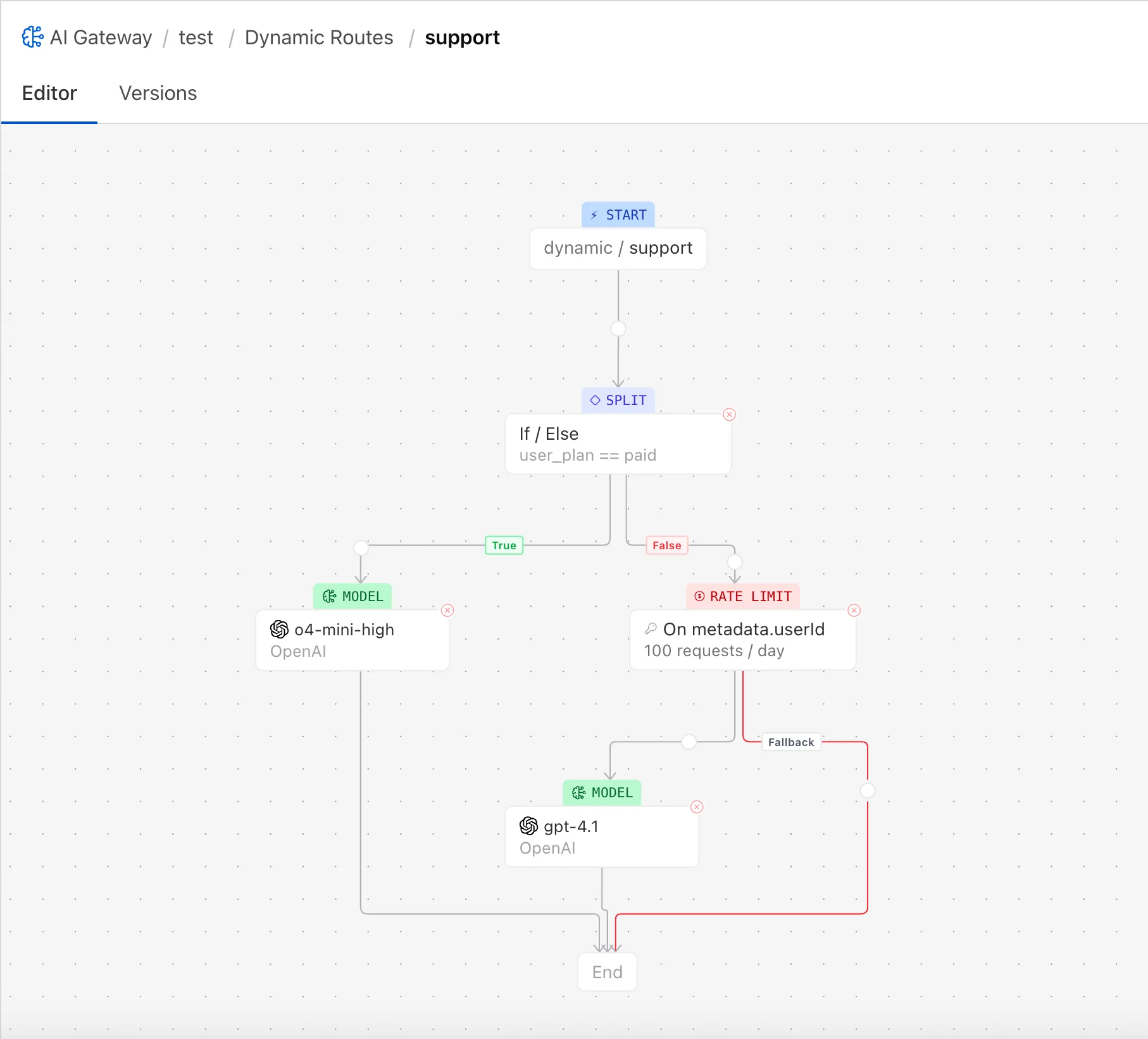
## Core Concepts
* **Route**: A named, versioned flow (for example, dynamic/support) that you can use as instead of the model name in your requests.
* **Nodes**
* **Start**: Entry point for the route.
* **Conditional**: If/Else branch based on expressions that reference request body, headers, or metadata (for example, user\_plan == "paid").
* **Percentage**: Routes requests probabilistically across multiple outputs, useful for A/B testing and gradual rollouts.
* **Model**: Calls a provider/model with the request parameters
* **Rate Limit**: Enforces number of requests quotas (per your key, per period) and switches to fallback when exceeded.
* **Budget Limit**: Enforces cost quotas (per your key, per period) and switches to fallback when exceeded.
* **End**: Terminates the flow and returns the final model response.
* **Metadata**: Arbitrary key-value context attached to the request (for example, userId, orgId, plan). You can pass this from your app so rules can reference it.
* **Versions**: Each change produces a new draft. Deploy to make it live with instant rollback.
## Getting Started
Warning
Ensure your gateway has [authentication](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/) turned on, and you have your upstream providers keys stored with [BYOK](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/).
1. Create a route.
* Go to **(Select your gateway)** > **Dynamic Routes** > **Add Route**, and name it (for example, `support`).
* Open **Editor**.
2. Define conditionals, limits and other settings.
* You can use [Custom Metadata](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/custom-metadata/) in your conditionals.
3. Configure model nodes.
* Example:
* Node A: Provider OpenAI, Model `o4-mini-high`
* Node B: Provider OpenAI, Model `gpt-4.1`
4. Save a version.
* Click **Save** to save the state. You can always roll back to earlier versions from **Versions**.
* Deploy the version to make it live.
5. Call the route from your code.
* Use the [OpenAI compatible](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) endpoint, and use the route name in place of the model, for example, `dynamic/support`.
---
title: Guardrails · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Guardrails help you deploy AI applications safely by intercepting
and evaluating both user prompts and model responses for harmful content.
Acting as a proxy between your application and model providers (such as
OpenAI, Anthropic, DeepSeek, and others), AI Gateway's Guardrails ensure a
consistent and secure experience across your entire AI ecosystem.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
tags: AI
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/index.md
---
Guardrails help you deploy AI applications safely by intercepting and evaluating both user prompts and model responses for harmful content. Acting as a proxy between your application and [model providers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/) (such as OpenAI, Anthropic, DeepSeek, and others), AI Gateway's Guardrails ensure a consistent and secure experience across your entire AI ecosystem.
Guardrails proactively monitor interactions between users and AI models, giving you:
* **Consistent moderation**: Uniform moderation layer that works across models and providers.
* **Enhanced safety and user trust**: Proactively protect users from harmful or inappropriate interactions.
* **Flexibility and control over allowed content**: Specify which categories to monitor and choose between flagging or outright blocking.
* **Auditing and compliance capabilities**: Receive updates on evolving regulatory requirements with logs of user prompts, model responses, and enforced guardrails.
## Video demo
## How Guardrails work
AI Gateway inspects all interactions in real time by evaluating content against predefined safety parameters. Guardrails work by:
1. Intercepting interactions: AI Gateway proxies requests and responses, sitting between the user and the AI model.
2. Inspecting content:
* User prompts: AI Gateway checks prompts against safety parameters (for example, violence, hate, or sexual content). Based on your settings, prompts can be flagged or blocked before reaching the model.
* Model responses: Once processed, the AI model response is inspected. If hazardous content is detected, it can be flagged or blocked before being delivered to the user.
3. Applying actions: Depending on your configuration, flagged content is logged for review, while blocked content is prevented from proceeding.
## Related resource
* [Cloudflare Blog: Keep AI interactions secure and risk-free with Guardrails in AI Gateway](https://blog.cloudflare.com/guardrails-in-ai-gateway/)
---
title: Rate limiting · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Rate limiting controls the traffic that reaches your application,
which prevents expensive bills and suspicious activity.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/rate-limiting/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/rate-limiting/index.md
---
Rate limiting controls the traffic that reaches your application, which prevents expensive bills and suspicious activity.
## Parameters
You can define rate limits as the number of requests that get sent in a specific time frame. For example, you can limit your application to 100 requests per 60 seconds.
You can also select if you would like a **fixed** or **sliding** rate limiting technique. With rate limiting, we allow a certain number of requests within a window of time. For example, if it is a fixed rate, the window is based on time, so there would be no more than `x` requests in a ten minute window. If it is a sliding rate, there would be no more than `x` requests in the last ten minutes.
To illustrate this, let us say you had a limit of ten requests per ten minutes, starting at 12:00. So the fixed window is 12:00-12:10, 12:10-12:20, and so on. If you sent ten requests at 12:09 and ten requests at 12:11, all 20 requests would be successful in a fixed window strategy. However, they would fail in a sliding window strategy since there were more than ten requests in the last ten minutes.
## Handling rate limits
When your requests exceed the allowed rate, you will encounter rate limiting. This means the server will respond with a `429 Too Many Requests` status code and your request will not be processed.
## Default configuration
* Dashboard
To set the default rate limiting configuration in the dashboard:
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Go to **Settings**.
4. Enable **Rate-limiting**.
5. Adjust the rate, time period, and rate limiting method as desired.
* API
To set the default rate limiting configuration using the API:
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
1. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
2. Using that API token and Account ID, send a [`POST` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/) to create a new Gateway and include a value for the `rate_limiting_interval`, `rate_limiting_limit`, and `rate_limiting_technique`.
This rate limiting behavior will be uniformly applied to all requests for that gateway.
---
title: Unified Billing · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Use the Cloudflare billing to pay for and authenticate your inference requests.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-21T07:17:16.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/unified-billing/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/unified-billing/index.md
---
Unified Billing allows users to connect to various AI providers (such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google AI Studio) and receive a single Cloudflare bill. To use Unified Billing, you must purchase and load credits into your Cloudflare account in the Cloudflare dashboard, which you can then spend with AI Gateway.
## Pre-requisites
* Ensure your Cloudflare account has [sufficient credits loaded](#load-credits).
* Ensure you have [authenticated](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/) your AI Gateway.
## Load credits
To load credits for AI Gateway:
1. In the Cloudflare dashboard, go to the **AI Gateway** page.
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
The **Credits Available** card on the top right shows how many AI gateway credits you have on your account currently.
2. In **Credits Available**, select **Manage**.
3. If your account does not have an available payment method, AI Gateway will prompt you to add a payment method to purchase credits. Add a payment method.
4. Select **Top-up credits**.
5. Add the amount of credits you want to purchase, then select **Confirm and pay**.
### Auto-top up
You can configure AI Gateway to automatically replenish your credits when they fall below a certain threshold. To configure auto top-up:
1. In the Cloudflare dashboard, go to the **AI Gateway** page.
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
2. In **Credits Available**, select **Manage**.
3. Select **Setup auto top-up credits**.
4. Choose a threshold and a recharge amount for auto top-up.
When your balance falls below the set threshold, AI Gateway will automatically apply the auto top-up amount to your account.
## Use Unified Billing
Call any supported provider without passing an API Key. The request will automatically use Cloudflare's key and deduct credits from your account.
For example, you can use the Unified API:
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CLOUDFLARE_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "google-ai-studio/gemini-2.5-pro",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Spend limits
Set spend limits to prevent unexpected charges on your loaded credits. You can define daily, weekly, or monthly limits. When a limit is reached, the AI Gateway automatically stops processing requests until the period resets or you increase the limit.
### Zero Data Retention (ZDR)
Zero Data Retention (ZDR) routes Unified Billing traffic through provider endpoints that do not retain prompts or responses. Enable it with the gateway-level `zdr` setting, which maps to ZDR-capable upstream provider configurations. This setting only applies to Unified Billing requests that use Cloudflare-managed credentials. It does not apply to BYOK or other AI Gateway requests.
ZDR does not control AI Gateway logging. To disable request/response logging in AI Gateway, update the logging settings separately in [Logging](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/).
ZDR is currently supported for:
* [OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/)
* [Anthropic](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/)
If ZDR is enabled for a provider that does not support it, AI Gateway falls back to the standard (non-ZDR) Unified Billing configuration.
#### Default configuration
* Dashboard
To set ZDR as the default for Unified Billing in the dashboard:
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select your gateway.
4. Go to **Settings** and toggle **Zero Data Retention (ZDR)**.
* API
To set ZDR as the default for Unified Billing using the API:
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
2. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
3. Send a [`PUT` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/update/) to update the gateway and include `zdr: true` or `zdr: false` in the request body.
#### Per-request override (`cf-aig-zdr`)
Use the `cf-aig-zdr` header to override the gateway default for a single Unified Billing request. Set it to `true` to force ZDR, or `false` to disable ZDR for the request.
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CLOUDFLARE_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-zdr: true' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Explain Zero Data Retention."
}
]
}'
```
### Supported providers
Unified Billing supports the following AI providers:
* [OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/)
* [Anthropic](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/)
* [Google AI Studio](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/)
* [xAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/grok/)
* [Groq](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/groq/)
---
title: Agents · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Build AI-powered Agents on Cloudflare
lastUpdated: 2025-01-29T20:30:56.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/agents/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/agents/index.md
---
---
title: Workers AI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: This guide will walk you through setting up and deploying a Workers
AI project. You will use Workers, an AI Gateway binding, and a large language
model (LLM) to deploy your first AI-powered application on the Cloudflare
global network.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-29T10:38:24.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/aig-workers-ai-binding/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/aig-workers-ai-binding/index.md
---
This guide will walk you through setting up and deploying a Workers AI project. You will use [Workers](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/), an AI Gateway binding, and a large language model (LLM), to deploy your first AI-powered application on the Cloudflare global network.
## Prerequisites
1. Sign up for a [Cloudflare account](https://dash.cloudflare.com/sign-up/workers-and-pages).
2. Install [`Node.js`](https://docs.npmjs.com/downloading-and-installing-node-js-and-npm).
Node.js version manager
Use a Node version manager like [Volta](https://volta.sh/) or [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm) to avoid permission issues and change Node.js versions. [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/install-and-update/), discussed later in this guide, requires a Node version of `16.17.0` or later.
## 1. Create a Worker Project
You will create a new Worker project using the create-Cloudflare CLI (C3). C3 is a command-line tool designed to help you set up and deploy new applications to Cloudflare.
Create a new project named `hello-ai` by running:
* npm
```sh
npm create cloudflare@latest -- hello-ai
```
* yarn
```sh
yarn create cloudflare hello-ai
```
* pnpm
```sh
pnpm create cloudflare@latest hello-ai
```
Running `npm create cloudflare@latest` will prompt you to install the create-cloudflare package and lead you through setup. C3 will also install [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/), the Cloudflare Developer Platform CLI.
For setup, select the following options:
* For *What would you like to start with?*, choose `Hello World example`.
* For *Which template would you like to use?*, choose `Worker only`.
* For *Which language do you want to use?*, choose `TypeScript`.
* For *Do you want to use git for version control?*, choose `Yes`.
* For *Do you want to deploy your application?*, choose `No` (we will be making some changes before deploying).
This will create a new `hello-ai` directory. Your new `hello-ai` directory will include:
* A "Hello World" Worker at `src/index.ts`.
* A [Wrangler configuration file](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/)
Go to your application directory:
```bash
cd hello-ai
```
## 2. Connect your Worker to Workers AI
You must create an AI binding for your Worker to connect to Workers AI. Bindings allow your Workers to interact with resources, like Workers AI, on the Cloudflare Developer Platform.
To bind Workers AI to your Worker, add the following to the end of your [Wrangler configuration file](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/):
* wrangler.jsonc
```jsonc
{
"ai": {
"binding": "AI"
}
}
```
* wrangler.toml
```toml
[ai]
binding = "AI"
```
Your binding is [available in your Worker code](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/reference/migrate-to-module-workers/#bindings-in-es-modules-format) on [`env.AI`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/runtime-apis/handlers/fetch/).
You will need to have your `gateway id` for the next step. You can learn [how to create an AI Gateway in this tutorial](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/).
## 3. Run an inference task containing AI Gateway in your Worker
You are now ready to run an inference task in your Worker. In this case, you will use an LLM, [`llama-3.1-8b-instruct-fast`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/models/llama-3.1-8b-instruct-fast/), to answer a question. Your gateway ID is found on the dashboard.
Update the `index.ts` file in your `hello-ai` application directory with the following code:
```typescript
export interface Env {
// If you set another name in the [Wrangler configuration file](/workers/wrangler/configuration/) as the value for 'binding',
// replace "AI" with the variable name you defined.
AI: Ai;
}
export default {
async fetch(request, env): Promise {
// Specify the gateway label and other options here
const response = await env.AI.run(
"@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct-fast",
{
prompt: "What is the origin of the phrase Hello, World",
},
{
gateway: {
id: "GATEWAYID", // Use your gateway label here
skipCache: true, // Optional: Skip cache if needed
},
},
);
// Return the AI response as a JSON object
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response), {
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
});
},
} satisfies ExportedHandler;
```
Up to this point, you have created an AI binding for your Worker and configured your Worker to be able to execute the Llama 3.1 model. You can now test your project locally before you deploy globally.
## 4. Develop locally with Wrangler
While in your project directory, test Workers AI locally by running [`wrangler dev`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/commands/#dev):
```bash
npx wrangler dev
```
Workers AI local development usage charges
Using Workers AI always accesses your Cloudflare account in order to run AI models and will incur usage charges even in local development.
You will be prompted to log in after you run `wrangler dev`. When you run `npx wrangler dev`, Wrangler will give you a URL (most likely `localhost:8787`) to review your Worker. After you go to the URL Wrangler provides, you will see a message that resembles the following example:
````json
{
"response": "A fascinating question!\n\nThe phrase \"Hello, World!\" originates from a simple computer program written in the early days of programming. It is often attributed to Brian Kernighan, a Canadian computer scientist and a pioneer in the field of computer programming.\n\nIn the early 1970s, Kernighan, along with his colleague Dennis Ritchie, were working on the C programming language. They wanted to create a simple program that would output a message to the screen to demonstrate the basic structure of a program. They chose the phrase \"Hello, World!\" because it was a simple and recognizable message that would illustrate how a program could print text to the screen.\n\nThe exact code was written in the 5th edition of Kernighan and Ritchie's book \"The C Programming Language,\" published in 1988. The code, literally known as \"Hello, World!\" is as follows:\n\n```
main()
{
printf(\"Hello, World!\");
}
```\n\nThis code is still often used as a starting point for learning programming languages, as it demonstrates how to output a simple message to the console.\n\nThe phrase \"Hello, World!\" has since become a catch-all phrase to indicate the start of a new program or a small test program, and is widely used in computer science and programming education.\n\nSincerely, I'm glad I could help clarify the origin of this iconic phrase for you!"
}
````
## 5. Deploy your AI Worker
Before deploying your AI Worker globally, log in with your Cloudflare account by running:
```bash
npx wrangler login
```
You will be directed to a web page asking you to log in to the Cloudflare dashboard. After you have logged in, you will be asked if Wrangler can make changes to your Cloudflare account. Scroll down and select **Allow** to continue.
Finally, deploy your Worker to make your project accessible on the Internet. To deploy your Worker, run:
```bash
npx wrangler deploy
```
Once deployed, your Worker will be available at a URL like:
```bash
https://hello-ai..workers.dev
```
Your Worker will be deployed to your custom [`workers.dev`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/routing/workers-dev/) subdomain. You can now visit the URL to run your AI Worker.
By completing this tutorial, you have created a Worker, connected it to Workers AI through an AI Gateway binding, and successfully ran an inference task using the Llama 3.1 model.
---
title: Vercel AI SDK · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: >-
The Vercel AI SDK is a TypeScript library for building AI applications. The
SDK supports many different AI providers, tools for streaming completions, and
more.
To use Cloudflare AI Gateway with Vercel AI SDK, you will need to use the
ai-gateway-provider package.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-07T13:57:43.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/vercel-ai-sdk/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/vercel-ai-sdk/index.md
---
The [Vercel AI SDK](https://sdk.vercel.ai/) is a TypeScript library for building AI applications. The SDK supports many different AI providers, tools for streaming completions, and more. To use Cloudflare AI Gateway with Vercel AI SDK, you will need to use the `ai-gateway-provider` package.
## Installation
```bash
npm install ai-gateway-provider
```
## Examples
Make a request to
 OpenAI
Unified
API with
Stored Key (BYOK)
### Fallback Providers
To specify model or provider fallbacks to handle request failures and ensure reliability, you can pass an array of models to the `model` option.
```js
const { text } = await generateText({
model: aigateway([
openai.chat("gpt-5.1"), anthropic("claude-sonnet-4-5")
]),
prompt: 'Write a vegetarian lasagna recipe for 4 people.',
});
```
---
title: AI Gateway Binding Methods · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: This guide provides an overview of how to use the latest Cloudflare
Workers AI Gateway binding methods. You will learn how to set up an AI Gateway
binding, access new methods, and integrate them into your Workers.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-29T10:38:24.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
tags: Bindings
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/worker-binding-methods/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/worker-binding-methods/index.md
---
This guide provides an overview of how to use the latest Cloudflare Workers AI Gateway binding methods. You will learn how to set up an AI Gateway binding, access new methods, and integrate them into your Workers.
## 1. Add an AI Binding to your Worker
To connect your Worker to Workers AI, add the following to your [Wrangler configuration file](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/):
* wrangler.jsonc
```jsonc
{
"ai": {
"binding": "AI"
}
}
```
* wrangler.toml
```toml
[ai]
binding = "AI"
```
This configuration sets up the AI binding accessible in your Worker code as `env.AI`.
If you're using TypeScript, run [`wrangler types`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/commands/#types) whenever you modify your Wrangler configuration file. This generates types for the `env` object based on your bindings, as well as [runtime types](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/languages/typescript/).
## 2. Basic Usage with Workers AI + Gateway
To perform an inference task using Workers AI and an AI Gateway, you can use the following code:
```typescript
const resp = await env.AI.run(
"@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
{
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
{
gateway: {
id: "my-gateway",
},
},
);
```
Additionally, you can access the latest request log ID with:
```typescript
const myLogId = env.AI.aiGatewayLogId;
```
## 3. Access the Gateway Binding
You can access your AI Gateway binding using the following code:
```typescript
const gateway = env.AI.gateway("my-gateway");
```
Once you have the gateway instance, you can use the following methods:
### 3.1. `patchLog`: Send Feedback
The `patchLog` method allows you to send feedback, score, and metadata for a specific log ID. All object properties are optional, so you can include any combination of the parameters:
```typescript
gateway.patchLog("my-log-id", {
feedback: 1,
score: 100,
metadata: {
user: "123",
},
});
```
* **Returns**: `Promise` (Make sure to `await` the request.)
* **Example Use Case**: Update a log entry with user feedback or additional metadata.
### 3.2. `getLog`: Read Log Details
The `getLog` method retrieves details of a specific log ID. It returns an object of type `Promise`. If this type is missing, ensure you have run [`wrangler types`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/languages/typescript/#generate-types).
```typescript
const log = await gateway.getLog("my-log-id");
```
* **Returns**: `Promise`
* **Example Use Case**: Retrieve log information for debugging or analytics.
### 3.3. `getUrl`: Get Gateway URLs
The `getUrl` method allows you to retrieve the base URL for your AI Gateway, optionally specifying a provider to get the provider-specific endpoint.
```typescript
// Get the base gateway URL
const baseUrl = await gateway.getUrl();
// Output: https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/my-account-id/my-gateway/
// Get a provider-specific URL
const openaiUrl = await gateway.getUrl("openai");
// Output: https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/my-account-id/my-gateway/openai
```
* **Parameters**: Optional `provider` (string or `AIGatewayProviders` enum)
* **Returns**: `Promise`
* **Example Use Case**: Dynamically construct URLs for direct API calls or debugging configurations.
#### SDK Integration Examples
The `getUrl` method is particularly useful for integrating with popular AI SDKs:
**OpenAI SDK:**
```typescript
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: "my api key", // defaults to process.env["OPENAI_API_KEY"]
baseURL: await env.AI.gateway("my-gateway").getUrl("openai"),
});
```
**Vercel AI SDK with OpenAI:**
```typescript
import { createOpenAI } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const openai = createOpenAI({
baseURL: await env.AI.gateway("my-gateway").getUrl("openai"),
});
```
**Vercel AI SDK with Anthropic:**
```typescript
import { createAnthropic } from "@ai-sdk/anthropic";
const anthropic = createAnthropic({
baseURL: await env.AI.gateway("my-gateway").getUrl("anthropic"),
});
```
### 3.4. `run`: Universal Requests
The `run` method allows you to execute universal requests. Users can pass either a single universal request object or an array of them. This method supports all AI Gateway providers.
Refer to the [Universal endpoint documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/) for details about the available inputs.
```typescript
const resp = await gateway.run({
provider: "workers-ai",
endpoint: "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
headers: {
authorization: "Bearer my-api-token",
},
query: {
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
});
```
* **Returns**: `Promise`
* **Example Use Case**: Perform a [universal request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/) to any supported provider.
## Conclusion
With these AI Gateway binding methods, you can now:
* Send feedback and update metadata with `patchLog`.
* Retrieve detailed log information using `getLog`.
* Get gateway URLs for direct API access with `getUrl`, making it easy to integrate with popular AI SDKs.
* Execute universal requests to any AI Gateway provider with `run`.
These methods offer greater flexibility and control over your AI integrations, empowering you to build more sophisticated applications on the Cloudflare Workers platform.
---
title: Analytics · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: >-
Your AI Gateway dashboard shows metrics on requests, tokens, caching, errors,
and cost. You can filter these metrics by time.
These analytics help you understand traffic patterns, token consumption, and
potential issues across AI providers. You can
view the following analytics:
lastUpdated: 2025-08-20T18:25:25.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/analytics/index.md
---
Your AI Gateway dashboard shows metrics on requests, tokens, caching, errors, and cost. You can filter these metrics by time. These analytics help you understand traffic patterns, token consumption, and potential issues across AI providers. You can view the following analytics:
* **Requests**: Track the total number of requests processed by AI Gateway.
* **Token Usage**: Analyze token consumption across requests, giving insight into usage patterns.
* **Costs**: Gain visibility into the costs associated with using different AI providers, allowing you to track spending, manage budgets, and optimize resources.
* **Errors**: Monitor the number of errors across the gateway, helping to identify and troubleshoot issues.
* **Cached Responses**: View the percentage of responses served from cache, which can help reduce costs and improve speed.
## View analytics
* Dashboard
To view analytics in the dashboard:
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Make sure you have your gateway selected.
* graphql
You can use GraphQL to query your usage data outside of the AI Gateway dashboard. See the example query below. You will need to use your Cloudflare token when making the request, and change `{account_id}` to match your account tag.
```bash
curl https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/graphql \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer TOKEN \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"query": "query{\n viewer {\n accounts(filter: { accountTag: \"{account_id}\" }) {\n requests: aiGatewayRequestsAdaptiveGroups(\n limit: $limit\n filter: { datetimeHour_geq: $start, datetimeHour_leq: $end }\n orderBy: [datetimeMinute_ASC]\n ) {\n count,\n dimensions {\n model,\n provider,\n gateway,\n ts: datetimeMinute\n }\n \n }\n \n }\n }\n}",
"variables": {
"limit": 1000,
"start": "2023-09-01T10:00:00.000Z",
"end": "2023-09-30T10:00:00.000Z",
"orderBy": "date_ASC"
}
}'
```
---
title: Costs · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Cost metrics are only available for endpoints where the models
return token data and the model name in their responses.
lastUpdated: 2025-05-15T16:26:01.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/costs/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/costs/index.md
---
Cost metrics are only available for endpoints where the models return token data and the model name in their responses.
## Track costs across AI providers
AI Gateway makes it easier to monitor and estimate token based costs across all your AI providers. This can help you:
* Understand and compare usage costs between providers.
* Monitor trends and estimate spend using consistent metrics.
* Apply custom pricing logic to match negotiated rates.
Note
The cost metric is an **estimation** based on the number of tokens sent and received in requests. While this metric can help you monitor and predict cost trends, refer to your provider's dashboard for the most **accurate** cost details.
Caution
Providers may introduce new models or change their pricing. If you notice outdated cost data or are using a model not yet supported by our cost tracking, please [submit a request](https://forms.gle/8kRa73wRnvq7bxL48)
## Custom costs
AI Gateway allows users to set custom costs when operating under special pricing agreements or negotiated rates. Custom costs can be applied at the request level, and when applied, they will override the default or public model costs. For more information on configuration of custom costs, please visit the [Custom Costs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/custom-costs/) configuration page.
---
title: Custom metadata · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Custom metadata in AI Gateway allows you to tag requests with user
IDs or other identifiers, enabling better tracking and analysis of your
requests. Metadata values can be strings, numbers, or booleans, and will
appear in your logs, making it easy to search and filter through your data.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/custom-metadata/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/custom-metadata/index.md
---
Custom metadata in AI Gateway allows you to tag requests with user IDs or other identifiers, enabling better tracking and analysis of your requests. Metadata values can be strings, numbers, or booleans, and will appear in your logs, making it easy to search and filter through your data.
## Key Features
* **Custom Tagging**: Add user IDs, team names, test indicators, and other relevant information to your requests.
* **Enhanced Logging**: Metadata appears in your logs, allowing for detailed inspection and troubleshooting.
* **Search and Filter**: Use metadata to efficiently search and filter through logged requests.
Note
AI Gateway allows you to pass up to five custom metadata entries per request. If more than five entries are provided, only the first five will be saved; additional entries will be ignored. Ensure your custom metadata is limited to five entries to avoid unprocessed or lost data.
## Supported Metadata Types
* String
* Number
* Boolean
Note
Objects are not supported as metadata values.
## Implementations
### Using cURL
To include custom metadata in your request using cURL:
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-metadata: {"team": "AI", "user": 12345, "test":true}' \
--data '{"model": "gpt-4o", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What should I eat for lunch?"}]}'
```
### Using SDK
To include custom metadata in your request using the OpenAI SDK:
```javascript
import OpenAI from "openai";
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
baseURL: "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai",
});
try {
const chatCompletion = await openai.chat.completions.create(
{
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What should I eat for lunch?" }],
max_tokens: 50,
},
{
headers: {
"cf-aig-metadata": JSON.stringify({
user: "JaneDoe",
team: 12345,
test: true
}),
},
}
);
const response = chatCompletion.choices[0].message;
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response));
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
return new Response(e);
}
},
};
```
### Using Binding
To include custom metadata in your request using [Bindings](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/runtime-apis/bindings/):
```javascript
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
const aiResp = await env.AI.run(
'@cf/mistral/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.1',
{ prompt: 'What should I eat for lunch?' },
{ gateway: { id: 'gateway_id', metadata: { "team": "AI", "user": 12345, "test": true} } }
);
return new Response(aiResp);
},
};
```
---
title: Logging · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Logging is a fundamental building block for application
development. Logs provide insights during the early stages of development and
are often critical to understanding issues occurring in production.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-20T18:25:25.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/index.md
---
Logging is a fundamental building block for application development. Logs provide insights during the early stages of development and are often critical to understanding issues occurring in production.
Your AI Gateway dashboard shows logs of individual requests, including the user prompt, model response, provider, timestamp, request status, token usage, cost, and duration. These logs persist, giving you the flexibility to store them for your preferred duration and do more with valuable request data.
By default, each gateway can store up to 10 million logs. You can customize this limit per gateway in your gateway settings to align with your specific requirements. If your storage limit is reached, new logs will stop being saved. To continue saving logs, you must delete older logs to free up space for new logs. To learn more about your plan limits, refer to [Limits](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/limits/).
We recommend using an authenticated gateway when storing logs to prevent unauthorized access and protects against invalid requests that can inflate log storage usage and make it harder to find the data you need. Learn more about setting up an [authenticated gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/).
## Default configuration
Logs, which include metrics as well as request and response data, are enabled by default for each gateway. This logging behavior will be uniformly applied to all requests in the gateway. If you are concerned about privacy or compliance and want to turn log collection off, you can go to settings and opt out of logs. If you need to modify the log settings for specific requests, you can override this setting on a per-request basis.
To change the default log configuration in the dashboard:
1. In the Cloudflare dashboard, go to the **AI Gateway** page.
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
2. Select **Settings**.
3. Change the **Logs** setting to your preference.
## Per-request logging
To override the default logging behavior set in the settings tab, you can define headers on a per-request basis.
### Collect logs (`cf-aig-collect-log`)
The `cf-aig-collect-log` header allows you to bypass the default log setting for the gateway. If the gateway is configured to save logs, the header will exclude the log for that specific request. Conversely, if logging is disabled at the gateway level, this header will save the log for that request.
In the example below, we use `cf-aig-collect-log` to bypass the default setting to avoid saving the log.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-collect-log: false \
--data ' {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is the email address and phone number of user123?"
}
]
}
'
```
## Managing log storage
To manage your log storage effectively, you can:
* Set Storage Limits: Configure a limit on the number of logs stored per gateway in your gateway settings to ensure you only pay for what you need.
* Enable Automatic Log Deletion: Activate the Automatic Log Deletion feature in your gateway settings to automatically delete the oldest logs once the log limit you've set or the default storage limit of 10 million logs is reached. This ensures new logs are always saved without manual intervention.
## How to delete logs
To manage your log storage effectively and ensure continuous logging, you can delete logs using the following methods:
### Automatic Log Deletion
To maintain continuous logging within your gateway's storage constraints, enable Automatic Log Deletion in your Gateway settings. This feature automatically deletes the oldest logs once the log limit you've set or the default storage limit of 10 million logs is reached, ensuring new logs are saved without manual intervention.
### Manual deletion
To manually delete logs through the dashboard, navigate to the Logs tab in the dashboard. Use the available filters such as status, cache, provider, cost, or any other options in the dropdown to refine the logs you wish to delete. Once filtered, select Delete logs to complete the action.
See full list of available filters and their descriptions below:
| Filter category | Filter options | Filter by description |
| - | - | - |
| Status | error, status | error type or status. |
| Cache | cached, not cached | based on whether they were cached or not. |
| Provider | specific providers | the selected AI provider. |
| AI Models | specific models | the selected AI model. |
| Cost | less than, greater than | cost, specifying a threshold. |
| Request type | Universal, Workers AI Binding, WebSockets | the type of request. |
| Tokens | Total tokens, Tokens In, Tokens Out | token count (less than or greater than). |
| Duration | less than, greater than | request duration. |
| Feedback | equals, does not equal (thumbs up, thumbs down, no feedback) | feedback type. |
| Metadata Key | equals, does not equal | specific metadata keys. |
| Metadata Value | equals, does not equal | specific metadata values. |
| Log ID | equals, does not equal | a specific Log ID. |
| Event ID | equals, does not equal | a specific Event ID. |
### API deletion
You can programmatically delete logs using the AI Gateway API. For more comprehensive information on the `DELETE` logs endpoint, check out the [Cloudflare API documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/subresources/logs/methods/delete/).
---
title: OpenTelemetry · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: AI Gateway supports exporting traces to OpenTelemetry-compatible
backends, enabling you to monitor and analyze AI request performance alongside
your existing observability infrastructure.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-20T22:24:40.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/otel-integration/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/otel-integration/index.md
---
AI Gateway supports exporting traces to OpenTelemetry-compatible backends, enabling you to monitor and analyze AI request performance alongside your existing observability infrastructure.
## Overview
The OpenTelemetry (OTEL) integration automatically exports trace spans for AI requests processed through your gateway. These spans include detailed information about:
* Request model and provider
* Token usage (input and output)
* Request prompts and completions
* Cost estimates
* Custom metadata
This integration follows the [OpenTelemetry specification](https://opentelemetry.io/docs/specs/otel/) for distributed tracing and uses the OTLP (OpenTelemetry Protocol) JSON format.
## Configuration
To enable OpenTelemetry tracing for your gateway, configure one or more OTEL exporters in your gateway settings. Each exporter requires:
* **URL**: The endpoint URL of your OTEL collector (must accept OTLP/JSON format)
* **Authorization** (optional): A reference to a secret containing your authorization header value
* **Headers** (optional): Additional custom headers to include in export requests
### Configuration via Dashboard
1. Navigate to your AI Gateway in the Cloudflare dashboard
2. Go to **Settings** tab
3. Add an OTEL exporter with your collector endpoint URL
4. If authentication is required, configure a secret for the authorization header
## Exported Span Attributes
AI Gateway exports spans with the following attributes following the [Semantic Conventions for Gen AI](https://opentelemetry.io/docs/specs/semconv/gen-ai/):
### Standard Attributes
| Attribute | Type | Description |
| - | - | - |
| `gen_ai.request.model` | string | The AI model used for the request |
| `gen_ai.model.provider` | string | The AI provider (e.g., `openai`, `anthropic`) |
| `gen_ai.usage.input_tokens` | int | Number of input tokens consumed |
| `gen_ai.usage.output_tokens` | int | Number of output tokens generated |
| `gen_ai.prompt_json` | string | JSON-encoded prompt/messages sent to the model |
| `gen_ai.completion_json` | string | JSON-encoded completion/response from the model |
| `gen_ai.usage.cost` | double | Estimated cost of the request |
### Custom Metadata
Any custom metadata added to your requests via the `cf-aig-metadata` header will also be included as span attributes. This allows you to correlate traces with user IDs, team names, or other business context.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-metadata: {"user_id": "user123", "team": "engineering"}' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
The above request will include `user_id` and `team` as additional span attributes in the exported trace.
Note
Custom metadata attributes that start with `gen_ai.` are reserved for standard GenAI semantic conventions and will not be added as custom attributes.
## Trace Context Propagation
AI Gateway supports trace context propagation, allowing you to link AI Gateway spans with your application's traces. You can provide trace context using custom headers:
* `cf-aig-otel-trace-id` (optional): A 32-character hex string to use as the trace ID
* `cf-aig-otel-parent-span-id` (optional): A 16-character hex string to use as the parent span ID
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'cf-aig-otel-trace-id: a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6' \
--header 'cf-aig-otel-parent-span-id: a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
```
When these headers are provided, the AI Gateway span will use them to link with your existing trace. If not provided, AI Gateway will generate a new trace ID automatically.
## Common OTEL Backends
AI Gateway's OTEL integration works with any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend that accepts OTLP/JSON format, including:
* [Honeycomb](https://www.honeycomb.io/)
* [Braintrust](https://www.braintrust.dev/docs/integrations/sdk-integrations/opentelemetry)
* [Langfuse](https://langfuse.com/integrations/native/opentelemetry)
Note
We do not support OTLP protobuf format, so providers that use it (e.g., Datadog) will not work with AI Gateway's OTEL integration.
Refer to your observability platform's documentation for the correct OTLP endpoint URL and authentication requirements.
---
title: Audit logs · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Audit logs provide a comprehensive summary of changes made within
your Cloudflare account, including those made to gateways in AI Gateway. This
functionality is available on all plan types, free of charge, and is enabled
by default.
lastUpdated: 2025-09-05T08:34:36.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/audit-logs/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/audit-logs/index.md
---
[Audit logs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/account-security/review-audit-logs/) provide a comprehensive summary of changes made within your Cloudflare account, including those made to gateways in AI Gateway. This functionality is available on all plan types, free of charge, and is enabled by default.
## Viewing Audit Logs
To view audit logs for AI Gateway, in the Cloudflare dashboard, go to the **Audit logs** page.
[Go to **Audit logs**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/audit-log)
For more information on how to access and use audit logs, refer to [review audit logs documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/account-security/review-audit-logs/).
## Logged Operations
The following configuration actions are logged:
| Operation | Description |
| - | - |
| gateway created | Creation of a new gateway. |
| gateway deleted | Deletion of an existing gateway. |
| gateway updated | Edit of an existing gateway. |
## Example Log Entry
Below is an example of an audit log entry showing the creation of a new gateway:
```json
{
"action": {
"info": "gateway created",
"result": true,
"type": "create"
},
"actor": {
"email": "",
"id": "3f7b730e625b975bc1231234cfbec091",
"ip": "fe32:43ed:12b5:526::1d2:13",
"type": "user"
},
"id": "5eaeb6be-1234-406a-87ab-1971adc1234c",
"interface": "UI",
"metadata": {},
"newValue": "",
"newValueJson": {
"cache_invalidate_on_update": false,
"cache_ttl": 0,
"collect_logs": true,
"id": "test",
"rate_limiting_interval": 0,
"rate_limiting_limit": 0,
"rate_limiting_technique": "fixed"
},
"oldValue": "",
"oldValueJson": {},
"owner": {
"id": "1234d848c0b9e484dfc37ec392b5fa8a"
},
"resource": {
"id": "89303df8-1234-4cfa-a0f8-0bd848e831ca",
"type": "ai_gateway.gateway"
},
"when": "2024-07-17T14:06:11.425Z"
}
```
---
title: Limits · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: The following limits apply to gateway configurations, logs, and
related features in Cloudflare's platform.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/limits/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/limits/index.md
---
The following limits apply to gateway configurations, logs, and related features in Cloudflare's platform.
| Feature | Limit |
| - | - |
| [Cacheable request size](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/) | 25 MB per request |
| [Cache TTL](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#cache-ttl-cf-aig-cache-ttl) | 1 month |
| [Custom metadata](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/custom-metadata/) | 5 entries per request |
| [Datasets](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/evaluations/set-up-evaluations/) | 10 per gateway |
| Gateways free plan | 10 per account |
| Gateways paid plan | 20 per account |
| Gateway name length | 64 characters |
| Log storage rate limit | 500 logs per second per gateway |
| Logs stored [paid plan](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing/) | 10 million per gateway 1 |
| Logs stored [free plan](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing/) | 100,000 per account 2 |
| [Log size stored](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/) | 10 MB per log 3 |
| [Logpush jobs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/logpush/) | 4 per account |
| [Logpush size limit](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/logpush/) | 1MB per log |
1 If you have reached 10 million logs stored per gateway, new logs will stop being saved. To continue saving logs, you must delete older logs in that gateway to free up space or create a new gateway. Refer to [Auto Log Cleanup](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/#auto-log-cleanup) for more details on how to automatically delete logs.
2 If you have reached 100,000 logs stored per account, across all gateways, new logs will stop being saved. To continue saving logs, you must delete older logs. Refer to [Auto Log Cleanup](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/#auto-log-cleanup) for more details on how to automatically delete logs.
3 Logs larger than 10 MB will not be stored.
Need a higher limit?
To request an increase to a limit, complete the [Limit Increase Request Form](https://forms.gle/cuXu1QnQCrSNkkaS8). If the limit can be increased, Cloudflare will contact you with next steps.
---
title: Pricing · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: AI Gateway is available to use on all plans.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-10T11:01:10.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing/index.md
---
AI Gateway is available to use on all plans.
AI Gateway's core features available today are offered for free, and all it takes is a Cloudflare account and one line of code to [get started](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/). Core features include: dashboard analytics, caching, and rate limiting.
We will continue to build and expand AI Gateway. Some new features may be additional core features that will be free while others may be part of a premium plan. We will announce these as they become available.
You can monitor your usage in the AI Gateway dashboard.
## Persistent logs
Persistent logs are available on all plans, with a free allocation for both free and paid plans. Charges for additional logs beyond those limits are based on the number of logs stored per month.
### Free allocation and overage pricing
| Plan | Free logs stored | Overage pricing |
| - | - | - |
| Workers Free | 100,000 logs total | N/A - Upgrade to Workers Paid |
| Workers Paid | 1,000,000 logs total | N/A |
Allocations are based on the total logs stored across all gateways. For guidance on managing or deleting logs, please see our [documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging).
## Logpush
Logpush is only available on the Workers Paid plan.
| | Paid plan |
| - | - |
| Requests | 10 million / month, +$0.05/million |
## Fine print
Prices subject to change. If you are an Enterprise customer, reach out to your account team to confirm pricing details.
---
title: Deploy a Worker that connects to OpenAI via AI Gateway · Cloudflare AI
Gateway docs
description: Learn how to deploy a Worker that makes calls to OpenAI through AI Gateway
lastUpdated: 2025-11-14T10:07:26.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
tags: AI,JavaScript
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/deploy-aig-worker/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/deploy-aig-worker/index.md
---
In this tutorial, you will learn how to deploy a Worker that makes calls to OpenAI through AI Gateway. AI Gateway helps you better observe and control your AI applications with more analytics, caching, rate limiting, and logging.
This tutorial uses the most recent v4 OpenAI node library, an update released in August 2023.
## Before you start
All of the tutorials assume you have already completed the [Get started guide](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/get-started/guide/), which gets you set up with a Cloudflare Workers account, [C3](https://github.com/cloudflare/workers-sdk/tree/main/packages/create-cloudflare), and [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/install-and-update/).
## 1. Create an AI Gateway and OpenAI API key
On the AI Gateway page in the Cloudflare dashboard, create a new AI Gateway by clicking the plus button on the top right. You should be able to name the gateway as well as the endpoint. Click on the API Endpoints button to copy the endpoint. You can choose from provider-specific endpoints such as OpenAI, HuggingFace, and Replicate. Or you can use the universal endpoint that accepts a specific schema and supports model fallback and retries.
For this tutorial, we will be using the OpenAI provider-specific endpoint, so select OpenAI in the dropdown and copy the new endpoint.
You will also need an OpenAI account and API key for this tutorial. If you do not have one, create a new OpenAI account and create an API key to continue with this tutorial. Make sure to store your API key somewhere safe so you can use it later.
## 2. Create a new Worker
Create a Worker project in the command line:
* npm
```sh
npm create cloudflare@latest -- openai-aig
```
* yarn
```sh
yarn create cloudflare openai-aig
```
* pnpm
```sh
pnpm create cloudflare@latest openai-aig
```
For setup, select the following options:
* For *What would you like to start with?*, choose `Hello World example`.
* For *Which template would you like to use?*, choose `Worker only`.
* For *Which language do you want to use?*, choose `JavaScript`.
* For *Do you want to use git for version control?*, choose `Yes`.
* For *Do you want to deploy your application?*, choose `No` (we will be making some changes before deploying).
Go to your new open Worker project:
```sh
cd openai-aig
```
Inside of your new openai-aig directory, find and open the `src/index.js` file. You will configure this file for most of the tutorial.
Initially, your generated `index.js` file should look like this:
```js
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
return new Response("Hello World!");
},
};
```
## 3. Configure OpenAI in your Worker
With your Worker project created, we can learn how to make your first request to OpenAI. You will use the OpenAI node library to interact with the OpenAI API. Install the OpenAI node library with `npm`:
* npm
```sh
npm i openai
```
* yarn
```sh
yarn add openai
```
* pnpm
```sh
pnpm add openai
```
In your `src/index.js` file, add the import for `openai` above `export default`:
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
```
Within your `fetch` function, set up the configuration and instantiate your `OpenAIApi` client with the AI Gateway endpoint you created:
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai", // paste your AI Gateway endpoint here
});
},
};
```
To make this work, you need to use [`wrangler secret put`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/commands/#secret-put) to set your `OPENAI_API_KEY`. This will save the API key to your environment so your Worker can access it when deployed. This key is the API key you created earlier in the OpenAI dashboard:
* npm
```sh
npx wrangler secret put OPENAI_API_KEY
```
* yarn
```sh
yarn wrangler secret put OPENAI_API_KEY
```
* pnpm
```sh
pnpm wrangler secret put OPENAI_API_KEY
```
To make this work in local development, create a new file `.dev.vars` in your Worker project and add this line. Make sure to replace `OPENAI_API_KEY` with your own OpenAI API key:
```txt
OPENAI_API_KEY = ""
```
## 4. Make an OpenAI request
Now we can make a request to the OpenAI [Chat Completions API](https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/gpt/chat-completions-api).
You can specify what model you'd like, the role and prompt, as well as the max number of tokens you want in your total request.
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai",
});
try {
const chatCompletion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is a neuron?" }],
max_tokens: 100,
});
const response = chatCompletion.choices[0].message;
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response));
} catch (e) {
return new Response(e);
}
},
};
```
## 5. Deploy your Worker application
To deploy your application, run the `npx wrangler deploy` command to deploy your Worker application:
* npm
```sh
npx wrangler deploy
```
* yarn
```sh
yarn wrangler deploy
```
* pnpm
```sh
pnpm wrangler deploy
```
You can now preview your Worker at \.\.workers.dev.
## 6. Review your AI Gateway
When you go to AI Gateway in your Cloudflare dashboard, you should see your recent request being logged. You can also [tweak your settings](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/) to manage your logs, caching, and rate limiting settings.
---
title: Create your first AI Gateway using Workers AI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: This tutorial guides you through creating your first AI Gateway
using Workers AI on the Cloudflare dashboard.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-09T15:47:46.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/create-first-aig-workers/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/tutorials/create-first-aig-workers/index.md
---
This tutorial guides you through creating your first AI Gateway using Workers AI on the Cloudflare dashboard. The intended audience is beginners who are new to AI Gateway and Workers AI. Creating an AI Gateway enables the user to efficiently manage and secure AI requests, allowing them to utilize AI models for tasks such as content generation, data processing, or predictive analysis with enhanced control and performance.
## Sign up and log in
1. **Sign up**: If you do not have a Cloudflare account, [sign up](https://cloudflare.com/sign-up).
2. **Log in**: Access the Cloudflare dashboard by logging in to the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/login).
## Create gateway
Then, create a new AI Gateway.
* Dashboard
[Go to **AI Gateway**](https://dash.cloudflare.com/?to=/:account/ai/ai-gateway)
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select **Create Gateway**.
4. Enter your **Gateway name**. Note: Gateway name has a 64 character limit.
5. Select **Create**.
* API
To set up an AI Gateway using the API:
1. [Create an API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with the following permissions:
* `AI Gateway - Read`
* `AI Gateway - Edit`
2. Get your [Account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account/find-account-and-zone-ids/).
3. Using that API token and Account ID, send a [`POST` request](https://developers.cloudflare.com/api/resources/ai_gateway/methods/create/) to the Cloudflare API.
## Connect Your AI Provider
1. In the AI Gateway section, select the gateway you created.
2. Select **Workers AI** as your provider to set up an endpoint specific to Workers AI. You will receive an endpoint URL for sending requests.
## Configure Your Workers AI
1. Go to **AI** > **Workers AI** in the Cloudflare dashboard.
2. Select **Use REST API** and follow the steps to create and copy the API token and Account ID.
3. **Send Requests to Workers AI**: Use the provided API endpoint. For example, you can run a model via the API using a curl command. Replace `{account_id}`, `{gateway_id}` and `{cf_api_token}` with your actual account ID and API token:
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/workers-ai/@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {cf_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{"prompt": "What is Cloudflare?"}'
```
The expected output would be similar to :
```bash
{"result":{"response":"I'd be happy to explain what Cloudflare is.\n\nCloudflare is a cloud-based service that provides a range of features to help protect and improve the performance, security, and reliability of websites, applications, and other online services. Think of it as a shield for your online presence!\n\nHere are some of the key things Cloudflare does:\n\n1. **Content Delivery Network (CDN)**: Cloudflare has a network of servers all over the world. When you visit a website that uses Cloudflare, your request is sent to the nearest server, which caches a copy of the website's content. This reduces the time it takes for the content to load, making your browsing experience faster.\n2. **DDoS Protection**: Cloudflare protects against Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. This happens when a website is overwhelmed with traffic from multiple sources to make it unavailable. Cloudflare filters out this traffic, ensuring your site remains accessible.\n3. **Firewall**: Cloudflare acts as an additional layer of security, filtering out malicious traffic and hacking attempts, such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.\n4. **SSL Encryption**: Cloudflare offers free SSL encryption, which secure sensitive information (like passwords, credit card numbers, and browsing data) with an HTTPS connection (the \"S\" stands for Secure).\n5. **Bot Protection**: Cloudflare has an AI-driven system that identifies and blocks bots trying to exploit vulnerabilities or scrape your content.\n6. **Analytics**: Cloudflare provides insights into website traffic, helping you understand your audience and make informed decisions.\n7. **Cybersecurity**: Cloudflare offers advanced security features, such as intrusion protection, DNS filtering, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) protection.\n\nOverall, Cloudflare helps protect against cyber threats, improves website performance, and enhances security for online businesses, bloggers, and individuals who need to establish a strong online presence.\n\nWould you like to know more about a specific aspect of Cloudflare?"},"success":true,"errors":[],"messages":[]}%
```
## View Analytics
Monitor your AI Gateway to view usage metrics.
1. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway** in the dashboard.
2. Select your gateway to view metrics such as request counts, token usage, caching efficiency, errors, and estimated costs. You can also turn on additional configurations like logging and rate limiting.
## Optional - Next steps
To build more with Workers, refer to [Tutorials](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/tutorials/).
If you have any questions, need assistance, or would like to share your project, join the Cloudflare Developer community on [Discord](https://discord.cloudflare.com) to connect with other developers and the Cloudflare team.
---
title: Unified API (OpenAI compat) · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Cloudflare's AI Gateway offers an OpenAI-compatible
/chat/completions endpoint, enabling integration with multiple AI providers
using a single URL. This feature simplifies the integration process, allowing
for seamless switching between different models without significant code
modifications.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-07T13:57:43.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
tags: AI
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/index.md
---
Cloudflare's AI Gateway offers an OpenAI-compatible `/chat/completions` endpoint, enabling integration with multiple AI providers using a single URL. This feature simplifies the integration process, allowing for seamless switching between different models without significant code modifications.
## Endpoint URL
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Replace `{account_id}` and `{gateway_id}` with your Cloudflare account and gateway IDs.
## Parameters
Switch providers by changing the `model` and `apiKey` parameters.
Specify the model using `{provider}/{model}` format. For example:
* `openai/gpt-5-mini`
* `google-ai-studio/gemini-2.5-flash`
* `anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-5`
## Examples
Make a request to
 OpenAI
using
OpenAI JS SDK
with
Stored Key (BYOK)
## Supported Providers
The OpenAI-compatible endpoint supports models from the following providers:
* [Anthropic](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/)
* [OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/)
* [Groq](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/groq/)
* [Mistral](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/mistral/)
* [Cohere](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cohere/)
* [Perplexity](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/perplexity/)
* [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/)
* [Google-AI-Studio](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/)
* [Google Vertex AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/vertex/)
* [xAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/grok/)
* [DeepSeek](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepseek/)
* [Cerebras](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cerebras/)
* [Baseten](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/baseten/)
* [Parallel](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/parallel/)
---
title: Universal Endpoint · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: You can use the Universal Endpoint to contact every provider.
lastUpdated: 2026-01-29T10:38:24.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/universal/index.md
---
Note
It is recommended to use the Dynamic Routes to implement model fallback feature
You can use the Universal Endpoint to contact every provider.
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}
```
AI Gateway offers multiple endpoints for each Gateway you create - one endpoint per provider, and one Universal Endpoint. The Universal Endpoint requires some adjusting to your schema, but supports additional features. Some of these features are, for example, retrying a request if it fails the first time, or configuring a [fallback model/provider](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/fallbacks/).
You can use the Universal endpoint to contact every provider. The payload is expecting an array of message, and each message is an object with the following parameters:
* `provider` : the name of the provider you would like to direct this message to. Can be OpenAI, workers-ai, or any of our supported providers.
* `endpoint`: the pathname of the provider API you’re trying to reach. For example, on OpenAI it can be `chat/completions`, and for Workers AI this might be [`@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/models/llama-3.1-8b-instruct/). See more in the sections that are specific to [each provider](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/).
* `authorization`: the content of the Authorization HTTP Header that should be used when contacting this provider. This usually starts with 'Token' or 'Bearer'.
* `query`: the payload as the provider expects it in their official API.
## cURL example
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id} \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '[
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
},
{
"provider": "openai",
"endpoint": "chat/completions",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {open_ai_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"stream": true,
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
}
]'
```
The above will send a request to Workers AI Inference API, if it fails it will proceed to OpenAI. You can add as many fallbacks as you need, just by adding another JSON in the array.
## WebSockets API beta
The Universal Endpoint can also be accessed via a [WebSockets API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/) which provides a single persistent connection, enabling continuous communication. This API supports all AI providers connected to AI Gateway, including those that do not natively support WebSockets.
## WebSockets example
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/my-account-id/my-gateway/",
{
headers: {
"cf-aig-authorization": "Bearer AI_GATEWAY_TOKEN",
},
},
);
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
type: "universal.create",
request: {
eventId: "my-request",
provider: "workers-ai",
endpoint: "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
headers: {
Authorization: "Bearer WORKERS_AI_TOKEN",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
query: {
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
},
}),
);
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(message.toString());
});
```
## Workers Binding example
* wrangler.jsonc
```jsonc
{
"ai": {
"binding": "AI",
},
}
```
* wrangler.toml
```toml
[ai]
binding = "AI"
```
```typescript
type Env = {
AI: Ai;
};
export default {
async fetch(request: Request, env: Env) {
return env.AI.gateway("my-gateway").run({
provider: "workers-ai",
endpoint: "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
headers: {
authorization: "Bearer my-api-token",
},
query: {
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
});
},
};
```
## Header configuration hierarchy
The Universal Endpoint allows you to set fallback models or providers and customize headers for each provider or request. You can configure headers at three levels:
1. **Provider level**: Headers specific to a particular provider.
2. **Request level**: Headers included in individual requests.
3. **Gateway settings**: Default headers configured in your gateway dashboard.
Since the same settings can be configured in multiple locations, AI Gateway applies a hierarchy to determine which configuration takes precedence:
* **Provider-level headers** override all other configurations.
* **Request-level headers** are used if no provider-level headers are set.
* **Gateway-level settings** are used only if no headers are configured at the provider or request levels.
This hierarchy ensures consistent behavior, prioritizing the most specific configurations. Use provider-level and request-level headers for fine-tuned control, and gateway settings for general defaults.
## Hierarchy example
This example demonstrates how headers set at different levels impact caching behavior:
* **Request-level header**: The `cf-aig-cache-ttl` is set to `3600` seconds, applying this caching duration to the request by default.
* **Provider-level header**: For the fallback provider (OpenAI), `cf-aig-cache-ttl` is explicitly set to `0` seconds, overriding the request-level header and disabling caching for responses when OpenAI is used as the provider.
This shows how provider-level headers take precedence over request-level headers, allowing for granular control of caching behavior.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id} \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-cache-ttl: 3600' \
--data '[
{
"provider": "workers-ai",
"endpoint": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {cloudflare_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"query": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a friendly assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
},
{
"provider": "openai",
"endpoint": "chat/completions",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer {open_ai_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"cf-aig-cache-ttl": "0"
},
"query": {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"stream": true,
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
}
]'
```
---
title: Provider Native · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: "Here is a quick list of the providers we support:"
lastUpdated: 2025-08-27T13:32:22.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: true
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/index.md
---
Here is a quick list of the providers we support:
* [Amazon Bedrock](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/bedrock/)
* [Anthropic](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/)
* [Azure OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/azureopenai/)
* [Baseten](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/baseten/)
* [Cartesia](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cartesia/)
* [Cerebras](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cerebras/)
* [Cohere](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cohere/)
* [Deepgram](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepgram/)
* [DeepSeek](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepseek/)
* [ElevenLabs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/elevenlabs/)
* [Fal AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/fal/)
* [Google AI Studio](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/)
* [Google Vertex AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/vertex/)
* [Groq](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/groq/)
* [HuggingFace](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/huggingface/)
* [Ideogram](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/ideogram/)
* [Mistral AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/mistral/)
* [OpenAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/)
* [OpenRouter](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openrouter/)
* [Parallel](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/parallel/)
* [Perplexity](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/perplexity/)
* [Replicate](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/replicate/)
* [xAI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/grok/)
* [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/)
---
title: WebSockets API · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: "The AI Gateway WebSockets API provides a persistent connection for
AI interactions, eliminating repeated handshakes and reducing latency. This
API is divided into two categories:"
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/index.md
---
The AI Gateway WebSockets API provides a persistent connection for AI interactions, eliminating repeated handshakes and reducing latency. This API is divided into two categories:
* **Realtime APIs** - Designed for AI providers that offer low-latency, multimodal interactions over WebSockets.
* **Non-Realtime APIs** - Supports standard WebSocket communication for AI providers, including those that do not natively support WebSockets.
## When to use WebSockets
WebSockets are long-lived TCP connections that enable bi-directional, real-time and non realtime communication between client and server. Unlike HTTP connections, which require repeated handshakes for each request, WebSockets maintain the connection, supporting continuous data exchange with reduced overhead. WebSockets are ideal for applications needing low-latency, real-time data, such as voice assistants.
## Key benefits
* **Reduced overhead**: Avoid overhead of repeated handshakes and TLS negotiations by maintaining a single, persistent connection.
* **Provider compatibility**: Works with all AI providers in AI Gateway. Even if your chosen provider does not support WebSockets, Cloudflare handles it for you, managing the requests to your preferred AI provider.
## Key differences
| Feature | Realtime APIs | Non-Realtime APIs |
| - | - | - |
| **Purpose** | Enables real-time, multimodal AI interactions for providers that offer dedicated WebSocket endpoints. | Supports WebSocket-based AI interactions with providers that do not natively support WebSockets. |
| **Use Case** | Streaming responses for voice, video, and live interactions. | Text-based queries and responses, such as LLM requests. |
| **AI Provider Support** | [Limited to providers offering real-time WebSocket APIs.](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/#supported-providers) | [All AI providers in AI Gateway.](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/) |
| **Streaming Support** | Providers natively support real-time data streaming. | AI Gateway handles streaming via WebSockets. |
For details on implementation, refer to the next sections:
* [Realtime WebSockets API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/)
* [Non-Realtime WebSockets API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/non-realtime-api/)
---
title: Set up Data Loss Prevention (DLP) · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Add Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to any AI Gateway to start scanning
AI prompts and responses for sensitive data.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-22T21:11:06.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/set-up-dlp/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dlp/set-up-dlp/index.md
---
Add Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to any AI Gateway to start scanning AI prompts and responses for sensitive data.
## Prerequisites
* An existing [AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/)
## Enable DLP for AI Gateway
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select a gateway where you want to enable DLP.
4. Go to the **Firewall** tab.
5. Toggle **Data Loss Prevention (DLP)** to **On**.
## Add DLP policies
After enabling DLP, you can create policies to define how sensitive data should be handled:
1. Under the DLP section, click **Add Policy**.
2. Configure the following fields for each policy:
* **Policy ID**: Enter a unique name for this policy (e.g., "Block-PII-Requests")
* **DLP Profiles**: Select the DLP profiles to check against. AI requests/responses will be checked against each of the selected profiles. Available profiles include:
* **Financial Information** - Credit cards, bank accounts, routing numbers
* **Personal Identifiable Information (PII)** - Names, addresses, phone numbers
* **Government Identifiers** - SSNs, passport numbers, driver's licenses
* **Healthcare Information** - Medical record numbers, patient data
* **Custom Profiles** - Organization-specific data patterns
Note
DLP profiles can be created and managed in the [Zero Trust DLP dashboard](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/data-loss-prevention/dlp-profiles/).
* **Action**: Choose the action to take when any of the selected profiles match:
* **Flag** - Record the detection for audit purposes without blocking
* **Block** - Prevent the request/response from proceeding
* **Check**: Select what to scan:
* **Request** - Scan user prompts sent to AI providers
* **Response** - Scan AI model responses before returning to users
* **Both** - Scan both requests and responses
3. Click **Save** to save your policy configuration.
## Manage DLP policies
You can create multiple DLP policies with different configurations:
* **Add multiple policies**: Click **Add Policy** to create additional policies with different profile combinations or actions
* **Enable/disable policies**: Use the toggle next to each policy to individually enable or disable them without deleting the configuration
* **Edit policies**: Click on any existing policy to modify its settings
* **Save changes**: Always click **Save** after making any changes to apply them
## Test your configuration
After configuring DLP settings:
1. Make a test AI request through your gateway that contains sample sensitive data.
2. Check the **AI Gateway Logs** to verify DLP scanning is working.
3. Review the detection results and adjust profiles or actions as needed.
## Monitor DLP events
### Viewing DLP logs in AI Gateway
DLP events are integrated into your AI Gateway logs:
1. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway** > your gateway > **Logs**.
2. Click on any log entry to view detailed information. For requests where DLP policies were triggered, additional details are included:
* **DLP Action Taken**: Shows whether the action was "Flag" or "Block"
* **DLP Policies Matched**: Detailed information about each policy that matched, including:
* Which DLP profiles triggered within each policy
* Whether the match occurred in the request or response
* Specific entries that matched within each DLP profile
### Filter DLP events
To view only DLP-related requests:
1. On the **Logs** tab, click **Add Filter**.
2. Select **DLP Action** from the filter options.
3. Choose to filter by:
* **FLAG** - Show only requests where sensitive data was flagged
* **BLOCK** - Show only requests that were blocked due to DLP policies
## Error handling
When DLP policies are triggered, your application will receive additional information through response headers and error codes.
### DLP response header
When a request matches DLP policies (whether flagged or blocked), an additional `cf-aig-dlp` header is returned containing detailed information about the match:
#### Header schema
```json
{
"findings": [
{
"profile": {
"context": {},
"entry_ids": ["string"],
"profile_id": "string"
},
"policy_ids": ["string"],
"check": "REQUEST" | "RESPONSE"
}
],
"action": "BLOCK" | "FLAG"
}
```
#### Example header value
```json
{
"findings": [
{
"profile": {
"context": {},
"entry_ids": [
"a1b2c3d4-e5f6-7890-abcd-ef1234567890",
"f7e8d9c0-b1a2-3456-789a-bcdef0123456"
],
"profile_id": "12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef"
},
"policy_ids": ["block_financial_data"],
"check": "REQUEST"
}
],
"action": "BLOCK"
}
```
Use this header to programmatically detect which DLP profiles and entries were matched, which policies triggered, and whether the match occurred in the request or response.
### Error codes for blocked requests
When DLP blocks a request, your application will receive structured error responses:
* **Request blocked by DLP**
* `"code": 2029`
* `"message": "Request content blocked due to DLP policy violations"`
* **Response blocked by DLP**
* `"code": 2030`
* `"message": "Response content blocked due to DLP policy violations"`
Handle these errors in your application:
```js
try {
const res = await env.AI.run('@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct', {
prompt: userInput
}, {
gateway: {id: 'your-gateway-id'}
})
return Response.json(res)
} catch (e) {
if ((e as Error).message.includes('2029')) {
return new Response('Request contains sensitive data and cannot be processed.')
}
if ((e as Error).message.includes('2030')) {
return new Response('AI response was blocked due to sensitive content.')
}
return new Response('AI request failed')
}
```
## Best practices
* **Start with flagging**: Begin with "Flag" actions to understand what data is being detected before implementing blocking
* **Tune confidence levels**: Adjust detection sensitivity based on your false positive tolerance
* **Use appropriate profiles**: Select DLP profiles that match your data protection requirements
* **Monitor regularly**: Review DLP events to ensure policies are working as expected
* **Test thoroughly**: Validate DLP behavior with sample sensitive data before production deployment
## Troubleshooting
### DLP not triggering
* Verify DLP toggle is enabled for your gateway
* Ensure selected DLP profiles are appropriate for your test data
* Confirm confidence levels aren't set too high
### Unexpected blocking
* Review DLP logs to see which profiles triggered
* Consider lowering confidence levels for problematic profiles
* Test with different sample data to understand detection patterns
* Adjust profile selections if needed
For additional support with DLP configuration, refer to the [Cloudflare Data Loss Prevention documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/data-loss-prevention/) or contact your Cloudflare support team.
---
title: JSON Configuration · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: "Instead of using the dashboard editor UI to define the route
graph, you can do it using the REST API. Routes are internally represented
using a simple JSON structure:"
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/json-configuration/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/json-configuration/index.md
---
Instead of using the **dashboard editor UI** to define the route graph, you can do it using the REST API. Routes are internally represented using a simple JSON structure:
```json
{
"id": "",
"name": "",
"elements": []
}
```
## Supported elements
Dynamic routing supports several types of elements that you can combine to create sophisticated routing flows. Each element has specific inputs, outputs, and configuration options.
### Start Element
Marks the beginning of a route. Every route must start with a Start element.
* **Inputs**: None
* **Outputs**:
* `next`: Forwards the unchanged request to the next element
```json
{
"id": "",
"type": "start",
"outputs": {
"next": { "elementId": "" }
}
}
```
### Conditional Element (If/Else)
Evaluates a condition based on request parameters and routes the request accordingly.
* **Inputs**: Request
* **Outputs**:
* `true`: Forwards request to provided element if condition evaluates to true
* `false`: Forwards request to provided element if condition evaluates to false
```json
{
"id": "",
"type": "conditional",
"properties": {
"condition": {
"metadata.plan": { "$eq": "free" } // Supports MongoDB-like operators
}
},
"outputs": {
"true": { "elementId": "" },
"false": { "elementId": "" }
}
}
```
### Percentage Split
Routes requests probabilistically across multiple outputs, useful for A/B testing and gradual rollouts.
* **Inputs**: Request
* **Outputs**: Up to 5 named percentage outputs, plus an optional `else` fallback
* Each output has a fractional probability (must total 100%)
* `else` output handles remaining percentage if other branches don't sum to 100%
```json
{
"id": "",
"type": "percentage",
"outputs": {
"10%": { "elementId": "" },
"50%": { "elementId": "" },
"else": { "elementId": "" }
}
}
```
### Rate/Budget Limit
Apply limits based on request metadata. Supports both count-based and cost-based limits.
* **Inputs**: Request
* **Outputs**:
* `success`: Forwards request to provided element if request is not rate limited
* `fallback`: Optional output for rate-limited requests (route terminates if not provided)
**Properties**:
* `limitType`: "count" or "cost"
* `key`: Request field to use for rate limiting (e.g. "metadata.user\_id")
* `limit`: Maximum allowed requests/cost
* `interval`: Time window in seconds
* `technique`: "sliding" or "fixed" window
```json
{
"id": "",
"type": "rate_limit",
"properties": {
"limitType": "count",
"key": "metadata.user_id",
"limit": 100,
"interval": 3600,
"technique": "sliding"
},
"outputs": {
"success": { "elementId": "node_model_workers_ai" },
"fallback": { "elementId": "node_model_openai_mini" }
}
}
```
### Model
Executes inference using a specified model and provider with configurable timeout and retry settings.
* **Inputs**: Request
* **Outputs**:
* `success`: Forwards request to provided element if model successfully starts streaming a response
* `fallback`: Optional output if model fails after all retries or times out
**Properties**:
* `provider`: AI provider (e.g. "openai", "anthropic")
* `model`: Specific model name
* `timeout`: Request timeout in milliseconds
* `retries`: Number of retry attempts
```json
{
"id": "",
"type": "model",
"properties": {
"provider": "openai",
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"timeout": 60000,
"retries": 4
},
"outputs": {
"success": { "elementId": "" },
"fallback": { "elementId": "" }
}
}
```
### End element
Marks the end of a route. Returns the last successful model response, or an error if no model response was generated.
* **Inputs**: Request
* **Outputs**: None
```json
{
"id": "",
"type": "end"
}
```
---
title: Using a dynamic route · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: The response from a dynamic route is the same as the response from
a model. There is additional metadata used to notify the model and provider
used, you can check the following headers
lastUpdated: 2026-01-21T09:55:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/usage/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/dynamic-routing/usage/index.md
---
Warning
Ensure your gateway has [authentication](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/authentication/) turned on and you have your upstream providers keys stored with [BYOK](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/).
## Examples
### OpenAI SDK
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const cloudflareToken = "CF_AIG_TOKEN";
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/compat`;
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: cloudflareToken,
baseURL,
});
try {
const model = "dynamic/";
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: "What is a neuron?" }];
const chatCompletion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages,
});
const response = chatCompletion.choices[0].message;
console.log(response);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
```
### Fetch
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "dynamic/",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Workers
```ts
export interface Env {
AI: Ai;
}
export default {
async fetch(request: Request, env: Env) {
const response = await env.AI.gateway("default").run({
provider: "compat",
endpoint: "chat/completion",
headers: {},
query: {
model: "dynamic/",
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: "What is Cloudflare?",
},
],
},
});
return Response(response);
},
};
```
## Response Metadata
The response from a dynamic route is the same as the response from a model. There is additional metadata used to notify the model and provider used, you can check the following headers
* `cf-aig-model` - The model used
* `cf-aig-provider` - The slug of provider used
---
title: Set up Guardrails · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Add Guardrails to any gateway to start evaluating and potentially
modifying responses.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/set-up-guardrail/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/set-up-guardrail/index.md
---
Add Guardrails to any gateway to start evaluating and potentially modifying responses.
1. Log into the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com/) and select your account.
2. Go to **AI** > **AI Gateway**.
3. Select a gateway.
4. Go to **Guardrails**.
5. Switch the toggle to **On**.
6. To customize categories, select **Change** > **Configure specific categories**.
7. Update your choices for how Guardrails works on specific prompts or responses (**Flag**, **Ignore**, **Block**).
* For **Prompts**: Guardrails will evaluate and transform incoming prompts based on your security policies.
* For **Responses**: Guardrails will inspect the model's responses to ensure they meet your content and formatting guidelines.
8. Select **Save**.
Usage considerations
For additional details about how to implement Guardrails, refer to [Usage considerations](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/usage-considerations/).
## Viewing Guardrail results in Logs
After enabling Guardrails, you can monitor results through **AI Gateway Logs** in the Cloudflare dashboard. Guardrail logs are marked with a **green shield icon**, and each logged request includes an `eventID`, which links to its corresponding Guardrail evaluation log(s) for easy tracking. Logs are generated for all requests, including those that **pass** Guardrail checks.
## Error handling and blocked requests
When a request is blocked by guardrails, you will receive a structured error response. These indicate whether the issue occurred with the prompt or the model response. Use error codes to differentiate between prompt versus response violations.
* **Prompt blocked**
* `"code": 2016`
* `"message": "Prompt blocked due to security configurations"`
* **Response blocked**
* `"code": 2017`
* `"message": "Response blocked due to security configurations"`
You should catch these errors in your application logic and implement error handling accordingly.
For example, when using [Workers AI with a binding](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/aig-workers-ai-binding/):
```js
try {
const res = await env.AI.run('@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct', {
prompt: "how to build a gun?"
}, {
gateway: {id: 'gateway_id'}
})
return Response.json(res)
} catch (e) {
if ((e as Error).message.includes('2016')) {
return new Response('Prompt was blocked by guardrails.')
}
if ((e as Error).message.includes('2017')) {
return new Response('Response was blocked by guardrails.')
}
return new Response('Unknown AI error')
}
```
---
title: Supported model types · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: "AI Gateway's Guardrails detects the type of AI model being used
and applies safety checks accordingly:"
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/supported-model-types/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/supported-model-types/index.md
---
AI Gateway's Guardrails detects the type of AI model being used and applies safety checks accordingly:
* **Text generation models**: Both prompts and responses are evaluated.
* **Embedding models**: Only the prompt is evaluated, as the response consists of numerical embeddings, which are not meaningful for moderation.
* **Unknown models**: If the model type cannot be determined, only the prompt is evaluated, while the response bypass Guardrails.
Note
Guardrails does not yet support streaming responses. Support for streaming is planned for a future update.
---
title: Usage considerations · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Guardrails currently uses Llama Guard 3 8B on Workers AI to perform
content evaluations. The underlying model may be updated in the future, and we
will reflect those changes within Guardrails.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/usage-considerations/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/guardrails/usage-considerations/index.md
---
Guardrails currently uses [Llama Guard 3 8B](https://ai.meta.com/research/publications/llama-guard-llm-based-input-output-safeguard-for-human-ai-conversations/) on [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/) to perform content evaluations. The underlying model may be updated in the future, and we will reflect those changes within Guardrails.
Since Guardrails runs on Workers AI, enabling it incurs usage on Workers AI. You can monitor usage through the Workers AI Dashboard.
## Additional considerations
* **Model availability**: If at least one hazard category is set to `block`, but AI Gateway is unable to receive a response from Workers AI, the request will be blocked. Conversely, if a hazard category is set to `flag` and AI Gateway cannot obtain a response from Workers AI, the request will proceed without evaluation. This approach prioritizes availability, allowing requests to continue even when content evaluation is not possible.
* **Latency impact**: Enabling Guardrails adds some latency. Enabling Guardrails introduces additional latency to requests. Typically, evaluations using Llama Guard 3 8B on Workers AI add approximately 500 milliseconds per request. However, larger requests may experience increased latency, though this increase is not linear. Consider this when balancing safety and performance.
* **Handling long content**: When evaluating long prompts or responses, Guardrails automatically segments the content into smaller chunks, processing each through separate Guardrail requests. This approach ensures comprehensive moderation but may result in increased latency for longer inputs.
* **Supported languages**: Llama Guard 3.3 8B supports content safety classification in the following languages: English, French, German, Hindi, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, and Thai.
* **Streaming support**: Streaming is not supported when using Guardrails.
Note
Llama Guard is provided as-is without any representations, warranties, or guarantees. Any rules or examples contained in blogs, developer docs, or other reference materials are provided for informational purposes only. You acknowledge and understand that you are responsible for the results and outcomes of your use of AI Gateway.
---
title: Workers Logpush · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: >-
AI Gateway allows you to securely export logs to an external storage location,
where you can decrypt and process them.
You can toggle Workers Logpush on and off in the Cloudflare dashboard
settings. This product is available on the Workers Paid plan. For pricing
information, refer to Pricing.
lastUpdated: 2025-07-24T13:05:17.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/logpush/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/observability/logging/logpush/index.md
---
AI Gateway allows you to securely export logs to an external storage location, where you can decrypt and process them. You can toggle Workers Logpush on and off in the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) settings. This product is available on the Workers Paid plan. For pricing information, refer to [Pricing](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/reference/pricing).
This guide explains how to set up Workers Logpush for AI Gateway, generate an RSA key pair for encryption, and decrypt the logs once they are received.
You can store up to 10 million logs per gateway. If your limit is reached, new logs will stop being saved and will not be exported through Workers Logpush. To continue saving and exporting logs, you must delete older logs to free up space for new logs. Workers Logpush has a limit of 4 jobs and a maximum request size of 1 MB per log.
Note
To export logs using Workers Logpush, you must have logs turned on for the gateway.
Need a higher limit?
To request an increase to a limit, complete the [Limit Increase Request Form](https://forms.gle/cuXu1QnQCrSNkkaS8). If the limit can be increased, Cloudflare will contact you with next steps.
## How logs are encrypted
We employ a hybrid encryption model efficiency and security. Initially, an AES key is generated for each log. This AES key is what actually encrypts the bulk of your data, chosen for its speed and security in handling large datasets efficiently.
Now, for securely sharing this AES key, we use RSA encryption. Here's what happens: the AES key, although lightweight, needs to be transmitted securely to the recipient. We encrypt this key with the recipient's RSA public key. This step leverages RSA's strength in secure key distribution, ensuring that only someone with the corresponding RSA private key can decrypt and use the AES key.
Once encrypted, both the AES-encrypted data and the RSA-encrypted AES key are sent together. Upon arrival, the recipient's system uses the RSA private key to decrypt the AES key. With the AES key now accessible, it is straightforward to decrypt the main data payload.
This method combines the best of both worlds: the efficiency of AES for data encryption with the secure key exchange capabilities of RSA, ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and performance are all optimally maintained throughout the data lifecycle.
## Setting up Workers Logpush
To configure Workers Logpush for AI Gateway, follow these steps:
## 1. Generate an RSA key pair locally
You need to generate a key pair to encrypt and decrypt the logs. This script will output your RSA privateKey and publicKey. Keep the private key secure, as it will be used to decrypt the logs. Below is a sample script to generate the keys using Node.js and OpenSSL.
* JavaScript
```js
const crypto = require("crypto");
const { privateKey, publicKey } = crypto.generateKeyPairSync("rsa", {
modulusLength: 4096,
publicKeyEncoding: {
type: "spki",
format: "pem",
},
privateKeyEncoding: {
type: "pkcs8",
format: "pem",
},
});
console.log(publicKey);
console.log(privateKey);
```
Run the script by executing the below code on your terminal. Replace `file name` with the name of your JavaScript file.
```bash
node {file name}
```
* OpenSSL
1. Generate private key: Use the following command to generate a RSA private key:
```bash
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out private_key.pem -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096
```
2. Generate public key: After generating the private key, you can extract the corresponding public key using:
```bash
openssl rsa -pubout -in private_key.pem -out public_key.pem
```
## 2. Upload public key to gateway settings
Once you have generated the key pair, upload the public key to your AI Gateway settings. This key will be used to encrypt your logs. In order to enable Workers Logpush, you will need logs enabled for that gateway.
## 3. Set up Logpush
To set up Logpush, refer to [Logpush](https://developers.cloudflare.com/logs/logpush/) documentation.
## 4. Receive encrypted logs
After configuring Workers Logpush, logs will be sent encrypted using the public key you uploaded. To access the data, you will need to decrypt it using your private key. The logs will be sent to the object storage provider that you have selected.
## 5. Decrypt logs
To decrypt the encrypted log bodies and metadata from AI Gateway, you can use the following Node.js script or OpenSSL:
* JavaScript
To decrypt the encrypted log bodies and metadata from AI Gateway, download the logs to a folder, in this case its named `my_log.log.gz`.
Then copy this JavaScript file into the same folder and place your private key in the top variable.
```js
const privateKeyStr = `-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
....
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----`;
const crypto = require("crypto");
const privateKey = crypto.createPrivateKey(privateKeyStr);
const fs = require("fs");
const zlib = require("zlib");
const readline = require("readline");
async function importAESGCMKey(keyBuffer) {
try {
// Ensure the key length is valid for AES
if ([128, 192, 256].includes(256)) {
return await crypto.webcrypto.subtle.importKey(
"raw",
keyBuffer,
{
name: "AES-GCM",
length: 256,
},
true, // Whether the key is extractable (true in this case to allow for export later if needed)
["encrypt", "decrypt"], // Use for encryption and decryption
);
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid AES key length. Must be 128, 12, or 256 bits.");
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to import key:", error);
throw error;
}
}
async function decryptData(encryptedData, aesKey, iv) {
const decryptedData = await crypto.subtle.decrypt(
{ name: "AES-GCM", iv: iv },
aesKey,
encryptedData,
);
return new TextDecoder().decode(decryptedData);
}
async function decryptBase64(privateKey, data) {
if (data.key === undefined) {
return data;
}
const aesKeyBuf = crypto.privateDecrypt(
{
key: privateKey,
oaepHash: "SHA256",
},
Buffer.from(data.key, "base64"),
);
const aesKey = await importAESGCMKey(aesKeyBuf);
const decryptedData = await decryptData(
Buffer.from(data.data, "base64"),
aesKey,
Buffer.from(data.iv, "base64"),
);
return decryptedData.toString();
}
async function run() {
let lineReader = readline.createInterface({
input: fs.createReadStream("my_log.log.gz").pipe(zlib.createGunzip()),
});
lineReader.on("line", async (line) => {
line = JSON.parse(line);
const { Metadata, RequestBody, ResponseBody, ...remaining } = line;
console.log({
...remaining,
Metadata: await decryptBase64(privateKey, Metadata),
RequestBody: await decryptBase64(privateKey, RequestBody),
ResponseBody: await decryptBase64(privateKey, ResponseBody),
});
console.log("--");
});
}
run();
```
Run the script by executing the below code on your terminal. Replace `file name` with the name of your JavaScript file.
```bash
node {file name}
```
The script reads the encrypted log file `(my_log.log.gz)`, decrypts the metadata, request body, and response body, and prints the decrypted data. Ensure you replace the `privateKey` variable with your actual private RSA key that you generated in step 1.
* OpenSSL
1. Decrypt the encrypted log file using the private key.
Assuming that the logs were encrypted with the public key (for example `public_key.pem`), you can use the private key (`private_key.pem`) to decrypt the log file.
For example, if the encrypted logs are in a file named `encrypted_logs.bin`, you can decrypt it like this:
```bash
openssl rsautl -decrypt -inkey private_key.pem -in encrypted_logs.bin -out decrypted_logs.txt
```
* `-decrypt` tells OpenSSL that we want to decrypt the file.
* `-inkey private_key.pem` specifies the private key that will be used to decrypt the logs.
* `-in encrypted_logs.bin` is the encrypted log file.
* `-out decrypted_logs.txt`decrypted logs will be saved into this file.
1. View the decrypted logs Once decrypted, you can view the logs by simply running:
```bash
cat decrypted_logs.txt
```
This command will output the decrypted logs to the terminal.
---
title: Anthropic · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Anthropic helps build reliable, interpretable, and steerable AI systems.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-25T12:59:29.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/anthropic/index.md
---
[Anthropic](https://www.anthropic.com/) helps build reliable, interpretable, and steerable AI systems.
## Endpoint
**Base URL**
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/anthropic
```
## Examples
### cURL
With API Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/anthropic/v1/messages \
--header 'x-api-key: {anthropic_api_key}' \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'anthropic-version: 2023-06-01' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "claude-sonnet-4-5",
"max_tokens": 1024,
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Cloudflare?"}
]
}'
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/anthropic/v1/messages \
--header 'x-api-key: {anthropic_api_key}' \
--header 'anthropic-version: 2023-06-01' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "claude-sonnet-4-5",
"max_tokens": 1024,
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Cloudflare?"}
]
}'
```
With Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/anthropic/v1/messages \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'anthropic-version: 2023-06-01' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "claude-sonnet-4-5",
"max_tokens": 1024,
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Cloudflare?"}
]
}'
```
### Anthropic SDK
With Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```js
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{accountId}/{gatewayId}/anthropic`;
const anthropic = new Anthropic({
apiKey: "{ANTHROPIC_API_KEY}",
baseURL,
defaultHeaders: {
Authorization: `Bearer {cf_api_token}`,
},
});
const message = await anthropic.messages.create({
model: "claude-sonnet-4-5",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }],
max_tokens: 1024,
});
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```js
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{accountId}/{gatewayId}/anthropic`;
const anthropic = new Anthropic({
apiKey: "{ANTHROPIC_API_KEY}",
baseURL,
});
const message = await anthropic.messages.create({
model: "claude-sonnet-4-5",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }],
max_tokens: 1024,
});
```
With Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```js
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{accountId}/{gatewayId}/anthropic`;
const anthropic = new Anthropic({
baseURL,
defaultHeaders: {
Authorization: `Bearer {cf_api_token}`,
},
});
const message = await anthropic.messages.create({
model: "claude-sonnet-4-5",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }],
max_tokens: 1024,
});
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Anthropic models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "anthropic/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Azure OpenAI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Azure OpenAI allows you apply natural language algorithms on your data.
lastUpdated: 2025-12-16T12:18:45.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/azureopenai/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/azureopenai/index.md
---
[Azure OpenAI](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/products/ai-services/openai-service/) allows you apply natural language algorithms on your data.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/azure-openai/{resource_name}/{deployment_name}
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Azure OpenAI, you will need:
* AI Gateway account ID
* AI Gateway gateway name
* Azure OpenAI API key
* Azure OpenAI resource name
* Azure OpenAI deployment name (aka model name)
## URL structure
Your new base URL will use the data above in this structure: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/azure-openai/{resource_name}/{deployment_name}`. Then, you can append your endpoint and api-version at the end of the base URL, like `.../chat/completions?api-version=2023-05-15`.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl 'https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway}/azure-openai/{resource_name}/{deployment_name}/chat/completions?api-version=2023-05-15' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'api-key: {azure_api_key}' \
--data '{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use `openai` JavaScript SDK
```js
import { AzureOpenAI } from "openai";
const azure_openai = new AzureOpenAI({
apiKey: "{azure_api_key}",
baseURL: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway}/azure-openai/{resource_name}/`,
apiVersion: "2023-05-15",
defaultHeaders: { "cf-aig-authorization": "{cf-api-token}" }, // if authenticated
});
const result = await azure_openai.chat.completions.create({
model: '{deployment_name}',
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "Hello" }],
});
```
---
title: Baseten · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Baseten provides infrastructure for building and deploying machine
learning models at scale. Baseten offers access to various language models
through a unified chat completions API.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-25T09:00:21.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/baseten/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/baseten/index.md
---
[Baseten](https://www.baseten.co/) provides infrastructure for building and deploying machine learning models at scale. Baseten offers access to various language models through a unified chat completions API.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/baseten
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Baseten, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Baseten API token.
* The name of the Baseten model you want to use.
## OpenAI-compatible chat completions API
Baseten provides an OpenAI-compatible chat completions API for supported models.
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/baseten/v1/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {baseten_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "openai/gpt-oss-120b",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use OpenAI SDK with JavaScript
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const apiKey = "{baseten_api_token}";
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/baseten`;
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey,
baseURL,
});
const model = "openai/gpt-oss-120b";
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }];
const chatCompletion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages,
});
console.log(chatCompletion);
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Baseten models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "baseten/{model}"
}
```
## Model-specific endpoints
For models that don't use the OpenAI-compatible API, you can access them through their specific model endpoints.
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/baseten/model/{model_id} \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {baseten_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"prompt": "What is Cloudflare?",
"max_tokens": 100
}'
```
### Use with JavaScript
```js
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const basetenApiToken = "{baseten_api_token}";
const modelId = "{model_id}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/baseten`;
const response = await fetch(`${baseURL}/model/${modelId}`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Authorization": `Bearer ${basetenApiToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
prompt: "What is Cloudflare?",
max_tokens: 100,
}),
});
const result = await response.json();
console.log(result);
```
---
title: Amazon Bedrock · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Amazon Bedrock allows you to build and scale generative AI
applications with foundation models.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-04T19:27:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/bedrock/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/bedrock/index.md
---
[Amazon Bedrock](https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/) allows you to build and scale generative AI applications with foundation models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/aws-bedrock`
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Amazon Bedrock, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Amazon Bedrock API token.
* The name of the Amazon Bedrock model you want to use.
## Make a request
When making requests to Amazon Bedrock, replace `https://bedrock-runtime.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/` in the URL you're currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/aws-bedrock/bedrock-runtime/us-east-1/`, then add the model you want to run at the end of the URL.
With Bedrock, you will need to sign the URL before you make requests to AI Gateway. You can try using the [`aws4fetch`](https://github.com/mhart/aws4fetch) SDK.
## Examples
### Use `aws4fetch` SDK with TypeScript
```typescript
import { AwsClient } from "aws4fetch";
interface Env {
accessKey: string;
secretAccessKey: string;
}
export default {
async fetch(
request: Request,
env: Env,
ctx: ExecutionContext,
): Promise {
// replace with your configuration
const cfAccountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayName = "{gateway_id}";
const region = "us-east-1";
// added as secrets (https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/secrets/)
const accessKey = env.accessKey;
const secretKey = env.secretAccessKey;
const awsClient = new AwsClient({
accessKeyId: accessKey,
secretAccessKey: secretKey,
region: region,
service: "bedrock",
});
const requestBodyString = JSON.stringify({
inputText: "What does ethereal mean?",
});
const stockUrl = new URL(
`https://bedrock-runtime.${region}.amazonaws.com/model/amazon.titan-embed-text-v1/invoke`,
);
const headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
};
// sign the original request
const presignedRequest = await awsClient.sign(stockUrl.toString(), {
method: "POST",
headers: headers,
body: requestBodyString,
});
// Gateway Url
const gatewayUrl = new URL(
`https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${cfAccountId}/${gatewayName}/aws-bedrock/bedrock-runtime/${region}/model/amazon.titan-embed-text-v1/invoke`,
);
// make the request through the gateway url
const response = await fetch(gatewayUrl, {
method: "POST",
headers: presignedRequest.headers,
body: requestBodyString,
});
if (
response.ok &&
response.headers.get("content-type")?.includes("application/json")
) {
const data = await response.json();
return new Response(JSON.stringify(data));
}
return new Response("Invalid response", { status: 500 });
},
};
```
---
title: Cartesia · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Cartesia provides advanced text-to-speech services with
customizable voice models.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cartesia/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cartesia/index.md
---
[Cartesia](https://docs.cartesia.ai/) provides advanced text-to-speech services with customizable voice models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cartesia
```
## URL Structure
When making requests to Cartesia, replace `https://api.cartesia.ai/v1` in the URL you are currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cartesia`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Cartesia, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Cartesia API token.
* The model ID and voice ID for the Cartesia voice model you want to use.
## Example
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cartesia/tts/bytes \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Cartesia-Version: 2024-06-10' \
--header 'X-API-Key: {cartesia_api_token}' \
--data '{
"transcript": "Welcome to Cloudflare - AI Gateway!",
"model_id": "sonic-english",
"voice": {
"mode": "id",
"id": "694f9389-aac1-45b6-b726-9d9369183238"
},
"output_format": {
"container": "wav",
"encoding": "pcm_f32le",
"sample_rate": 44100
}
}
```
---
title: Cerebras · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Cerebras offers developers a low-latency solution for AI model inference.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-27T13:32:22.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cerebras/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cerebras/index.md
---
[Cerebras](https://inference-docs.cerebras.ai/) offers developers a low-latency solution for AI model inference.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cerebras
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Cerebras, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Cerebras API token.
* The name of the Cerebras model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cerebras/chat/completions \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer CEREBRAS_TOKEN' \
--data '{
"model": "llama3.1-8b",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Cerebras models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "cerebras/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Cohere · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Cohere build AI models designed to solve real-world business challenges.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cohere/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/cohere/index.md
---
[Cohere](https://cohere.com/) build AI models designed to solve real-world business challenges.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cohere
```
## URL structure
When making requests to [Cohere](https://cohere.com/), replace `https://api.cohere.ai/v1` in the URL you're currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cohere`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Cohere, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Cohere API token.
* The name of the Cohere model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cohere/v1/chat \
--header 'Authorization: Token {cohere_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"chat_history": [
{"role": "USER", "message": "Who discovered gravity?"},
{"role": "CHATBOT", "message": "The man who is widely credited with discovering gravity is Sir Isaac Newton"}
],
"message": "What year was he born?",
"connectors": [{"id": "web-search"}]
}'
```
### Use Cohere SDK with Python
If using the [`cohere-python-sdk`](https://github.com/cohere-ai/cohere-python), set your endpoint like this:
```js
import cohere
import os
api_key = os.getenv('API_KEY')
account_id = '{account_id}'
gateway_id = '{gateway_id}'
base_url = f"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/cohere/v1"
co = cohere.Client(
api_key=api_key,
base_url=base_url,
)
message = "hello world!"
model = "command-r-plus"
chat = co.chat(
message=message,
model=model
)
print(chat)
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Cohere models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "cohere/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Deepgram · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Deepgram provides Voice AI APIs for speech-to-text, text-to-speech,
and voice agents.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-03T18:39:09.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepgram/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepgram/index.md
---
[Deepgram](https://developers.deepgram.com/home) provides Voice AI APIs for speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and voice agents.
Note
Deepgram is also available through Workers AI, see [Deepgram Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/#deepgram-workers-ai).
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepgram
```
## URL Structure
When making requests to Deepgram, replace `https://api.deepgram.com/` in the URL you are currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepgram/`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Deepgram, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Deepgram API token.
## Example
### SDK
```ts
import { createClient, LiveTranscriptionEvents } from "@deepgram/sdk";
const deepgram = createClient("{deepgram_api_key}", {
global: {
websocket: {
options: {
url: "wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepgram/",
_nodeOnlyHeaders: {
"cf-aig-authorization": "Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}"
}
}
}
}
});
const connection = deepgram.listen.live({
model: "nova-3",
language: "en-US",
smart_format: true,
});
connection.send(...);
```
---
title: DeepSeek · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: DeepSeek helps you build quickly with DeepSeek's advanced AI models.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepseek/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/deepseek/index.md
---
[DeepSeek](https://www.deepseek.com/) helps you build quickly with DeepSeek's advanced AI models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepseek
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to DeepSeek, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active DeepSeek AI API token.
* The name of the DeepSeek AI model you want to use.
## URL structure
Your new base URL will use the data above in this structure:
`https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepseek/`.
You can then append the endpoint you want to hit, for example: `chat/completions`.
So your final URL will come together as:
`https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepseek/chat/completions`.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepseek/chat/completions \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer DEEPSEEK_TOKEN' \
--data '{
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use DeepSeek with JavaScript
If you are using the OpenAI SDK, you can set your endpoint like this:
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: env.DEEPSEEK_TOKEN,
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/deepseek",
});
try {
const chatCompletion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "deepseek-chat",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }],
});
const response = chatCompletion.choices[0].message;
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response));
} catch (e) {
return new Response(e);
}
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access DeepSeek models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "deepseek/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Fal AI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Fal AI provides access to 600+ production-ready generative media
models through a single, unified API. The service offers the world's largest
collection of open image, video, voice, and audio generation models, all
accessible with one line of code.
lastUpdated: 2025-09-22T08:12:39.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/fal/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/fal/index.md
---
[Fal AI](https://fal.ai/) provides access to 600+ production-ready generative media models through a single, unified API. The service offers the world's largest collection of open image, video, voice, and audio generation models, all accessible with one line of code.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/fal
```
## URL structure
When making requests to Fal AI, replace `https://fal.run` in the URL you're currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/fal`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Fal AI, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Fal AI API token.
* The name of the Fal AI model you want to use.
## Default synchronous API
By default, requests to the Fal AI endpoint will hit the synchronous API at `https://fal.run/`.
### cURL example
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/fal/fal-ai/fast-sdxl \
--header 'Authorization: Key {fal_ai_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"prompt": "Make an image of a cat flying an aeroplane"
}'
```
## Custom target URLs
If you need to hit a different target URL, you can supply the entire Fal target URL in the `x-fal-target-url` header.
### cURL example with custom target URL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/fal \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {fal_ai_token}' \
--header 'x-fal-target-url: https://queue.fal.run/fal-ai/bytedance/seedream/v4/edit' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"prompt": "Dress the model in the clothes and hat. Add a cat to the scene and change the background to a Victorian era building.",
"image_urls": [
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_1.png",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_2.png",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_3.png",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_4.png"
]
}'
```
## WebSocket API
Fal AI also supports real-time interactions through WebSockets. For WebSocket connections and examples, see the [Realtime WebSockets API documentation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/#fal-ai).
## JavaScript SDK integration
The `x-fal-target-url` format is compliant with the Fal SDKs, so AI Gateway can be easily passed as a `proxyUrl` in the SDKs.
### JavaScript SDK example
```js
import { fal } from "@fal-ai/client";
fal.config({
credentials: "{fal_ai_token}", // OR pass a cloudflare api token if using BYOK on AI Gateway
proxyUrl: "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/fal"
});
const result = await fal.subscribe("fal-ai/bytedance/seedream/v4/edit", {
"input": {
"prompt": "Dress the model in the clothes and hat. Add a cat to the scene and change the background to a Victorian era building.",
"image_urls": [
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_1.png",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_2.png",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_3.png",
"https://storage.googleapis.com/falserverless/example_inputs/seedream4_edit_input_4.png"
]
}
});
console.log(result.data.images[0]);
```
---
title: ElevenLabs · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: ElevenLabs offers advanced text-to-speech services, enabling
high-quality voice synthesis in multiple languages.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/elevenlabs/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/elevenlabs/index.md
---
[ElevenLabs](https://elevenlabs.io/) offers advanced text-to-speech services, enabling high-quality voice synthesis in multiple languages.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/elevenlabs
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to ElevenLabs, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active ElevenLabs API token.
* The model ID of the ElevenLabs voice model you want to use.
## Example
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/elevenlabs/v1/text-to-speech/JBFqnCBsd6RMkjVDRZzb?output_format=mp3_44100_128 \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'xi-api-key: {elevenlabs_api_token}' \
--data '{
"text": "Welcome to Cloudflare - AI Gateway!",
"model_id": "eleven_multilingual_v2"
}'
```
---
title: Google AI Studio · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Google AI Studio helps you build quickly with Google Gemini models.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-25T12:59:29.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/google-ai-studio/index.md
---
[Google AI Studio](https://ai.google.dev/aistudio) helps you build quickly with Google Gemini models.
## Endpoint
**Base URL:**
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-ai-studio
```
Then you can append the endpoint you want to hit, for example: `v1/models/{model}:{generative_ai_rest_resource}`
So your final URL will come together as: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-ai-studio/v1/models/{model}:{generative_ai_rest_resource}`.
## Examples
### cURL
With API Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```bash
curl "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_name}/google-ai-studio/v1/models/gemini-2.5-flash:generateContent" \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'x-goog-api-key: {google_studio_api_key}' \
--data '{
"contents": [
{
"role":"user",
"parts": [
{"text":"What is Cloudflare?"}
]
}
]
}'
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```bash
curl "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_name}/google-ai-studio/v1/models/gemini-2.5-flash:generateContent" \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'x-goog-api-key: {google_studio_api_key}' \
--data '{
"contents": [
{
"role":"user",
"parts": [
{"text":"What is Cloudflare?"}
]
}
]
}'
```
With Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```bash
curl "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_name}/google-ai-studio/v1/models/gemini-2.5-flash:generateContent" \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--data '{
"contents": [
{
"role":"user",
"parts": [
{"text":"What is Cloudflare?"}
]
}
]
}'
```
### `@google/genai`
If you are using the `@google/genai` package, you can set your endpoint like this:
With Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```js
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({
apiKey: "{google_studio_api_key}",
httpOptions: {
baseUrl: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${account_id}/${gateway_name}/google-ai-studio`,
headers: {
'cf-aig-authorization': 'Bearer {cf_aig_token}',
}
}
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: "What is Cloudflare?",
});
console.log(response.text);
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```js
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({
apiKey: "{google_studio_api_key}",
httpOptions: {
baseUrl: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${account_id}/${gateway_name}/google-ai-studio`,
}
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: "What is Cloudflare?",
});
console.log(response.text);
```
With Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```js
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({
apiKey: "{cf_aig_token}",
httpOptions: {
baseUrl: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${account_id}/${gateway_name}/google-ai-studio`,
}
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: "What is Cloudflare?",
});
console.log(response.text);
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Google AI Studio models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "google-ai-studio/{model}"
}
```
---
title: xAI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: When making requests to Grok, replace https://api.x.ai/v1 in the
URL you are currently using with
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/grok/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/grok/index.md
---
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok
```
## URL structure
When making requests to [Grok](https://docs.x.ai/docs#getting-started), replace `https://api.x.ai/v1` in the URL you are currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Grok, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active xAI API token.
* The name of the xAI model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok/v1/chat/completions \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {xai_api_token}' \
--data '{
"model": "grok-4",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use OpenAI SDK with JavaScript
If you are using the OpenAI SDK with JavaScript, you can set your endpoint like this:
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: "",
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok",
});
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "grok-4",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content:
"You are Grok, a chatbot inspired by the Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy.",
},
{
role: "user",
content: "What is the meaning of life, the universe, and everything?",
},
],
});
console.log(completion.choices[0].message);
```
### Use OpenAI SDK with Python
If you are using the OpenAI SDK with Python, you can set your endpoint like this:
```python
import os
from openai import OpenAI
XAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("XAI_API_KEY")
client = OpenAI(
api_key=XAI_API_KEY,
base_url="https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok",
)
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="grok-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are Grok, a chatbot inspired by the Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the meaning of life, the universe, and everything?"},
],
)
print(completion.choices[0].message)
```
### Use Anthropic SDK with JavaScript
If you are using the Anthropic SDK with JavaScript, you can set your endpoint like this:
```js
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
const anthropic = new Anthropic({
apiKey: "",
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok",
});
const msg = await anthropic.messages.create({
model: "grok-beta",
max_tokens: 128,
system:
"You are Grok, a chatbot inspired by the Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy.",
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: "What is the meaning of life, the universe, and everything?",
},
],
});
console.log(msg);
```
### Use Anthropic SDK with Python
If you are using the Anthropic SDK with Python, you can set your endpoint like this:
```python
import os
from anthropic import Anthropic
XAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("XAI_API_KEY")
client = Anthropic(
api_key=XAI_API_KEY,
base_url="https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/grok",
)
message = client.messages.create(
model="grok-beta",
max_tokens=128,
system="You are Grok, a chatbot inspired by the Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy.",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is the meaning of life, the universe, and everything?",
},
],
)
print(message.content)
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Grok models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "grok/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Groq · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Groq delivers high-speed processing and low-latency performance.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/groq/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/groq/index.md
---
[Groq](https://groq.com/) delivers high-speed processing and low-latency performance.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/groq
```
## URL structure
When making requests to [Groq](https://groq.com/), replace `https://api.groq.com/openai/v1` in the URL you're currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/groq`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Groq, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Groq API token.
* The name of the Groq model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/groq/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {groq_api_key}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
],
"model": "llama3-8b-8192"
}'
```
### Use Groq SDK with JavaScript
If using the [`groq-sdk`](https://www.npmjs.com/package/groq-sdk), set your endpoint like this:
```js
import Groq from "groq-sdk";
const apiKey = env.GROQ_API_KEY;
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/groq`;
const groq = new Groq({
apiKey,
baseURL,
});
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }];
const model = "llama3-8b-8192";
const chatCompletion = await groq.chat.completions.create({
messages,
model,
});
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Groq models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "groq/{model}"
}
```
---
title: HuggingFace · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: HuggingFace helps users build, deploy and train machine learning models.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/huggingface/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/huggingface/index.md
---
[HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co/) helps users build, deploy and train machine learning models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/huggingface
```
## URL structure
When making requests to HuggingFace Inference API, replace `https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/` in the URL you're currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/huggingface`. Note that the model you're trying to access should come right after, for example `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/huggingface/bigcode/starcoder`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to HuggingFace, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active HuggingFace API token.
* The name of the HuggingFace model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/huggingface/bigcode/starcoder \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {hf_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"inputs": "console.log"
}'
```
### Use HuggingFace.js library with JavaScript
If you are using the HuggingFace.js library, you can set your inference endpoint like this:
```js
import { HfInferenceEndpoint } from "@huggingface/inference";
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const model = "gpt2";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/huggingface/${model}`;
const apiToken = env.HF_API_TOKEN;
const hf = new HfInferenceEndpoint(baseURL, apiToken);
```
---
title: Ideogram · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Ideogram provides advanced text-to-image generation models with
exceptional text rendering capabilities and visual quality.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-25T09:00:35.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/ideogram/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/ideogram/index.md
---
[Ideogram](https://ideogram.ai/) provides advanced text-to-image generation models with exceptional text rendering capabilities and visual quality.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/ideogram
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Ideogram, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Ideogram API key.
* The name of the Ideogram model you want to use (e.g., `V_3`).
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/ideogram/v1/ideogram-v3/generate \
--header 'Api-Key: {ideogram_api_key}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"prompt": "A serene landscape with mountains and a lake at sunset",
"model": "V_3"
}'
```
### Use with JavaScript
```js
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const ideogramApiKey = "{ideogram_api_key}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/ideogram`;
const response = await fetch(`${baseURL}/v1/ideogram-v3/generate`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Api-Key": ideogramApiKey,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
prompt: "A serene landscape with mountains and a lake at sunset",
model: "V_3",
}),
});
const result = await response.json();
console.log(result);
```
---
title: Mistral AI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Mistral AI helps you build quickly with Mistral's advanced AI models.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/mistral/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/mistral/index.md
---
[Mistral AI](https://mistral.ai) helps you build quickly with Mistral's advanced AI models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/mistral
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to the Mistral AI, you will need:
* AI Gateway Account ID
* AI Gateway gateway name
* Mistral AI API token
* Mistral AI model name
## URL structure
Your new base URL will use the data above in this structure: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/mistral/`.
Then you can append the endpoint you want to hit, for example: `v1/chat/completions`
So your final URL will come together as: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/mistral/v1/chat/completions`.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/mistral/v1/chat/completions \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer MISTRAL_TOKEN' \
--data '{
"model": "mistral-large-latest",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use `@mistralai/mistralai` package with JavaScript
If you are using the `@mistralai/mistralai` package, you can set your endpoint like this:
```js
import { Mistral } from "@mistralai/mistralai";
const client = new Mistral({
apiKey: MISTRAL_TOKEN,
serverURL: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/mistral`,
});
await client.chat.create({
model: "mistral-large-latest",
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: "What is Cloudflare?",
},
],
});
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Mistral models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "mistral/{model}"
}
```
---
title: OpenAI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: OpenAI helps you build with GPT models.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-25T12:59:29.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openai/index.md
---
[OpenAI](https://openai.com/about/) helps you build with GPT models.
## Endpoint
**Base URL**
```plaintext
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai
```
When making requests to OpenAI, replace `https://api.openai.com/v1` in the URL you are currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai`.
**Chat completions endpoint**
`https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions`
**Responses endpoint**
`https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/responses`
## Examples
### OpenAI SDK
With Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY",
defaultHeaders: {
"cf-aig-authorization": `Bearer {cf_api_token}`,
},
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai",
});
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "Hello, world!" }],
});
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY",
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai",
});
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "Hello, world!" }],
});
```
With Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: "{cf_api_token}",
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai",
});
// Ensure your OpenAI API key is stored with BYOK
// or Unified Billing has credits
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "Hello, world!" }],
});
```
### cURL
Responses API with API Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/responses \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}' \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-5.1",
"input": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Write a one-sentence bedtime story about a unicorn."
}
]
}'
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/responses \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-5.1",
"input": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Write a one-sentence bedtime story about a unicorn."
}
]
}'
```
Chat Completions with API Key in Request
* With Authenticated Gateway
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}' \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
* Unauthenticated Gateway
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
Responses API with Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/responses \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-5.1",
"input": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Write a one-sentence bedtime story about a unicorn."
}
]
}'
```
Chat Completions with Stored Keys (BYOK) / Unified Billing
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai/chat/completions \
--header 'cf-aig-authorization: Bearer {CF_AIG_TOKEN}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
---
title: OpenRouter · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: OpenRouter is a platform that provides a unified interface for
accessing and using large language models (LLMs).
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openrouter/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/openrouter/index.md
---
[OpenRouter](https://openrouter.ai/) is a platform that provides a unified interface for accessing and using large language models (LLMs).
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openrouter
```
## URL structure
When making requests to [OpenRouter](https://openrouter.ai/), replace `https://openrouter.ai/api/v1/chat/completions` in the URL you are currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openrouter/chat/completions`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to OpenRouter, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active OpenRouter API token or a token from the original model provider.
* The name of the OpenRouter model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl -X POST https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openrouter/v1/chat/completions \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer OPENROUTER_TOKEN' \
--data '{
"model": "openai/gpt-5-mini",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use OpenAI SDK with JavaScript
If you are using the OpenAI SDK with JavaScript, you can set your endpoint like this:
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: env.OPENROUTER_TOKEN,
baseURL:
"https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/ACCOUNT_TAG/GATEWAY/openrouter",
});
try {
const chatCompletion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "openai/gpt-5-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }],
});
const response = chatCompletion.choices[0].message;
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response));
} catch (e) {
return new Response(e);
}
```
---
title: Parallel · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Parallel is a web API purpose-built for AIs, providing
production-ready outputs with minimal hallucination and evidence-based
results.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-03T11:34:42.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/parallel/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/parallel/index.md
---
[Parallel](https://parallel.ai/) is a web API purpose-built for AIs, providing production-ready outputs with minimal hallucination and evidence-based results.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/parallel
```
## URL structure
When making requests to Parallel, you can route to any Parallel endpoint through AI Gateway by appending the path after `parallel`. For example, to access the Tasks API at `/v1/tasks/runs`, use:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/parallel/v1/tasks/runs
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Parallel, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Parallel API key.
## Examples
### Tasks API
The [Tasks API](https://docs.parallel.ai/task-api/task-quickstart) allows you to create comprehensive research and analysis tasks.
#### cURL example
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/parallel/v1/tasks/runs \
--header 'x-api-key: {parallel_api_key}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"input": "Create a comprehensive market research report on the HVAC industry in the USA including an analysis of recent M&A activity and other relevant details.",
"processor": "ultra"
}'
```
### Search API
The [Search API](https://docs.parallel.ai/search-api/search-quickstart) enables advanced search with configurable parameters.
#### cURL example
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/parallel/v1beta/search \
--header 'x-api-key: {parallel_api_key}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"objective": "When was the United Nations established? Prefer UN'\''s websites.",
"search_queries": [
"Founding year UN",
"Year of founding United Nations"
],
"processor": "base",
"max_results": 10,
"max_chars_per_result": 6000
}'
```
## Chat API
The [Chat API](https://docs.parallel.ai/chat-api/chat-quickstart) is supported through AI Gateway's Unified Chat Completions API. See below for more details:
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Parallel models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "parallel/{model}"
}
```
#### JavaScript SDK example
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const apiKey = "{parallel_api_key}";
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/compat`;
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey,
baseURL,
});
try {
const model = "parallel/speed";
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: "Hello!" }];
const chatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages,
});
const response = chatCompletion.choices[0].message;
console.log(response);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
```
### FindAll API
The [FindAll API](https://docs.parallel.ai/findall-api/findall-quickstart) enables structured data extraction from complex queries.
#### cURL example
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/parallel/v1beta/findall/ingest \
--header 'x-api-key: {parallel_api_key}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"query": "Find all AI companies that recently raised money and get their website, CEO name, and CTO name."
}'
```
---
title: Perplexity · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Perplexity is an AI powered answer engine.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/perplexity/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/perplexity/index.md
---
[Perplexity](https://www.perplexity.ai/) is an AI powered answer engine.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/perplexity-ai
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Perplexity, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Perplexity API token.
* The name of the Perplexity model you want to use.
## Examples
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/perplexity-ai/chat/completions \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {perplexity_token}' \
--data '{
"model": "mistral-7b-instruct",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
### Use Perplexity through OpenAI SDK with JavaScript
Perplexity does not have their own SDK, but they have compatibility with the OpenAI SDK. You can use the OpenAI SDK to make a Perplexity call through AI Gateway as follows:
```js
import OpenAI from "openai";
const apiKey = env.PERPLEXITY_API_KEY;
const accountId = "{account_id}";
const gatewayId = "{gateway_id}";
const baseURL = `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/${accountId}/${gatewayId}/perplexity-ai`;
const perplexity = new OpenAI({
apiKey,
baseURL,
});
const model = "mistral-7b-instruct";
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: "What is Cloudflare?" }];
const maxTokens = 20;
const chatCompletion = await perplexity.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages,
max_tokens: maxTokens,
});
```
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Perplexity models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "perplexity/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Replicate · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Replicate runs and fine tunes open-source models.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-29T17:51:26.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/replicate/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/replicate/index.md
---
[Replicate](https://replicate.com/) runs and fine tunes open-source models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/replicate
```
## URL structure
When making requests to Replicate, replace `https://api.replicate.com/v1` in the URL you're currently using with `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/replicate`.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Replicate, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Replicate API token. You can create one at [replicate.com/settings/api-tokens](https://replicate.com/settings/api-tokens)
* The name of the Replicate model you want to use, like `anthropic/claude-4.5-haiku` or `google/nano-banana`.
## Example
### cURL
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/replicate/predictions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {replicate_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"version": "anthropic/claude-4.5-haiku",
"input":
{
"prompt": "Write a haiku about Cloudflare"
}
}'
```
---
title: Google Vertex AI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Google Vertex AI enables developers to easily build and deploy
enterprise ready generative AI experiences.
lastUpdated: 2025-11-24T18:38:12.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/vertex/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/vertex/index.md
---
[Google Vertex AI](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai) enables developers to easily build and deploy enterprise ready generative AI experiences.
Below is a quick guide on how to set your Google Cloud Account:
1. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Account
* Sign up for a [GCP account](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai). New users may be eligible for credits (valid for 90 days).
2. Enable the Vertex AI API
* Navigate to [Enable Vertex AI API](https://console.cloud.google.com/marketplace/product/google/aiplatform.googleapis.com) and activate the API for your project.
3. Apply for access to desired models.
## Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-vertex-ai
```
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Google Vertex, you will need:
* AI Gateway account tag
* AI Gateway gateway name
* Google Vertex API key
* Google Vertex Project Name
* Google Vertex Region (for example, us-east4)
* Google Vertex model
## URL structure
Your new base URL will use the data above in this structure: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-vertex-ai/v1/projects/{project_name}/locations/{region}`.
Then you can append the endpoint you want to hit, for example: `/publishers/google/models/{model}:{generative_ai_rest_resource}`
So your final URL will come together as: `https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-vertex-ai/v1/projects/{project_name}/locations/{region}/publishers/google/models/gemini-2.5-flash:generateContent`
## Authenticating with Vertex AI
Authenticating with Vertex AI normally requires generating short-term credentials using the [Google Cloud SDKs](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/authentication) with a complicated setup, but AI Gateway simplifies this for you with multiple options:
### Option 1: Service Account JSON
AI Gateway supports passing a Google service account JSON directly in the `Authorization` header on requests or through AI Gateway's [Bring Your Own Keys](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/) feature.
You can [create a service account key](https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/keys-create-delete) in the Google Cloud Console. Ensure that the service account has the required permissions for the Vertex AI endpoints and models you plan to use.
AI Gateway uses your service account JSON to generate short-term access tokens which are cached and used for consecutive requests, and are automatically refreshed when they expire.
Note
The service account JSON must include an additional key called `region` with the GCP region code (for example, `us-east1`) you intend to use for your [Vertex AI endpoint](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/reference/rest#service-endpoint). You can also pass the region code `global` to use the global endpoint.
#### Example service account JSON structure
```json
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "your-project-id",
"private_key_id": "your-private-key-id",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nYOUR_PRIVATE_KEY\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "your-service-account@your-project.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "your-client-id",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/your-service-account%40your-project.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"region": "us-east1"
}
```
You can pass this JSON in the `Authorization` header or configure it in [Bring Your Own Keys](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys/).
### Option 2: Direct Access Token
If you are already using the Google Cloud SDKs and generating a short-term access token (for example, with `gcloud auth print-access-token`), you can directly pass this as a Bearer token in the `Authorization` header of the request.
Note
This option is only supported for the provider-specific endpoint, not for the unified chat completions endpoint.
```bash
curl "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-vertex-ai/v1/projects/{project_name}/locations/{region}/publishers/google/models/gemini-2.5-flash:generateContent" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ya29.c.b0Aaekm1K..." \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"contents": {
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Tell me more about Cloudflare"
}
]
}
}'
```
## Using Unified Chat Completions API
AI Gateway provides a [Unified API](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) that works across providers. For Google Vertex AI, you can use the standard chat completions format. Note that the model field includes the provider prefix, so your model string will look like `google-vertex-ai/google/gemini-2.5-pro`.
### Endpoint
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
### Example with OpenAI SDK
```javascript
import OpenAI from 'openai';
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: '{service_account_json}',
baseURL: 'https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat'
});
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: 'google-vertex-ai/google/gemini-2.5-pro',
messages: [
{
role: 'user',
content: 'What is Cloudflare?'
}
]
});
console.log(response.choices[0].message.content);
```
### Example with cURL
```bash
curl "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer {service_account_json}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"model": "google-vertex-ai/google/gemini-2.5-pro",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}'
```
Note
See the [Authenticating with Vertex AI](#authenticating-with-vertex-ai) section below for details on the service account JSON structure and authentication options.
## Using Provider-Specific Endpoint
You can also use the provider-specific endpoint to access the full Vertex AI API.
### cURL
```bash
curl "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/google-vertex-ai/v1/projects/{project_name}/locations/{region}/publishers/google/models/gemini-2.5-flash:generateContent" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer {vertex_api_key}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"contents": {
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Tell me more about Cloudflare"
}
]
}'
```
---
title: Workers AI · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Use AI Gateway for analytics, caching, and security on requests to
Workers AI. Workers AI integrates seamlessly with AI Gateway, allowing you to
execute AI inference via API requests or through an environment binding for
Workers scripts. The binding simplifies the process by routing requests
through your AI Gateway with minimal setup.
lastUpdated: 2025-08-19T11:42:14.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
tags: AI
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/providers/workersai/index.md
---
Use AI Gateway for analytics, caching, and security on requests to [Workers AI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/). Workers AI integrates seamlessly with AI Gateway, allowing you to execute AI inference via API requests or through an environment binding for Workers scripts. The binding simplifies the process by routing requests through your AI Gateway with minimal setup.
## Prerequisites
When making requests to Workers AI, ensure you have the following:
* Your AI Gateway Account ID.
* Your AI Gateway gateway name.
* An active Workers AI API token.
* The name of the Workers AI model you want to use.
## REST API
To interact with a REST API, update the URL used for your request:
* **Previous**:
```txt
https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/{account_id}/ai/run/{model_id}
```
* **New**:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/workers-ai/{model_id}
```
For these parameters:
* `{account_id}` is your Cloudflare [account ID](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/get-started/rest-api/#1-get-api-token-and-account-id).
* `{gateway_id}` refers to the name of your existing [AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/#create-gateway).
* `{model_id}` refers to the model ID of the [Workers AI model](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/models/).
## Examples
First, generate an [API token](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/api/get-started/create-token/) with `Workers AI Read` access and use it in your request.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/workers-ai/@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {cf_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{"prompt": "What is Cloudflare?"}'
```
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/workers-ai/@cf/huggingface/distilbert-sst-2-int8 \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {cf_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{ "text": "Cloudflare docs are amazing!" }'
```
### OpenAI compatible endpoints
Workers AI supports OpenAI compatible endpoints for [text generation](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/models/) (`/v1/chat/completions`) and [text embedding models](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/models/) (`/v1/embeddings`). This allows you to use the same code as you would for your OpenAI commands, but swap in Workers AI easily.
```bash
curl https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/workers-ai/v1/chat/completions \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer {cf_api_token}' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Cloudflare?"
}
]
}
'
```
## Workers Binding
You can integrate Workers AI with AI Gateway using an environment binding. To include an AI Gateway within your Worker, add the gateway as an object in your Workers AI request.
* JavaScript
```js
export default {
async fetch(request, env) {
const response = await env.AI.run(
"@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
{
prompt: "Why should you use Cloudflare for your AI inference?",
},
{
gateway: {
id: "{gateway_id}",
skipCache: false,
cacheTtl: 3360,
},
},
);
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response));
},
};
```
* TypeScript
```ts
export interface Env {
AI: Ai;
}
export default {
async fetch(request: Request, env: Env): Promise {
const response = await env.AI.run(
"@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
{
prompt: "Why should you use Cloudflare for your AI inference?",
},
{
gateway: {
id: "{gateway_id}",
skipCache: false,
cacheTtl: 3360,
},
},
);
return new Response(JSON.stringify(response));
},
} satisfies ExportedHandler;
```
For a detailed step-by-step guide on integrating Workers AI with AI Gateway using a binding, see [Integrations in AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/integrations/aig-workers-ai-binding/).
Workers AI supports the following parameters for AI gateways:
* `id` string
* Name of your existing [AI Gateway](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/get-started/#create-gateway). Must be in the same account as your Worker.
* `skipCache` boolean(default: false)
* Controls whether the request should [skip the cache](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#skip-cache-cf-aig-skip-cache).
* `cacheTtl` number
* Controls the [Cache TTL](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/features/caching/#cache-ttl-cf-aig-cache-ttl).
## OpenAI-Compatible Endpoint
You can also use the [OpenAI-compatible endpoint](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/) (`/ai-gateway/usage/chat-completion/`) to access Workers AI models using the OpenAI API schema. To do so, send your requests to:
```txt
https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/compat/chat/completions
```
Specify:
```json
{
"model": "workers-ai/{model}"
}
```
---
title: Non-realtime WebSockets API · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: The Non-realtime WebSockets API allows you to establish persistent
connections for AI requests without requiring repeated handshakes. This
approach is ideal for applications that do not require real-time interactions
but still benefit from reduced latency and continuous communication.
lastUpdated: 2025-12-15T14:49:17.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/non-realtime-api/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/non-realtime-api/index.md
---
The Non-realtime WebSockets API allows you to establish persistent connections for AI requests without requiring repeated handshakes. This approach is ideal for applications that do not require real-time interactions but still benefit from reduced latency and continuous communication.
## Set up WebSockets API
1. Generate an AI Gateway token with appropriate AI Gateway Run and opt in to using an authenticated gateway.
2. Modify your Universal Endpoint URL by replacing `https://` with `wss://` to initiate a WebSocket connection:
```plaintext
wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}
```
3. Open a WebSocket connection authenticated with a Cloudflare token with the AI Gateway Run permission.
Note
Alternatively, we also support authentication via the `sec-websocket-protocol` header if you are using a browser WebSocket.
## Example request
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/my-account-id/my-gateway/",
{
headers: {
"cf-aig-authorization": "Bearer AI_GATEWAY_TOKEN",
},
},
);
ws.on("open", () => {
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
type: "universal.create",
request: {
eventId: "my-request",
provider: "workers-ai",
endpoint: "@cf/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct",
headers: {
Authorization: "Bearer WORKERS_AI_TOKEN",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
query: {
prompt: "tell me a joke",
},
},
}),
);
})
ws.on("message", (message) => {
console.log(message.toString());
});
```
## Example response
```json
{
"type": "universal.created",
"metadata": {
"cacheStatus": "MISS",
"eventId": "my-request",
"logId": "01JC3R94FRD97JBCBX3S0ZAXKW",
"step": "0",
"contentType": "application/json"
},
"response": {
"result": {
"response": "Why was the math book sad? Because it had too many problems. Would you like to hear another one?"
},
"success": true,
"errors": [],
"messages": []
}
}
```
## Example streaming request
For streaming requests, AI Gateway sends an initial message with request metadata indicating the stream is starting:
```json
{
"type": "universal.created",
"metadata": {
"cacheStatus": "MISS",
"eventId": "my-request",
"logId": "01JC40RB3NGBE5XFRZGBN07572",
"step": "0",
"contentType": "text/event-stream"
}
}
```
After this initial message, all streaming chunks are relayed in real-time to the WebSocket connection as they arrive from the inference provider. Only the `eventId` field is included in the metadata for these streaming chunks. The `eventId` allows AI Gateway to include a client-defined ID with each message, even in a streaming WebSocket environment.
```json
{
"type": "universal.stream",
"metadata": {
"eventId": "my-request"
},
"response": {
"response": "would"
}
}
```
Once all chunks for a request have been streamed, AI Gateway sends a final message to signal the completion of the request. For added flexibility, this message includes all the metadata again, even though it was initially provided at the start of the streaming process.
```json
{
"type": "universal.done",
"metadata": {
"cacheStatus": "MISS",
"eventId": "my-request",
"logId": "01JC40RB3NGBE5XFRZGBN07572",
"step": "0",
"contentType": "text/event-stream"
}
}
```
---
title: Realtime WebSockets API · Cloudflare AI Gateway docs
description: Some AI providers support real-time, low-latency interactions over
WebSockets. AI Gateway allows seamless integration with these APIs, supporting
multimodal interactions such as text, audio, and video.
lastUpdated: 2025-10-09T17:51:29.000Z
chatbotDeprioritize: false
source_url:
html: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/
md: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/usage/websockets-api/realtime-api/index.md
---
Some AI providers support real-time, low-latency interactions over WebSockets. AI Gateway allows seamless integration with these APIs, supporting multimodal interactions such as text, audio, and video.
## Supported Providers
* [OpenAI](https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/realtime-websocket)
* [Google AI Studio](https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/multimodal-live)
* [Cartesia](https://docs.cartesia.ai/api-reference/tts/tts)
* [ElevenLabs](https://elevenlabs.io/docs/conversational-ai/api-reference/conversational-ai/websocket)
* [Fal AI](https://docs.fal.ai/model-apis/model-endpoints/websockets)
* [Deepgram (Workers AI)](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers-ai/models/?authors=deepgram)
## Authentication
For real-time WebSockets, authentication can be done using:
* Headers (for non-browser environments)
* `sec-websocket-protocol` (for browsers)
Note
Provider specific API Keys can also be alternatively configured on AI Gateway using our [BYOK](https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/configuration/bring-your-own-keys) feature. You must still include the `cf-aig-authorization` header in the websocket request.
## Examples
### OpenAI
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
const url =
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///openai?model=gpt-4o-realtime-preview-2024-12-17";
const ws = new WebSocket(url, {
headers: {
"cf-aig-authorization": process.env.CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY,
Authorization: "Bearer " + process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
"OpenAI-Beta": "realtime=v1",
},
});
ws.on("open", () => console.log("Connected to server."));
ws.on("message", (message) => console.log(JSON.parse(message.toString())));
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
type: "response.create",
response: { modalities: ["text"], instructions: "Tell me a joke" },
}),
);
```
### Google AI Studio
```javascript
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///google?api_key=",
["cf-aig-authorization."],
);
ws.on("open", () => console.log("Connected to server."));
ws.on("message", (message) => console.log(message.data));
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
setup: {
model: "models/gemini-2.5-flash",
generationConfig: { responseModalities: ["TEXT"] },
},
}),
);
```
### Cartesia
```javascript
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///cartesia?cartesia_version=2024-06-10&api_key=",
["cf-aig-authorization."],
);
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(message.data);
});
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
model_id: "sonic",
transcript: "Hello, world! I'm generating audio on ",
voice: { mode: "id", id: "a0e99841-438c-4a64-b679-ae501e7d6091" },
language: "en",
context_id: "happy-monkeys-fly",
output_format: {
container: "raw",
encoding: "pcm_s16le",
sample_rate: 8000,
},
add_timestamps: true,
continue: true,
}),
);
```
### ElevenLabs
```javascript
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///elevenlabs?agent_id=",
[
"xi-api-key.",
"cf-aig-authorization.",
],
);
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(message.data);
});
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
text: "This is a sample text ",
voice_settings: { stability: 0.8, similarity_boost: 0.8 },
generation_config: { chunk_length_schedule: [120, 160, 250, 290] },
}),
);
```
### Fal AI
Fal AI supports WebSocket connections for real-time model interactions through their HTTP over WebSocket API.
```javascript
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///fal/fal-ai/fast-lcm-diffusion",
["fal-api-key.", "cf-aig-authorization."],
);
ws.on("open", function open() {
console.log("Connected to server.");
});
ws.on("message", function incoming(message) {
console.log(message.data);
});
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
prompt: "generate an image of a cat flying an aeroplane",
}),
);
```
For more information on Fal AI's WebSocket API, see their [HTTP over WebSocket documentation](https://docs.fal.ai/model-apis/model-endpoints/websockets).
### Deepgram (Workers AI)
Workers AI provides Deepgram models for real-time speech-to-text (STT) and text-to-speech (TTS) capabilities through WebSocket connections.
#### Speech-to-Text (STT)
Workers AI supports two Deepgram STT models: `@cf/deepgram/nova-3` and `@cf/deepgram/flux`. The following example demonstrates real-time audio transcription from a microphone:
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
import mic from "mic";
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///workers-ai?model=@cf/deepgram/nova-3&encoding=linear16&sample_rate=16000&interim_results=true",
{
headers: {
"cf-aig-authorization": process.env.CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY,
},
},
);
// Configure microphone
const micInstance = mic({
rate: "16000",
channels: "1",
debug: false,
exitOnSilence: 6,
});
const micInputStream = micInstance.getAudioStream();
micInputStream.on("data", (data) => {
if (ws.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
ws.send(data);
}
});
micInputStream.on("error", (error) => {
console.error("Microphone error:", error);
});
ws.onopen = () => {
console.log("Connected to WebSocket");
console.log("Starting microphone...");
micInstance.start();
};
ws.onmessage = (event) => {
try {
const parse = JSON.parse(event.data);
if (parse.channel?.alternatives?.[0]?.transcript) {
if (parse.is_final) {
console.log(
"Final transcript:",
parse.channel.alternatives[0].transcript,
);
} else {
console.log(
"Interim transcript:",
parse.channel.alternatives[0].transcript,
);
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error parsing message:", error);
}
};
ws.onerror = (error) => {
console.error("WebSocket error:", error);
};
ws.onclose = () => {
console.log("WebSocket closed");
micInstance.stop();
};
```
#### Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Workers AI supports the Deepgram `@cf/deepgram/aura-1` model for TTS. The following example demonstrates converting text input to audio:
```javascript
import WebSocket from "ws";
import readline from "readline";
import Speaker from "speaker";
const ws = new WebSocket(
"wss://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1///workers-ai?model=@cf/deepgram/aura-1",
{
headers: {
"cf-aig-authorization": process.env.CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY,
},
},
);
// Speaker management
let currentSpeaker = null;
let isPlayingAudio = false;
// Setup readline for text input
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
prompt: "Enter text to speak (or \"quit\" to exit): ",
});
ws.onopen = () => {
console.log("Connected to Deepgram TTS WebSocket");
rl.prompt();
};
ws.onmessage = (event) => {
// Check if message is JSON (metadata, flushed, etc.) or raw audio
if (event.data instanceof Buffer || event.data instanceof ArrayBuffer) {
// Raw audio data - create new speaker if needed
if (!currentSpeaker) {
currentSpeaker = new Speaker({
channels: 1,
bitDepth: 16,
sampleRate: 24000,
});
isPlayingAudio = true;
}
currentSpeaker.write(Buffer.from(event.data));
} else {
try {
const message = JSON.parse(event.data);
switch (message.type) {
case "Metadata":
console.log("Model info:", message.model_name, message.model_version);
break;
case "Flushed":
console.log("Audio complete");
// End speaker after flush to prevent buffer underflow
if (currentSpeaker && isPlayingAudio) {
currentSpeaker.end();
currentSpeaker = null;
isPlayingAudio = false;
}
rl.prompt();
break;
case "Cleared":
console.log("Audio cleared, sequence:", message.sequence_id);
break;
case "Warning":
console.warn("Warning:", message.description);
break;
}
} catch (error) {
// Not JSON, might be raw audio as string
if (!currentSpeaker) {
currentSpeaker = new Speaker({
channels: 1,
bitDepth: 16,
sampleRate: 24000,
});
isPlayingAudio = true;
}
currentSpeaker.write(Buffer.from(event.data));
}
}
};
ws.onerror = (error) => {
console.error("WebSocket error:", error);
};
ws.onclose = () => {
console.log("WebSocket closed");
if (currentSpeaker) {
currentSpeaker.end();
}
rl.close();
process.exit(0);
};
// Handle user input
rl.on("line", (input) => {
const text = input.trim();
if (text.toLowerCase() === "quit") {
// Send Close message
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: "Close" }));
ws.close();
return;
}
if (text.length > 0) {
// Send text to TTS
ws.send(
JSON.stringify({
type: "Speak",
text: text,
}),
);
// Flush to get audio immediately
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: "Flush" }));
console.log("Flushing audio");
}
rl.prompt();
});
rl.on("close", () => {
if (ws.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
ws.close();
}
});
```